The responsibility to record all ongoing business transactions falls on the shoulders of many legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. According to Russian legislation, economic entities must constantly maintain accounting records, unless otherwise provided by Federal Law N 402 “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011.
The cornerstone of accounting can be considered an accounting entry, with the help of which any action of the company (purchase of materials, payment of salaries, etc.) is reflected in numbers - that is, the fact of a change in the state of the objects taken into account is recorded. Let's discuss how typical accounting entries are prepared and look at examples.
What is an accounting account?
It is very difficult for novice accountants to understand the preparation of entries without a clear understanding of what an account is, so it is better to move “from the stove”.
An accounting account is a certain position in business accounting necessary for continuous monitoring of the ongoing movement of property owned by the company, as well as the sources of its formation. This is done by using the double entry method, when one transaction is reflected twice - as a debit to one account and as a credit to another. All accounts that are used in the accounting of commercial companies are systematized and grouped in a special document - the chart of accounts.
Advice: when analyzing transactions and making entries, it is best to keep at hand the general chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations.
Accounting accounts are divided into three types depending on what object is subject to accounting:
- Active – designed to display in monetary terms information about the organization’s economic assets and resources. For example, materials (10), cash in the cash register (50), finished products (43), etc. The opening balance of active accounts is recorded only by debit, the ending balance is the same. Transactions that are characterized by an increase in the company's funds are indicated as a debit of the account. If resources decrease, the entry is credited.
- Passive - they take into account in monetary terms the state, movements and changes in the sources through which the company’s economic assets were formed. For example, depreciation of fixed assets (02), trade margin (42), authorized capital (80), etc. The opening and closing balances can only be for the loan. Entries that increase the account go to credit, and those that decrease it go to debit.
- Active-passive – insidious accounts that play the role of both passive and active. It is important to understand which account sign is triggered in each specific situation. The opening balance can be recorded both as a debit and as a credit; It is possible to have a debit and credit opening balance at the same time. For example, active-passive account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.” If a company has accounts receivable (that is, someone owes it), then the amount is written as a debit, and in the case of accounts payable (the company owes someone), the figure is reflected as a credit.
When accountants were forced to carry out calculations without using a computer, accounts were drawn in the form of original tablets, which were popularly called “airplanes.” Each account has its own scheme, they look like this.
- Typical active account scheme:
- Typical passive account scheme:
- Typical active-passive account scheme:
Typical entries for accounting of property and other assets
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Fixed assets | ||
| Fixed asset item purchased | 08 | 60 |
| Purchased equipment that requires installation | 07 | 60 |
| VAT on purchased fixed assets is reflected | 19 | 60 |
| Equipment handed over for installation | 08 | 07 |
| The fixed assets object was put into operation | 01 | 08 |
| Depreciation accrued | 20, 25, 26, 44 | 02 |
| Fixed asset object sold | 62 | 91 |
| The initial cost of the object is written off upon disposal (write-off, sale) | 91 | 01 |
| Accrued depreciation written off upon disposal | 02 | 91 |
| Reflects the financial result upon disposal of a fixed asset item | ||
| profit | 91 | 99 |
| lesion | 99 | 91 |
| Tangible current assets (inventories, finished products, goods) | ||
| Materials for production and other economic activities were purchased | 10 | 60 |
| Materials written off for production of products, performance of work, provision of services, wiring | 20 | 10 |
| Materials written off as general production expenses | 25 | 10 |
| Recorded write-off of inventory items for management needs | 26 | 10 |
| Unnecessary materials are sold outsourced | 91 | 10 |
| Purchased goods for resale | 41 | 60 |
| Cost of goods sold written off | 90 | 41 |
| Finished products released | 43 | 20 |
| Finished products sold to customers | 90 | 43 |
| At the time the result of the work is delivered to the customer, the cost of services provided and work performed is written off | 90 | 20 |
| Settlements with debtors | ||
| Products sold to customers, services provided | 62 | 90 |
| The advance previously received from the buyer is credited, posting | 62 | 62 |
| Advance paid to supplier | 60 | 51 |
| A loan was issued to a third party organization or to an employee of the organization | 58 | 51 |
| Cash flow accounting | ||
| Payment received from buyers | 51 | 62 |
| Paid for supplies to suppliers | 60, 76 | 51 |
| Funds have been received at the cash desk from the current account | 50 | 51 |
| Money transferred from one current account to another | 51 | 51 |
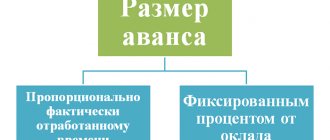
| Wages paid | 70 | 50, 51 |
| Taxes and contributions to the budget are transferred | 68, 69 | 51 |
| Money issued on account | 71 | 50, 51 |
| Paid for bank services | 91 | 51 |
How are accounting entries prepared?
Accounting entries are based on the principle of double entry: the transaction amount is recorded as a debit to one account and a credit to another, that is, a balance is always maintained, which is why the asset must always be equal to the liability.
Example: suppose the founder of an LLC made a contribution to the authorized capital in the amount of 10,000 rubles by depositing the money into a current account. Then we can draw the following conclusion - the company acquired assets (cash), and at the same time, obligations to the founder arose. The result will be the following double entry: Dt 51 “Current account” – Kt 80 “Authorized capital” – 10,000 rubles.
The meaning and essence of the wiring is easy to understand if you realize that nothing in this world comes out of nowhere and disappears without a trace. Everything is logical - we bought the materials, which means we paid money for them. In other words, there was an increase in materials, but a decrease in finances. There is an interesting point here: movement between items can occur without changing the total for assets and liabilities. For example, the production of goods was completed, therefore, they became finished goods. Two active accounts were affected - one decreased and the other increased by the same amount. Posting in this situation: Dt 43 “Finished products” - Kt 20 “Main production” .
See also: Do individual entrepreneurs have checkpoints?
And if a company pays a debt to a supplier from a current account, then there will be a simultaneous decrease in assets and liabilities, since this operation affects the active cash account and the active-passive (the passive sign is triggered, as our company must) account reflecting accounts payable. Posting: Dt 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” – Kt 51 “Settlement account” .
Business processes and business operations
In the activities of a manufacturing enterprise or organization that performs work or provides services, three processes are distinguished:
- supply,
- production,
- implementation.
Processes consist of a set of business operations.
A business transaction in accounting is an action (fact), the result of which is changes in the composition, distribution of property and the sources of its formation. For example, the movement of cash, material assets, liabilities.
Business processes in accounting are reflected as business transactions are carried out - in this case, the subject of accounting becomes the fact of the transaction and the result.
Business operations and processes of the enterprise - diagram
Accounting entries for specific business transactions
The number of balance sheet accounts approaches a hundred - of course, this is a lot, especially if you remember that some have numerous sub-accounts. This diversity leads to complications: there are a great many typical accounting entries - just imagine all the possible combinations. Moreover, it must be borne in mind that some transactions are recorded not in one, but in several transactions. It is probably impossible to consider all the options, but it is quite possible to highlight those that most organizations face. Let's discuss different cases, presenting information with answers in tables.
For fixed assets accounting
Fixed assets are tangible assets that are directly involved in production processes and are present in the activities of many companies (buildings, structures, transport, tools and even perennial crops and breeding livestock). Their distinctive feature is the period of use - it must exceed one year. For example, fixed assets (PE) include production equipment. Everyone understands that you can work with it for more than 12 months, but over time, its useful life expires, that is, banal wear and tear occurs. Therefore, the cost of fixed assets is gradually transferred to the cost of production through depreciation.
Let us present in the table the postings-responses for those typical accounting transactions that relate to fixed assets:
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting at their original cost, which is the sum of all costs associated with the acquisition of an asset. That is, this includes not only the direct costs of purchasing an OS or its construction, but also the cost of delivery, installation, consulting services, and the like. However, we must remember that, in accordance with PBU 6/01, assets whose value does not exceed 40,000 rubles can be reflected in accounting as part of inventories (inventory) - their receipt is reflected in account 10 “Materials”.
By accounting for intangible assets
A company's intangible assets have no physical form, yet they are capable of generating economic benefits and can be clearly identified. For example, intangible assets include the business reputation of a company and various objects of intellectual property - you cannot touch it with your hands, but exclusive rights to something (a trademark, a program, breeding achievements, etc.) often make it possible to receive significant income.
See also: How to calculate income tax from wages?
Answers to the main questions related to accounting of intangible assets are presented in the table:
Organizational expenses incurred during the formation of a legal entity cannot be classified as intangible assets (PBU 14/07).
According to inventory accounting
All companies involved in manufacturing are constantly faced with the need to purchase materials (inventory, or inventories). As a rule, even for novice accountants, their accounting does not cause difficulties - the answers and postings for typical transactions can be seen in the table:
Nowadays, fuel cards are widely used by many organizations whose activities are closely related to transport. Novice financiers often have difficulties with accounting for fuel and lubricants on fuel cards, since at present there is no clear legally approved procedure for carrying out this procedure - some believe that account 10 “Materials” can be used, but experts say that this approach is incorrect and advise use off-balance sheet accounts.
Advice: several years ago, a universal transfer document specially developed by the Federal Tax Service came into use among accountants, but not all companies wanted to get acquainted with it, fearing innovations. If you do not yet use UPD, then you should think about changing the situation, since this will allow you to significantly reduce document flow, and therefore significantly save time.
By accounting for production costs
For people starting to understand the preparation of accounting entries, it is sometimes quite problematic to deal with the accounting of production costs, because several accounts are intended for them. Usually, the accounting policy of the organization prescribes how the valuation of retiring inventories occurs (PBU 5/01). Let's look at the answers to the most common situations in the table:
Production cost accounts include 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 28, 29.
For accounting of finished products and goods
Many companies build their business on the sale of any goods, so it is important for novice accountants to understand how their accounting is carried out. Answers in the form of entries for typical business transactions involving the purchase and sale of marketable products can be found in the table:
If an organization is engaged in purchasing goods from suppliers, then great attention should be paid to checking the documentation provided by the counterparty. Remember that you have the right not to rush joyfully to the first offer if it seems unprofitable. In this case, a protocol of disagreements to the contract is usually drawn up, reflecting the position of the party who disagrees with any of the terms.
Important: the table shows only the basic standard accounting entries - in the accounting of goods and finished products, there are a lot of options possible, since they often need to be revalued and are sometimes made as a contribution to the authorized capital (or in general the company receives them for free). To become familiar with all situations, it is necessary to study in detail the Accounting Regulations and other special literature.
Cash accounting
While not all companies deal with the production of products, probably absolutely all of them work with money. For financial accounting, two accounts are most often used - 50 “Cash” and 51 “Current account”. From the names it is intuitively clear - money is usually stored either in the cash register or in a bank account. Let's look at typical transactions in the table that affect the organization's funds and give the answers in the form of transactions:
Novice accountants should remember that when carrying out transactions with funds, the appropriate documentation must be drawn up - payment orders, cash receipts and debit orders, advance reports, cash inventory reports, etc.
According to settlements with staff
Partial answers to questions on typical accounting entries affecting the payment of employees were given above; To make the information easier to perceive, we group them in a table:
Accounting for loans and borrowings
Who hasn’t needed a loan in these difficult times? Entrepreneurs are no exception - often business development requires additional financial investments, and there is simply nowhere to get them... Then businessmen usually go to banking institutions. Novice accountants will be able to process “credit” transactions without any problems, because there are not many options here - you need to reflect the loan received, calculate the monthly loan payment, etc. For clarity, we present typical postings-responses in the table:
The table most often contains two accounts - 66 and 67. You need to choose depending on the loan term: account 66 is called “Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings,” and 67 is called “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings.”
For transactions with authorized capital
Authorized capital is financial funds or any property that the founders contributed during the registration of the LLC. There is an opinion in society that a contribution to a management company necessarily represents money, but this is not at all true - if you are the owner of a building, then, of course, you can become the founder of an LLC by contributing your real estate to the authorized capital. What else can you use as a contribution? We will answer this question in the table, giving typical entries for accounting of authorized capital:
For accounting of financial results
Of course, the goal of any business activity is to generate income. The financial result is determined by the profit or loss generated by the end of the reporting period. If income exceeds expenses, then the property of the enterprise increases, that is, the company makes a profit; in the opposite situation, there is a loss. Let's consider in the table how entries are made for transactions related to the formation of the financial result:
Account 90 “Sales” reflects revenue as a debit, and as a credit – costs that relate to cost, as well as excise taxes and taxes. When the balance of account 90 is in credit at the end of the period, profit is recognized. If the balance is debit, then the company has incurred a loss. It should be remembered that account 99 is written off to 84 on the last day of the reporting period, that is, its balance becomes zero.
Existing types
You can consider how the problem of mapping specific business actions is solved. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation and accounting provisions are used as a practical guide to action.
An administrative officer must formulate the organization’s budget and its execution in full accordance with the listed documents. Otherwise, government control authorities will be held accountable in the form of a fine or criminal prosecution.
Memo to an accountant
Fixed Asset Accounting
Working with underlying assets. What is fixed asset accounting? Entries should reflect their receipt, depreciation, restoration, sale and liquidation. And now a brief explanation of the design:
- Receipt of fixed assets. Dt 08 Kt 60/10/70/69 - used to display expenses aimed at creating or acquiring OS. Dt 19 Kt 60 - input VAT. Dt 01 Kt 08 - fixed assets are formed and put into operation.
- Depreciation deductions. Dt 20/23/25/26/29/44 Kt 02 - transfer of the cost of fixed assets to manufactured products and services offered.
- OS recovery. Dt 08 Kt 60 - reflects the price of the contractor’s services. Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT is issued. Dt 08 Kt 10/69/70... - the costs of modernization are displayed if it was carried out on your own.
- OS sales. Dt 62 Kt 91 - the income received is displayed. Dt 91 Kt 68 - payment of VAT. Dt 02 Kt 01 - depreciation is written off. Dt 91 Kt 01 - the residual value is reset to zero.
- Liquidation of fixed assets. Dt 02 Kt 01 and Dt 91 Kt 01 - accumulated depreciation and residual value of fixed assets are written off accordingly.
Personal funds
Relevant for individual entrepreneurs. The decision to withdraw funds confuses many people. And it’s not surprising, because individual entrepreneurs do not fit into existing accounting provisions. Not surprisingly, they don't have to lead it.
Those who, for certain reasons, while on the simplified tax system, fill out all the documentation and have a need for accounting, use the option: Dt 51 Kt 84.03 - depositing personal funds, Dt 84.03 Kt 51 - withdrawing them.
On a note! As an alternative, accounts 75 and 84 can be used. Contributing money to individual entrepreneurs and using available funds at their own discretion does not raise questions for the tax service if these two options are used.
Administrative fines
If an offense has been committed, you have to pay for it. Fines are carried out on the following accounts:
- Dt 91.2 - Kt 76 - the amount is calculated.
- Dt 76 - Kt 51 - the fine was transferred to the budget.
- DT 99 - CT 68.4 - permanent tax liabilities are reflected.
You need to be sure that the numbers are accurate. If you have doubts, it’s better to recalculate
Traffic police fines
It’s better not to start breaking the law - it will cost you more. Accrual is carried out according to Dt 91.2 - Kt 76. Payment should be made according to Dt 76 - Kt 51/50.
Assignment of debt
This operation is displayed as follows:
- Dt 76 - Kt 62 reflects the debt to the counterparty. This posting is made immediately after signing the debt assignment agreement.
- Dt 62 - Kt 51/50 - this is the repayment of obligations to the counterparty.
- Dt 76 - Kt 51/50 reflects the receipt of payment amounts against the debt from the original debtor.
These are the postings that the supplier displays in its documentation. Acceptance of the assignment agreement always goes according to the listed invoices.
Funeral benefit
Part of the cost is providing assistance to those who need it. In the most extreme cases, family support. These include funeral benefits. Accounting entries are recorded as follows:
- Dt 69 - Kt 73 benefits are paid to an employee if a minor dies in his family. The amount is credited towards the funeral.
- Dt 69 - Kt 76 - this posting option is used if the benefit is received by a relative of a former employee or by the person who took upon himself the organization of the funeral. Paid in one lump sum. Posting to the same accounts occurs in the case of reimbursement of spent funds to the funeral service.
Sponsorship
To display it in documents, postings are used:
- Receipt of funds: Dt 51 - Kt 62/2.
- Accounting for the provision of services: Dt 62 - Kt 90/1.
- The expenses incurred are carried out according to: Dt 90/2 - Kt 44.
- Why are advances made according to: Dt 62/1 and Kt 62/2.
A donation to an organization or a specific person from a sponsor looks like this:
- Transfer of advance payment: Dt 60/2 - Kt 51.
- Inclusion of costs in expenses: Dt 44 - Kt 60/1.
- VAT accounting: Dt 19 - Kt 60/1.
- Offsetting the advance: Dt 60/1 - Kt 60/2.
Insurance compensation
If you want to distribute the risks, postings are made to the following accounts:
- Dt 76 - Kt 51/50: the amount of the insurance premium is paid.
- Dt 97 - Kt 76.1: the remaining part of payments is attributed to deferred expenses.
- Dt 20/23/25/26/44 - Kt 76: the entire amount of the insurance premium is written off.
- Dt 20/23/25/26/44 - Kt 97: posting for monthly expenses.
- Dt 76 - Kt 91.1: compensation accrued.
- Dt 51 - Kt 76: money received from the insurer.
Business income
For individual entrepreneurs, everything is almost as difficult as with personal finances. Since an individual entrepreneur is not required to keep accounting records, in practice they choose one of the free accounts and use it. At the same time, it is not necessary that there be a simplification. For example, if an individual entrepreneur wants to register income from his activities, you can use the scheme Dt 75 - Kt 51.
On a note! In this way, funds are withdrawn to a bank card.
Reimbursement of overspending on advance payment
If a debt has arisen, then the cash desk returns the employee’s personal funds that were spent on a business trip or on solving assigned tasks, provided that there is confirmation. An example of the implementation of postings in this case:
- Dt 71 - Kt 50 - from the cash register the employee is given a certain amount for reporting.
- Dt 10 - Kt 71 - goods were received (any, for example, a batch of teapots) / checks for transport services, accommodation, insurance, and so on.
- Dt 91 - Kt 19 - minus tax (VAT) at the expense of the enterprise’s own funds.
- Dt 71 - Kt 50 - the employee is reimbursed for overexpenses exceeding the amount paid in advance.
Accounting for a letter of credit
In this case, the wiring will be as follows:
- Dt 55 - Kt 66: opening a letter of credit by attracting a short-term loan or credit.
- Dt 55 - Kt 67: the same as with item No. 1, but for a long time.
- Dt 55 - Kt 51: funds are credited from the current account to the letter of credit.
- Dt 60 - Kt 55: finances are written off to pay for supplied products, services, work, as an advance, etc.
- Dt 76 Kt 55: funds are transferred for insuring the letter of credit.
- Dt 51 Kt 55: unused money is credited to the organization’s current account.
Accounting for factoring operations
A typical approach to display in accounting is:
- Dt 61 - Kt 90: used to account for debt on goods sold.
- Dt 90 - Kt 68: VAT on sales of products is reflected.
- Dt 76 - Kt 91: assignment of a monetary claim to a financial institution is displayed.
- Dt 91 - Kt 92: the amount of item 3 is written off.
- Dt 51 - Kt 76: the bank transfers funds provided under the factoring agreement.
- Dt 91 - Kt 76: the amount of the bank's remuneration is reflected.
- Dt 19 - Kt 76: the VAT amount from clause 6 is displayed.
- Dt 68 - Kt 19: VAT charged on the amount of remuneration in clause 6 is accepted for deduction.
Tax calculation
Budgetary and commercial organizations and institutions are required to pay wages, submit reports monthly and every year, and correctly calculate deductions. It is important not to make mistakes with the rules for taxation of salaries, bonuses, agency fees, leasing, insurance payments and many other points. A whole book would not be enough to describe all the intricacies associated with taxes. Additionally, each step considered has its own subtleties. It is not surprising that the tax code is one of the largest legislatively regulated documents.
Measure twice, cut once is a valuable principle in accounting.
But how then can you display the financial result and transactions without getting into trouble? The best option is to hire an experienced accountant who will deal with all the nuances. And this is not an understatement. After all, there is a single agricultural tax, simplified tax system, a common system, patents, property fees, overpayments, penalties, transport, land and many other taxes. Depending on a number of subtleties, postings can be made using accounts 19, 68, 69, 90, 91 and 99.
Assignment agreement
Postings to the account. and tax accounting vary depending on which side the registration is from. The following entries are relevant for the initial creditor (assignor):
- Dt 62 - Dt 90.1: trading operations are displayed.
- Dt 90.3 - Kt 68.2: VAT is charged.
- Dt 90.2 - Kt 41: the cost of the goods is indicated.
- Dt 90.9 - Kt 99: the profit received is displayed according to the supply agreement.
- Dt 76 - Kt 91: the sale of debt is recorded.
- Dt 91.2 - Kt 62: write-off of receivables.
- Dt 99 - Kt 91: the loss received due to the assignment is displayed.
The transaction participant acquiring the assigned right makes changes as follows:
- Dt 58 - Kt 76: asset acquisition and legal support costs are displayed.
- Dt 76 - Kt 51: payment is transferred to the assignor.
- Dt 51 - Kt 91.1: the debtor pays the money due.
- Dt 91.2 - Kt 58: all expenses incurred are taken into account.
- Dt 91.2 - Kt 68.2: VAT is charged.
- Dt 91.9 - Kt 99: profit was received under the assignment agreement.
In this case, you should be careful and carefully study all documents. It may turn out that the structure provides for the presence of a principal who has a priority right to carry out the transaction, which often leads to subsequent litigation.
Is it possible to make transactions online?
Today, many Internet services lure novice accountants with the opportunity to make transactions online - automatically, free of charge and in real time. Of course, no one forbids taking advantage of the offer, but it is worth understanding that the business operations of each specific company have their own subtleties and nuances, so it is easy to end up with incorrectly formed accounting entries. It is logical that a person involved in accounting should know the chart of accounts and PBU by heart, and the owners of this information usually do not need help in analyzing business transactions.
Important: if you still do not want to prepare accounting entries yourself, then it is better to use special software, for example 1C: Accounting.
Methods for installing wiring in an apartment
It is important to immediately make a reservation that the following options will only be relevant for buildings with walls made of concrete or brick. They are not suitable for wooden houses, so the methods are not universal.
The first method will be relevant for those houses where there is not even a layer of plaster on the walls. Then the wiring can be placed directly on the surface of the walls. There are also two methods here, which were already mentioned earlier:
- Place the cables in corrugated plastic pipes if the thickness of the finish allows.
- Simply lay the cables open if they have double or triple insulation.
The second method is encountered most often, because it is suitable for cases when:
- The plaster has already been applied.
- Its layer will not cover the wires and you will have to make grooves directly in the wall.
This is a more difficult and longer path, but most often it turns out to be the only suitable one. In addition to the fact that the grooves have to be made, the wires in them will also need to be carefully fixed - with plaster patches or plastic staples.
*(Dowel staples are especially suitable for ceiling wiring)
To make all the grooves correctly, it is better to make markings according to the diagram directly on the wall, then there will definitely not be any difficulties and there will be a chance to check everything again and correct something.
Now you need to determine how to lay the cables themselves. The lines from the distribution board to each junction box can be laid using the methods described in this table.
| Highway location | Peculiarities |
| Along the upper edge of the wall in a groove or corrugated pipe | Most often used |
| Over the floors until the floor screeds are poured (in plastic pipes) | This is the shortest way. Here, by the way, grooves are not useful either, since when the floor is filled, all the wires will be hidden. For such wiring, sockets built into baseboards are usually needed. By the way, now you can purchase special kits - a special plinth with cable channels, sockets, switches, junction boxes, etc. True, it is not suitable for any finish. |
| Along the ceiling | Here, most likely, you will have to make grooves, however, the consumption of materials will also be economical. Junction boxes can also be placed on the ceiling, but this will hardly be convenient when repairs are required. This method is only relevant when a suspended or suspended ceiling is intended to hide the lines. |
When installing the wiring yourself, only the first option is suitable, and despite the great advantages of the other two, it is no worse than them. It will just require more time, but since the plan to install the wiring with your own hands has reached the strobing stage, the hardest part is already over.
*(Grooves are the penultimate stage on the route of wiring)
Chart of accounts
The enterprise accounting system requires the presence of a clear system of accounts and instructions for their use. The system of accounts for recording business transactions using the double entry method is called a chart of accounts.
The chart of accounts adopted by the Ministry of Finance in 2000 is still in effect, with minor changes made in 2010.
The main task of the Chart of Accounts is to connect accounting indicators with reporting indicators. For its correct use, the Ministry of Finance has developed appropriate instructions.
The chart of accounts is a table in which accounts are grouped into sections by type of assets and liabilities. For ease of use, accounting programs often provide for reflection of the signs of sum and quantity accounting, whether the account is a foreign currency account, etc.
Fragment of the Chart of Accounts:
Recommendations for placement
- To connect stationary appliances, sockets are usually placed hidden (for example, on an oven, refrigerator, hob). However, it is necessary to provide access for emergency shutdown of devices.
- Above the kitchen countertop, sockets are installed at a height of 10 cm from the bottom of the socket. They should not be placed next to the hob or sink.
- Switches are usually placed at a height of 90 cm from the finished floor and 20 cm from the door.
If the socket or switch is placed on a narrow section of the wall, then it is better to install them in the center along the width.- Sockets are installed in the place where electrical appliances will be located. In addition, the number of outlets in the source must correspond to the number of devices used.
- If there is no reference to the height of the outlet, then it is better to install it at a height of at least 30 cm from the floor.
- If you are not sure where to place the sockets, then draw the location of the furniture on the walls. This usually helps you decide.
Additional requirements to comply with
- the wire is laid vertically, horizontally or parallel to inclined structures;
- It is forbidden to conduct wiring at the joints of the slabs because the house may shrink and crush the wire;
- If possible, do not use horizontal grooves, as they violate the strength of the walls.
- Avoid grooves in floor slabs because this affects their rigidity. You can use voids. One way to get around this point is to place the wiring directly along the ceiling. Then plaster the ceiling.
- When laying horizontal supply lines, you should retreat at least 15 cm from the ceiling. This is useful when installing suspended or suspended ceilings, which are mounted 10-15 cm from the ceiling.
- The wire is poured into the screed only in a corrugated or plastic container. While the screed is drying, the concrete has some movement that can damage the wire.
- It is prohibited to lay low-current and power cables nearby. The gap between them must be at least 8 cm. The power cable can induce an electromagnetic field. Low-current is antenna, telephone, twisted pair and security cable.
- The shield in the apartment is installed at eye level. It must be easily accessible for servicing and disconnecting consumers. This is an electrical safety standard.
General recommendations
- If you have old aluminum wiring, then it is better to change it completely.
- If the aluminum wiring is relatively new (up to 10 years), assess the degree of wear. If the insulation and the conductive cores themselves in boxes and sockets are in good condition, repairs are sufficient. Moreover, repairs must also be made with aluminum wire.
- If the wiring is copper (up to 15 years), then also evaluate its condition. If more than 15 years, then its service life has come to an end. It's better to change it.
- If it's a modern design solution, you shouldn't get attached to the old wiring. It is better to install your own panel in the apartment and install new wiring.