What is OSN
The general (standard) taxation system is the most complex taxation regime of all existing in Russia, characterized by a large number of taxes and the obligation to maintain full accounting and tax records.
By default, all entrepreneurs and organizations that have not decided on the choice of taxation system upon registration, as well as those that are no longer entitled to apply any of the special tax regimes: simplified tax system, PSN, UTII and Unified Agricultural Tax, are transferred to OSNO by default.
The general system is not subject to any restrictions on types of activities, number of employees, income received, etc. As a rule, most large companies work on OSNO and, as VAT payers, also prefer to work with those who pay this tax.
Types of taxation systems
The taxation system is a method of paying mandatory taxes determined by law in the form of cash payments to the state budget.
There are the following types of taxation:
- general taxation system (OSNO);
- simplified taxation system (STS);
- unified tax on imputed income (UTII);
- single agricultural tax (USAT);
- patent payment calculation system;
- fixed payments to the Pension Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
In what cases is the use of OSNO beneficial?
It is beneficial to use a general taxation system:
- if most of the counterparties are on OSNO and are thus interested in “input” VAT;
- when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation (VAT paid when importing goods can be deducted);
- the main part of the activity is related to wholesale trade;
- the organization is exempt from income tax (for example, educational institutions).
Free tax consultation
Features of OSNO
The general taxation system is also called the basic taxation system, and the abbreviation of this name may look like OSN or OSNO . We prefer the latter option.
Organizations on OSNO pay the following taxes:
- corporate income tax at a rate of 20%, with the exception of a few preferential categories of taxpayers;
- VAT at the rate of 0%, 10%, 20%;
- corporate property tax at a rate of up to 2.2%.
Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO pay:
- personal income tax at a rate of 13% (if the entrepreneur was a resident of the Russian Federation in the reporting year);
- VAT at the rate of 0%, 10%, 20%;
- property tax for individuals at a rate of up to 2%.
You can be on OSNO for the following reasons:
- The taxpayer initially does not meet the requirements and restrictions provided for the preferential tax regime, or subsequently ceased to satisfy them;
- A businessman must be a VAT payer;
- The taxpayer falls into the category of income tax benefits (for example, a medical or educational organization);
- Simply out of ignorance that there are other taxation systems: simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax and PSN (only for individual entrepreneurs);
- Some other good reasons, because if you decide to engage in activities for profit, it is difficult to assume that you deliberately chose the regime with the highest tax burden.
VAT calculator
Transition to OSNO in 2020
In order to start working on OSNO immediately after registering a business, you do not need to submit a notification about the application of OSNO to the Federal Tax Service. All organizations and individual entrepreneurs are automatically transferred to this regime if they did not choose a different taxation regime during registration or within 30 days after it.
Transition from simplified tax system to OSNO
To switch to the OSNO with the simplified tax system, you must, before January 15 of the year from which the transition to the general regime is planned, submit to the tax office at the place of registration a notice of refusal to use the simplified tax system in form No. 26.2-3.
If the notification is not submitted by January 15, it will be possible to switch to OSNO only starting next year.
A voluntary transition to OSNO is possible only from the next calendar year, but if an organization or individual entrepreneur loses the right to use the simplified tax system, they are automatically considered transferred to OSNO from the quarter in which non-compliance with the conditions for applying the simplified tax system was committed.
Transition from UTII to OSNO
To switch to OSNO from UTII, it is necessary, before January 5 of the year from which the transition to the general regime is planned, to submit to the tax authority at the place of registration an application for deregistration as a UTII payer in the form UTII-3 for organizations and UTII-4 for IP.
A voluntary transition to OSNO is possible only from the next calendar year, but if an organization and individual entrepreneur lose the right to use UTII, they are automatically considered transferred to OSNO from the quarter in which non-compliance with the conditions for applying UTII was committed.
Transition from Unified Agricultural Tax to OSNO
To switch to OSNO with Unified Agricultural Tax, it is necessary, before January 15 of the year from which the transition to the general regime is planned, to submit to the tax authority at the place of registration an application for refusal to use Unified Agricultural Tax in form No. 26.1-3.
A voluntary transition to OSNO is possible only from the next calendar year, but if an organization and individual entrepreneur lose the right to use the Unified Agricultural Tax, they are automatically considered transferred to the OSNO from the beginning of the reporting (six-month) or tax (year) period in which non-compliance with the conditions of application was committed Unified Agricultural Sciences.
You can switch to the unified agricultural tax again only one year after losing the right to use the unified agricultural tax.
Transition from Patent to OSNO
The transfer to the OSN from the PSN is carried out after 5 days from the date of submission to the tax authority of the application for termination of activities on the patent. If the right to use a patent is lost, the entrepreneur is transferred to the general system from the beginning of the period for which the patent was received.
Peculiarities
In the general tax regime, unlike special ones, there are no restrictions on the type of activity, the number of employees, or the amount of income. That is, any entrepreneur or organization can work in the general mode, and for this there is no need to meet any conditions or restrictions.
There is also no need to specifically switch to general taxation. If an organization or individual entrepreneur has not submitted an application to the tax office to apply a different regime, they automatically subject to the general regime.
Accounting services from RUB 1,667/month
If a taxpayer switched to one of the special regimes, but violated the terms of application, he also automatically ends up in the general regime.
OSNO pays more taxes, and therefore accounting and reporting is much more complex and extensive than in other regimes. This is the most significant disadvantage of the overall system.
What taxes must be paid on the general taxation system in 2020
Basic taxes OSNO
Note! The deadlines for paying taxes and filing reports for some individual entrepreneurs and organizations have been postponed due to the coronavirus epidemic. Read the article for details.
The table below shows all the main taxes that must be paid on OSNO:
| Type of tax | Tax rate | Payment deadline | Who pays |
| Corporate income tax | 20% | Advance payments (for organizations that meet the criteria of clause 3 of Article 286 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - within 28 days from the end of the reporting period (quarter) Monthly advance payments – by the 28th of each month Tax at the end of the year - until March 28 of the year following the reporting year | Organizations |
| Personal income tax | 13%, 30% | Advance payments until April 25, July 25, October 25 Tax at the end of the year - until July 15 of the year following the reporting year | IP |
| VAT | 0%, 10%, 20% | No later than the 25th day of each month following the expired tax period (quarter) 1/3 of the amount each month or a single amount until the 25th day of the month following the previous quarter | Organizations and individual entrepreneurs |
| Organizational property tax | not > 2.2% (set by local authorities) | Tax and advance payments are paid according to the deadlines established by the regulations of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation | Organizations |
| Property tax for individuals | from 0.1% to 2% (set by local authorities) | Tax for the year is due by December 1 of the year following the reporting year. | IP |
Taxes and payments for employees
Individual entrepreneurs and organizations on OSNO are required to withhold personal income tax on all income paid to their employees (including those working on a civil basis), as well as transfer insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds.
Learn more about taxes and payments for employees.
Fixed contributions for individual entrepreneurs
All individual entrepreneurs, regardless of the chosen taxation system and the presence of employees, are required to pay fixed insurance premiums “for themselves” every year.
In 2020, their size is 40,874 rubles.
Learn more about fixed individual entrepreneur contributions.
How does OSNO taxation work? ↑
As you know, making calculations and preparing reports on OSNO is quite difficult. Is it so? Let's figure out how to calculate taxes.
How to calculate the amount to be paid?
All tax calculations on the main system are carried out separately: separate formulas are used for VAT, property tax, etc.
Value added tax calculation
For example, you sell goods worth 11,800 rubles, and must pay tax at a rate of 18%. Of the total amount, you can take 10 thousand as profit, and 1.8 thousand is VAT. If you buy products for 1800, pay 180 in VAT, the rest as expenses.
Then you can calculate the remaining taxes. Income tax: from the amount of 10 thousand, subtract the costs (let's say 1 thousand) and multiply by 13% (or another rate that applies in your territorial district).
The calculation will be like this:
VAT: You received 1800 rubles, paid 180. VAT amount = 1620 rubles (the difference between the two indicators).
Making a payment
Taxes on OSNO must be paid within the following deadlines:
| Income tax | Until the 28th monthly, and the final annual payment – until 10/28. But there is one feature - payment is made every month in the case when the amount of profit exceeds 1,000,000 rubles per month. In other situations, you should pay tax once a quarter |
| VAT | Transfer each quarter in equal parts (advance payments) until the 20th of the next month after the reporting period |
| Personal income tax for employees | Upon actual receipt of cash or upon transfer of non-cash funds to the taxpayer’s account |
| Transport tax | Until 1.02 after the end of the tax period |
| Water tax | Quarterly |
| Land tax | Before February 1 in the year following the tax period |
| Payments to the Pension Fund | Until the 15th of the next month after the payment of earnings, that is, monthly |
| In the FSS | Until the 20th if paper reporting is submitted, until the 25th if electronic reporting is submitted |
| Amounts in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund | Quarterly until the 15th of each month |
| Property tax | By the 30th of each quarter (next month), and the final payment is due by October 30 |
| If the company’s activities are related to the sale of alcohol-containing goods | Every month you have to pay excise tax |
Drawing up accounting policies
Accounting policies must be drawn up for the purposes of accounting and carrying out activities on the SPE.
The following actions await you:
- Development of a draft accounting policy - the purpose is determined, the elements that will be used without fail are established, those that are undesirable for use are excluded, the content is prescribed.
- Approval of the document by a separate order of the enterprise administration.
The accounting policy is adopted once, and in the absence of changes, it is applied continuously. It is allowed to make clarifications and additions.
In relation to accounting, such a document is drawn up by an accountant, in relation to tax accounting - by the person who is responsible for its implementation.
For example, a company on OSNO operates in the field of trade. This means that when drawing up an accounting policy, it is worth considering the procedure for accounting for products and forming costs.
First, they indicate by what criteria the property object is included in the product. Often these are areas of use of assets - material inventories that were received for the purpose of sale.
How to find out the basic yield on UTII in 2020, see the article: table of basic yield on UTII. Is it possible to find out the tariff code in RSV-1 for 2020 for UTII through nalog.ru, read here.
Then reflect the accounting units. The next point is the assessment of products, the order of their receipt. They prescribe the features of accounting for transportation costs, carrying out wholesale sales operations, write-off methods, etc.
Reporting to OSNO in 2020
Below is all the main reporting that must be submitted by individual entrepreneurs and LLCs under the general taxation system:
Tax returns
VAT declaration
Quarterly, due date – no later than 25 days from the end of the quarter.
The format for submitting the declaration from 2020 is electronic. Submitting a declaration in paper form is equivalent to failure to submit reports and entails prosecution under Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
VAT payers are also required to maintain tax registers
: books of purchases and sales, journal of received and issued invoices.
More details about the VAT return
Income tax return
Submitted at the end of the reporting period (1st quarter, half year and 9 months) no later than 28 days from the end date of the period. The annual declaration is submitted by March 28.
If an organization makes advance payments on actually received profits, it must submit reports every month by the 28th.
More details about the income tax return
Personal income tax declaration
Form 3-NDFL is submitted once a year until April 30. Form 4-NDFL has been canceled since 2020.
More details about 3-NDFL.
Declaration on property tax of organizations
The declaration is submitted at the end of the year - by March 30 of the year following the reporting year. From 2020, settlements for advance payments have been cancelled.
More details about the property tax return
Declaration of property tax for individuals
Individual entrepreneurs do not submit a property tax return.
Single simplified declaration
If during the tax period an organization or individual entrepreneur does not have taxable objects and operations that result in the movement of funds through accounts and cash, they have the right, for certain taxes, to submit a single simplified declaration.
It should be noted that the EUD can be submitted to the OSN only for corporate income tax and VAT (provided that there are no VAT transactions). In relation to personal income tax, the submission of EUD is not allowed.
Learn more about the single simplified declaration.
KUDIR
The book of income and expenses is kept by individual entrepreneurs on OSNO and is necessary to determine the tax base for personal income tax.
It can be filled out in paper and electronic form, but, unlike, for example, KUDiR on the simplified tax system, it is subject to certification by the tax authority.
More details about KUDiR
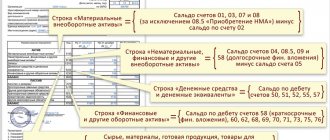
Financial statements
For small organizations
Organizations that are small businesses (the average number of employees is no more than 100 people and the total amount of income, both sales and non-sales, is not more than 800 million rubles per year) can conduct simplified accounting, as well as submit simplified reporting, which consists of balance sheet and income statement.
For large companies
Large organizations on OSNO (commercial) are required to maintain full accounting records and prepare financial statements, which consist of:
- Balance sheet.
- Statement of financial results (formerly called “Profit and Loss Statement”).
- Statement of changes in capital.
- Cash flow statement.
- Explanations for the balance sheet and these reports.
Starting with reporting for 2020, it must be submitted only electronically.
For non-profit organizations
For non-profit organizations, financial statements consist of a balance sheet, a report on the intended use of funds and appendices to them.
Starting with reporting for 2020, it must be submitted only electronically.
For individual entrepreneurs
Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO may not keep accounting records if they record income, expenses and business operations (KUDIR).
Reporting for employees
All employers are required to submit reports for their employees.
Learn more about reporting for employees