Features of the extraction process
The main feature of the reorganization of a company, carried out in the form of spinning off another company from it, is that during this process there is no liquidation.
In case of reorganization in all other forms, any of the reorganized entities ends its functioning. Reorganization in the form of spin-off is also accompanied by the transfer of part of the rights and obligations of the original enterprise to the created company. As a rule, a decision on such a reorganization is made by the authorized body of the enterprise if:
- it is necessary to divide or expand areas of activity;
- it is necessary to simplify the taxation system;
- it is necessary to divide the business between the owners;
- in any other situations.
At the same time, the transfer of rights and obligations under the transfer deed should be carried out fairly; the transferred obligations must correspond to and be secured by the transferred assets (see the ruling of the RF Supreme Court dated July 2, 2015 No. 301-ES15-7649 in case No. A43-16145/2012).
Moreover, the deed of transfer must clearly identify the legal successors. These requirements are due to the protection of creditors' rights. If the above principle of distribution is not observed, then the initial organization may be held jointly and severally liable (resolution of the plenum “On some issues of application of the Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 18, 2003 No. 19).
Legal magazine "Legal Insight"
Share: Facebook0
Google+0
Twitter0
LinkedIn0
Maxim Bunyakin , managing partner of Branan Legal Yulia Nenasheva , partner of Branan Legal
According to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, as of March 1, 2020, there were 25,962 legal entities in Russia in the process of reorganization. This demand from companies for reorganization is due to a number of factors: sanctions restrictions and capital amnesty, the general economic situation and the tax advantages of this mechanism, as well as the possibility of optimizing corporate governance in a group of companies. For many corporate lawyers, supporting restructuring is a complex task along with M&A transactions. In order to understand in more detail the practical issues of reorganization, on May 23 we invite in-house lawyers to a business breakfast. Registration via the link: https://branan-ligal.timepad.ru/event/960484/
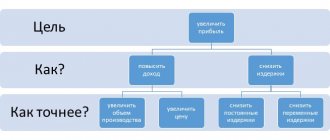
Reorganization is one of the effective and popular tools for solving business problems. With its help, in practice, problems of consolidating a business, dividing it between different groups of shareholders, spinning off individual businesses, transferring assets within the group or outside its perimeter are solved. It is reorganization that often becomes an effective tool for optimizing corporate governance in a large holding: when creating a sub-holding management model, increasing the independence of divisions or, conversely, strengthening the control of the parent company over the group companies.
Key benefits of the reorganization
The ability to transfer an existing business without suspending it. Reorganization is a complex legal mechanism for transferring all or part of the assets, property and liabilities between companies. Unlike individual transactions (purchase and sale, assignment of claims, transfer of debt, etc.), during reorganization there is a universal succession of all rights and obligations of the legal entity specified in the decision / transfer deed.
Depending on business goals, we can talk about either business consolidation (accession or merger) or its fragmentation (spin-off and division). In practice, companies in most cases choose acquisition (rather than merger) and spin-off (rather than division). This is mainly due to the ability not to freeze or suspend activities in anticipation of the creation of new legal entities (as happens during mergers and divisions) and, accordingly, the ability to open bank accounts, hire employees, conclude contracts with counterparties, register rights to property and etc.
An economical way to transfer assets. For cases of reorganization, tax legislation directly provides for a number of significant exceptions from the general taxation regime, for example:
- according to sub. 3 p. 3 art. 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not recognize the transfer of fixed assets, intangible assets and (or) other property of an organization to its legal successor(s) during the reorganization of this organization as a sale;
- in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 162.1. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not recognize the transfer by the taxpayer of the right of claim to the legal successor (legal successors) during the reorganization of the organization as payment for goods (work, services);
- by virtue of sub. 19th century 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to taxation (exempt from it) income of individuals received from joint-stock companies or other organizations by the shareholders of these companies, or by participants in other organizations during reorganization.
In addition, the transfer of property, rights and obligations during the reorganization process does not imply any settlements (including monetary transactions), or additional contributions for such transfer, which is especially important for intra-group reorganization. It is extremely important to consider that the reorganization must have a valid, demonstrable business purpose and not be used solely as a tool for tax optimization. This position is currently clearly supported by the relevant ministries and judicial practice.
Transparency of the process, legislative support for the interests of shareholders and creditors of the company. The legislation provides for the right of shareholders to demand the redemption of their shares if they did not participate in voting on the issue of reorganization or voted against such a decision (Article 75 of the Law on Joint Stock Companies). In these cases, the company is obliged to buy back shares owned by them from shareholders at a price not less than the market price, determined by an independent appraiser.
In case of reorganization, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 60) gives the creditor the right to demand in court the early fulfillment of the corresponding obligation by the debtor (the reorganized company), and if early fulfillment is impossible, then the termination of the obligation and compensation for related losses. Such claims may be made by creditors within 30 days after the publication of the last notice of reorganization. However, it must be taken into account that the mere fact of making a decision on reorganization does not qualify as a basis for early fulfillment of obligations to creditors. The creditor must prove the need for early fulfillment in court, that is, explain that after the reorganization the debtor will not be able to fulfill his obligations or will have difficulty fulfilling them. At the same time, since in practice large creditors can complicate or even block the reorganization, it is necessary to coordinate all planned changes with them in advance.
For shareholders, creditors and other third parties, reorganization is a fairly transparent process. The decision to hold it is made only by the general meeting of shareholders (participants) and only on the proposal of the board of directors (if there is one). Accordingly, in advance all shareholders (and in cases of mandatory disclosure of information - to any person) have access to information about the reorganization, including a description (justification) of the procedure and conditions for its implementation, parameters, a transfer act with detailed information on the composition of the transferred property, assets and liabilities. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Clause 1, Article 60) requires publications about the reorganization to be published twice, once a month. Information about the decision made on the reorganization, about its participants, as well as about its completion is mandatory entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and is available to all persons.
Choosing a reorganization mechanism
Before choosing a reorganization mechanism, you need to answer a number of questions. The result of the reorganization project and, accordingly, the successful continuation of the business will depend on correct and timely answers to them.
What are the key risks during reorganization? The top 5 risks of reorganization usually include: risks from creditors; tax risks (tax audit, justification of the business purpose of the reorganization); licensing risks (the need to transfer licenses to ensure business continuity); corporate risks; risks of project management (errors in planning deadlines, control over the project, coordination of a large number of participants). A practical tool for risk management is a detailed risk map with specific measures to minimize them and indicating those responsible for the activities.
How to build the correct reorganization schedule? The reorganization schedule should be as detailed as possible (detailed by day and individual actions, operations). On average, these are 500–700 points and events. In practice, we often see that companies prepare only a schedule of corporate events and mandatory procedures for working with government authorities. In our opinion, this approach is wrong. The schedule (reorganization roadmap) must cover absolutely all areas and divisions of the company.
How to work with creditors so that they do not block the reorganization? It is necessary to draw up in advance a convenient register of creditors, ranking them by risk level and volume of claims. Financial creditors and banks are traditionally in a high-risk group; it is necessary to carry out preliminary and maximally formalized work with them with the signing of legally significant documents. We should not forget about small claims, specific creditors and counterparties, such as parties to a corporate agreement, option agreements, etc. Based on the register of creditors, a plan for working with them is drawn up and implemented. Typically, compiling a register is a joint task of the legal and financial blocks.
When is it possible not to issue an issue during reorganization? The desire to optimize processes and, in particular, not to carry out emissions during reorganization is quite understandable. The legal possibilities available for this depend on many factors, including the capital structure and ownership of the companies participating in the reorganization, the ability to prepare such a structure, change it before the start of the reorganization, the provisions of the merger agreement, etc.
How to transfer licenses without risking business interruption? As a general rule, it will not be possible to transfer a license to a successor during a reorganization - he must register it in his own name. But there are exceptions for certain types of licenses. In addition, some reorganization mechanisms (the correct sequence of affiliation, “combined” reorganization, etc.) make it possible to minimize the risk associated with licensing.
When is a transfer deed needed ? According to the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a transfer deed is required only when dividing or separating. In fact, it is prepared and approved for other forms of reorganization, primarily for practical reasons to minimize risks with the re-registration of rights to property and the formation of financial statements of the successor. The question often arises about the possibility of changing the transfer deed after it has been drawn up (and after the inventory), since during the reorganization period property and obligations may change. It is legally incorrect to change and re-approve the transfer deed. We recommend including in it the so-called rules of succession, which establish the principles and special cases of changing the composition and volume of property, rights and obligations.
How to correctly determine conversion rates? To date, the legislation does not contain restrictions regarding the determination of conversion factors. They can be determined based on the ratio of the market value of the reorganized companies, the book value of their assets, etc. Also, different (non-proportional) coefficients can be used for certain groups of shareholders / participants. It is important to remember that during a reorganization, carried out, for example, in the form of a spin-off or division, all shareholders voting against or not participating in the voting must receive strictly proportional shares in the companies being created.
Why is the increasingly popular mechanism of separation with simultaneous addition used? Selection with simultaneous attachment allows you to solve a number of problems that are impossible or difficult to solve in other ways. For example, with the help of such a “combined” reorganization, it is possible to transfer part of the business to another group company, isolate certain types of business in the holding, reduce the period for transferring assets and liabilities, etc.
What non-legal skills does a lawyer-manager need during the reorganization process? It is the lawyer who often becomes the manager of a reorganization project. In this case, he, of course, must already possess completely non-legal skills and knowledge or quickly acquire them during the project. We are talking primarily about project management (planning, budgeting, creating working bodies, exercising control), understanding the essence of business and business processes, key financial and accounting aspects of reorganization, etc. Effective project management is impossible without knowledge of all key aspects reorganization.
Stages of reorganization
Before you begin reorganizing a company, you need to understand what actions will need to be taken. In general, the reorganization operation in the form of a spin-off is similar to other types of reorganization. To complete this procedure you will need to do the following:
- The authorized body must decide to conduct an inventory of property by creating an inventory commission. This is necessary to understand how much property, debts, rights and obligations the reorganized person has.
- Based on the results of the inventory, a transfer act is drawn up, which should reflect what rights and obligations remain with the original enterprise, and what is transferred to the newly formed company.
- The authorized body of the company must make an appropriate decision on the separation (depending on the organizational type of the company, this body may be a conference, members of the union, a general meeting of founders or shareholders, the owner of the property, a government body, etc.).
- Next, you should report the reorganization to the registration authority, creditors, and publish a message in the media. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 60 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, publication must be made twice, the time interval between publications must be 1 month.
- Then you need to agree on the transfer deed and register it with the authorized government agency.
The listed stages only in general terms characterize the reorganization operation in the form of separation . In practice, it may be complicated by some additional conditions.
REORGANIZATION IN THE FORM OF SEPARATION
Reorganization in the form of spin-off
is a type of reorganization in which the organization does not cease to exist.
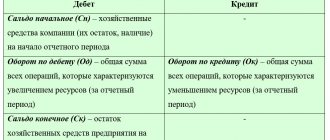
A legal entity is considered reorganized from the moment of state registration of newly emerged legal entities on the basis of a transfer act, which must contain provisions on succession for all obligations of the reorganized legal entity in relation to all its creditors and debtors, including obligations disputed by the parties, as well as the procedure for determining succession in connection with a change in the type, composition, value of property, the emergence, change, termination of the rights and obligations of the reorganized legal entity, which may occur after the date on which the transfer deed was drawn up.
During reorganization by separation, one or more legal entities are created, which will be considered newly created as a result of the reorganization.
Reorganization procedure
in an economic sense, mediates the division of capital between the founders.
In its pure form, it means the creation of a separate society, inheriting certain rights and obligations of the original society, and is aimed at dividing business. However, in its pure form it is extremely rare; most often in business activities, the procedure for reorganizing an LLC in the form of a spin-off is used for the so-called restructuring of the company’s debts, in which certain property and certain obligations are transferred to the spun-off company. THE BASIC PACKAGE OF SERVICES FOR REORGANIZATION IN THE FORM OF SEPARATION INCLUDES:
- Consulting the client on choosing a suitable organizational and legal form for the newly transformed enterprise; collection and analysis of documents
- Preparation of a package of necessary documents for the reorganization of the enterprise
- Making a seal
- Submitting an advertisement to the gazette of state registration of legal entities Registration of documents in the MIFTS, Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, statistics
- Notification of creditors
Reorganization in the form of a spin-off
allows you to divide a business in such a way as to separate liquid property from illiquid property and get rid of part of the liabilities attributable to illiquid property. That is why the legislation regulates in such detail the procedure for transferring responsibility from the enterprise from which the organizations are separated to its legal successors.
Reorganization of an LLC in the form of a spin-off is in practice used to divide the property of one company between its participants. At the stage of such a reorganization, problems may arise that often lead to legal disputes. To date, the following issues are being considered within the framework of disputes related to such reorganization:
- the ratio of the property transferred to the spun-off LLC and the actual value of the shares of the participants transferred to the spun-off company
- consequences of evasion by a spun-off LLC from state registration of the transfer of ownership of the property transferred to it
- joint liability of companies during reorganization in the form of spin-off
During reorganization by spin-off, the general meeting of participants of the reorganized legal entity submits for consideration the issue of reorganizing the company in the form of spin-off, the procedure and conditions of this reorganization, the creation of a new company, and the procedure for converting shares (shares) of the reorganized company into shares (shares) of the created company.
When one or more organizations are separated from a legal entity, part of the rights and obligations of the legal entity reorganized in the form of separation is transferred to each of them in accordance with the transfer act.
The transfer document is approved by the founders of the legal entity or the body that made the decision on the reorganization, and is submitted together with the constituent documents for state registration of the newly emerged legal entity. Failure to submit a deed of transfer along with the constituent documents, as well as the absence in it of a provision on succession of obligations of the reorganized legal entity, is grounds for refusal of state registration of the newly emerged legal entity.
If the transfer deed does not make it possible to determine the successor of the reorganized legal entity, the newly created legal entities bear joint liability for the obligations of the reorganized legal entity to its creditors.
Issues of separation from an LLC cause a lot of different disputes (legal), when certain parties for whom this procedure is unprofitable try to challenge it. Documents adopted during the reorganization procedure in the form of separation: decisions of general meetings, transfer deeds - undergo a strict and meticulous check, and often do not withstand it.
When faced with such a complex, multi-part legal procedure, you should turn to professionals who understand all the intricacies of the current legislation. In legal matters, clients can always count on a competent and responsible approach to business and prompt, clear actions.
Spin-off with change of legal form
The law does not prohibit a spin-off, as a result of which companies of one organizational form can create a completely different type. However, here you should be more attentive to the laws regulating the activities of organizations of one type or another.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
For example, paragraph 1 of Art. 56 of the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ (hereinafter referred to as the Federal Law on LLC) allows such a company to carry out reorganization in the form of transformation into a business company or partnership, as well as into a production cooperative. Consequently, during reorganization in the form of separation from an LLC, it is possible to form a new enterprise of a different organizational form, for example, a JSC. This will be considered a mixed reorganization when 2 forms are involved - allocation and transformation.
Allocation by decision of a government agency
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of forced reorganization in the form of separation based on a resolution of an authorized state body and a court. The special regulatory act that provides for this possibility is the federal law “On the Protection of Competition” dated July 26, 2006 No. 135-FZ. Yes, Art. 38 of this law provides that if an organization that occupies a dominant position constantly carries out monopolistic activities, the antimonopoly authority has the right to file a claim in court. Based on the results of consideration of such a statement of claim, the court may approve a decision to separate one or more new enterprises from such an organization.
Such a restriction of rights is determined by the goal of developing competitive relations in the market. The court is capable of adopting an act of reorganization of a commercial enterprise in the form of separation if the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- The structural divisions of the reorganized entity are separate or can be made separate.
- Organizations formed as a result of the spin-off will be able to operate independently in a specific product market.
- There is no technological relationship between the structural divisions of the reorganized legal entity.
The court decision is subject to execution by the owner of the enterprise's property, and the period for execution should not be less than 6 months.
Step-by-step instructions for reorganizing companies in the spin-off format
FIRST STAGE. Preparation of documents
To hold a meeting
To put on the agenda of the meeting for discussion the issues that are specified in paragraph 2, article 55 of Law No. 14-FZ. If an enterprise has several owners, then the decision on reorganization, its format and other important nuances must be made unanimously. It is necessary to draw up a protocol documenting the decision made on reorganization.
Based on this decision, an inventory order should be issued followed by drawing up a transfer act based on its results. It is an important document that records the transfer of a list of the parent company’s property to the newly formed legal entity.
Send notifications to counterparties and government agencies
- To the tax service and registration authority. According to the Law “On State Registration”, within 3 days after drawing up the protocol on reorganization, letters drawn up in form P12003 should be sent to the tax service, the registration authority.
- Pension Fund and Fiscal Service. It is also necessary to submit notifications to the Pension Fund of Russia and the Social Insurance Fund that the enterprise has entered into a reorganization procedure. This should be done within 3 working days.
- To creditors. After the meeting, it is necessary to notify creditors within 5 days of the decision to reorganize the enterprise in the form of a spin-off.
Draw up a separation balance sheet
This is a necessary document (clause 1 of Article 59 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), which contains clauses on succession regarding the rights and obligations of the reorganized company in relation to its creditors, as well as issues disputed by the parties. That is, the separation balance sheet determines the division and transfer of property from the parent organization to the newly formed one as a result of the reorganization.
Publication in "Vestnik"
To notify government bodies and interested parties, two notes are published in the “Bulletin of State Registration” with an interval of 1 month. An application for publication can be submitted on the official website of the newsletter www.vestnik-gosreg.ru. 30 days after publication, you can send documents to the tax service.
Tax obligations upon allocation
The tax obligations of a company that is subject to reorganization are determined by Art. 50 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part 1) dated July 31, 1998 No. 146-FZ. This rule states that these obligations are assigned to legal successors, regardless of whether they knew or not about the existence of unfulfilled obligations, fines or penalties.
It is noteworthy that the process of reorganization of the enterprise does not have any impact on the time period within which the successor is obliged to fulfill these obligations.
IMPORTANT! The above conditions of succession are a general rule and do not apply to reorganization carried out by way of separation, which is a kind of exception within the framework of tax law.
Thus, according to tax legislation, when a new legal entity is separated, it does not become the legal successor of the reorganized one. The latter, in turn, continues to bear the responsibility for paying taxes. However, if as a result of this procedure the reorganized company is unable to fulfill its obligations to the tax service and if it is proven that the reorganization was carried out with the aim of avoiding such fulfillment, then the court may oblige the spun-off companies to fulfill the obligation jointly and severally with the original organization.
Succession and public legal relations
The general rule of succession established by civil law also applies to rights and obligations that arise from public legal relations. The legislator has not established any rules excluding this possibility.
Accordingly, reorganization in the form of separation cannot be a reason for the rights and obligations arising from public legal relations to be terminated. They continue to exist with the spun-off company to the extent determined by the transfer deed.
This position is fully supported by the Supreme Court. In particular, by the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 3, 2014 No. 41-APG14-6, the highest judicial body considered that succession in the allocation also applies to tariff regulation.
Reorganization errors
If the declared business purpose is subtle, then the tax authorities' claims may be supported in court. Let's illustrate again with example 6.
Given: two on the OSN and LLC “Operating Company” on the simplified tax system. The first one owns property - a restaurant. The second leases this property and uses it for its intended purpose. It is important that the premises themselves were purchased quite recently and in the tax period preceding the events described below, a VAT refund was received from the budget.
Business owners came up with a simple plan: transfer assets to the simplified tax system, avoiding VAT restoration. To achieve this, the owner decided to reorganize in the form of a spin-off.
Further events developed as follows:
(1) Separation of Promezhutok LLC with the transfer of real estate to it. Let us recall that the decision to allocate was made in the next quarter after confirmation of the VAT deduction and receipt of reimbursement from the budget;
(2) After registration, Promezhutok LLC applies the simplified tax system, but from January 1 of the next year it switches to the simplified tax system. At the same time, the same application is submitted by the original one, who got rid of valuable property;
(3) A few months later, the procedure for merging Promezhutok LLC with the Operating Company (restaurant) begins.
The tax authority did not like such actions. In his opinion, Promezhutok LLC should have restored VAT. And since the merger was completed by the time the demand was presented, the Operating Company came under attack.
Let's look at the taxpayer's mistakes that led to the described result:
Firstly, the reorganization was announced immediately after receiving the VAT deduction. At the same time, the owner of the property did not conduct independent activities, which means he did not pay VAT on sales to the budget. Conclusion - the property was purchased to obtain a deduction. Obviously, the tax authority simply could not allow this to happen.
Secondly, during the separation, the balance of distribution of rights and obligations with the legal successor was not maintained. In this case, according to the separation balance sheet, the new Company received a restaurant complex, but no obligations were transferred to it.
Third, the business purpose of the reorganization. In this case, the taxpayer tried to prove that all the actions it took were aimed solely at reducing the operating company's expenses for paying rent. They even provided an audit report to substantiate the stated business goal.