What is a salary advance and what legal norms govern it?
The Labor Code does not stipulate the concept of an advance. But it states here that salaries must be paid to employees at least twice a month, so the first part of the payment is called an advance.
The obligation to pay an employee an advance from wages follows from the provisions of Art. 136 of the Labor Code. The obligation to pay wages twice a month is indicated here. At the same time, Rostrud in Letter No. 472-6-0 of 2007 indicates that there are no grounds for exempting the employer from paying an advance even at the request of the employee.
Provisions of Art. 136 of the Labor Code are mandatory for all employers and for all employees: both full-time and part-time employees.
The amount of the advance is determined at the discretion of the employer. The Labor Code does not regulate the issue of the amount of the advance payment. This position is given in the clarification Letter of the Ministry of Labor of 2013 No. 14-4-1702.
At the same time, experts, with reference to Resolution No. 566, emphasized that the amount of the advance towards wages for the first half of the month can be determined by agreement between the administration and the trade union, but this amount cannot be lower than the tariff rate for the time worked.
In practice, the following methods are used to determine the amount of the advance:
- Proportional to time worked.
- As a percentage of salary.
- In a fixed value.
According to the recommendations of the Ministry of Labor and Rostrud, when determining an advance payment, you should focus on the first method. As a result, for each half of the month the salary will be approximately the same, but the advance payment will not be a static and fixed amount, since the values of the time worked will differ.
What is an advance
The main document that regulates the relationship between employer and employees is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But the concept of “advance” is not directly spelled out in it.
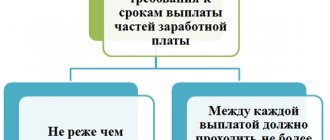
The need to pay wages in installments follows from the requirements of Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The law stipulates that employees must receive remuneration at least every half month.
More often than not, no one forbids it. In theory, an employer could pay employees weekly or even daily. But this is associated with unnecessary costs and hassle, so in most cases businessmen limit themselves to complying with the requirements of the law - i.e. Divide the monthly payment into two parts.
The first part, which the employee receives during the pay period, is traditionally called an advance.
Issue date
Specific terms for payment of advance payments are not specified in the Labor Code. But according to the legislative changes in Art. 136 of the Labor Code, advance payment and salary must be paid no later than the 15th day of the month following the billing month. This means that the employer must pay its employees for February by March 15 and no later. At the same time, the Labor Code does not prohibit the employer from paying an advance payment more than once a month, but more often: for example, once a decade or weekly.
The employer’s responsibilities include determining clear deadlines for paying the advance and fixing the date of its transfer to employees in one of the following local acts: an employment contract, a collective agreement or a wage regulation. The employer does not have the right to establish a variable period for paying wages: for example, “the advance is paid no later than the 20th of the month...” or “from the 15th to the 20th of the month.” This will be considered a violation of the requirements of the Labor Code, since the employer must set a specific date for the payment of wages.
According to the new rules, it turns out that the advance payment from wages is paid from the 16th to the 30th, and the final payment is paid from the 1st to the 15th (according to clarifications of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of 2020 No. 14-1 / B-911).
In practice, paying an advance on time is not always possible. So, if the advance payment deadline falls on a weekend, then the advance must be paid in advance . For example, an advance is paid to the company on the 7th of every month. In June, the 7th fell on a Sunday, so the advance must be paid to employees on the 5th.
Sometimes the employer decides to pay the advance ahead of schedule on his own initiative (for example, before the accountant who calculates the salary goes on vacation). Although the Labor Code only talks about liability for late payment of an advance, and its early payment is not directly prohibited, when checking, the labor inspectorate may count the fact of early payment as a violation. Indeed, in such a situation, it turns out that the time until the next salary payment will exceed half a month. Therefore, the employer should adhere to the deadlines established in local regulations.
How to calculate an advance in 2019-2020 according to the new rules?
The new rules for calculating advance payments, which were recently prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, affected mainly only the timing. And when determining the amount of the advance, one should proceed from the time actually worked in the first half of the month (letter of the Ministry of Labor dated August 10, 2017 No. 14-1/B-725).
See also: “Advance payment: how much interest to pay employees, Rostrud explained.”
Moreover, officials recommend taking into account when calculating the advance only those components of the salary that are directly tied to working time (salary, allowances for part-time work, etc.). As for payments, the amount of which can only be determined based on the results of the month (for example, bonuses for fulfilling a plan), then, according to the Ministry of Labor, they should not be used when calculating the advance payment.
For more information about the bonus as a component of remuneration, read the article “Is a bonus part of the salary?”
Let's consider how to calculate an advance in a new way - taking into account the latest clarifications from government bodies.
Example 1
The number of working days in the billing month is 20, the salary of engineer I. I. Petrov is 25,000 rubles. per month. During the first half of the month, Petrov I.I. worked 9 days. Thus, he must be paid an advance in the amount of:
A = 25,000 rub. / 20 days × 9 days = 11,250 rub.
Thus, the new formula for calculating the advance payment takes into account the actual time worked for the period from the 1st to the 15th of the billing month.
This calculation method is very labor-intensive. In fact, this doubles the workload of accounting services involved in payroll calculations. Therefore, in practice, when determining how a salary advance is calculated, it is usually set as a certain percentage of the salary amount.
The Ministry of Health and Social Development, in its letter dated February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709, recommends issuing wages and advances in comparable amounts. Since personal income tax is not withheld when paying an advance (more on this in the next section), to ensure comparability of payments, the optimal solution would be to set an advance in the amount of 40–45% of the salary.
Let's consider how to correctly calculate the advance payment for this option of calculating it.
Example 2
Petrov I.I.’s salary is 25,000 rubles. per month. The company has established an advance payment amount of 40% of the salary. Petrov I.I. does not use personal income tax deductions. In this case, he must receive an advance in the amount of:
A = 25,000 rub. × 40% = 10,000 rub.
And the salary in the amount:
Z = 25,000 rub. – 25,000 rub. × 13% – 10,000 rub. = 11,750 rub.
It is clear that the example considers the ideal option. In fact, the employee may be absent from the workplace for part of the billing month (due to illness, vacation, etc.). In this case, it is better to calculate the advance based on the time worked.
How to calculate the salary advance in a particular case must be specified in the local regulations of the enterprise.
How is it paid?
In general, personal income tax is not withheld from the advance payment. This position has been repeatedly cited in explanatory letters from the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service. It is justified by the fact that the withholding of personal income tax under clause 4 of Art. 226 is made on the day the employee actually receives income. The date of receipt of income means the last day of the month according to clause 2 of Art. 223 Tax Code.
Consequently, the employee receives the advance in full without reducing it for personal income tax. The employer should withhold income tax only upon final settlement with employees.
In this regard, it is undesirable to assign an advance payment on the 30th day of the month, since tax authorities may require the accrual and payment of personal income tax on it, which will cause confusion in the calculations.
The Labor Code does not regulate the specifics of advance payment. At the same time, the procedure for issuing an advance payment and salary is no different. In both cases, the algorithm will be like this:
- The employer prepares the payroll (usually using Form T-53).
- The employee signs it and receives the funds.
- The statement is subsequently attached to the expense order.
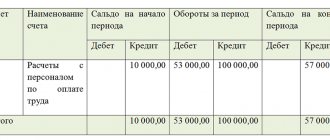
- The issuance of an advance from the organization's cash desk in cash is displayed using transactions Dt 70 Kt 50.
The method for issuing an advance in cash is indicated above, but it can also be transferred to the employee’s card in non-cash form. Postings when paying an advance to a card are as follows: Dt 70 Kt 51.
Payment of taxes
By law, the employer is required to withhold tax from the employee's salary and transfer it to the state treasury. According to Art. 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the date of receipt of funds, and accordingly, the calculation of tax is the last day of the billing month. This means that it is impossible to deduct the amount of personal income tax due from the advance payment.
There are two solutions to this situation:
- Pay the first part of your salary without withholding any taxes. And at the end of the month, calculate the balance and subtract the entire tax amount from it.
- Immediately withhold personal income tax from the advance payment, but do not transfer it to the budget. At the end of the billing period, deduct personal income tax from your salary and pay the tax in the total amount.
The indicated options for how to calculate an advance salary and withhold the required tax allow you to take into account the interests of controlling organizations and the employer’s enterprise.
Application for advance
By default, employees do not write any applications for advance payment. The advance payment is transferred to them within a strictly specified time frame. But if they would like to receive a certain amount in advance towards their future salary, then they should contact their employer with a written application.
The application must indicate the amount of advance they would like to receive and indicate the reason for the urgent need for money. A sample application for advance payment can be downloaded here.
It is worth noting that the employer is not obliged to satisfy this kind of application, and the decision on this issue remains at his discretion. Moreover, if an employee asks to transfer to him an advance amount that exceeds his monthly salary, then tax and labor inspectors may have claims against the employer in the future.
If the advance is not paid
For non-compliance with the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regarding the transfer of an advance part of the salary, the employer faces penalties. This is evidenced by Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offences. You can see the amount of monetary penalties due in the table:
| Tax status | Amount of punishment |
| Entity | 50,000 rub. |
| Executive | 10,000 rub. – 20,000 rub. |
| Individual entrepreneur | 1,000 rub. – 5,000 rub. |
Advance payments must be made to all employees without exception. Factors such as:
- part-time employment;
- small salary;
should not become an obstacle to the accrual of funds to the employee. This procedure is regulated by law and cannot be carried out at the discretion of the head of the organization.
Accounting entries for advance payment
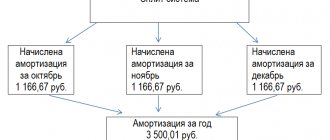
Accounting arrangements depend on the method of payment of the advance. Most often, it is transferred, like the rest of the salary, to a bank card . In this case, you must correctly indicate the purpose of the payment, mentioning the month of calculation, for example, “salary for half of August 2020.” Two entries are required: for the transfer of advance funds - debit 70, credit 50, and for the bank commission - debit 91-2, credit 51.
The law allows advance payment in other ways:
- in cash: you need to fill out a statement of the T-53 form provided for this or a KO-2 cash order;
- in non-monetary equivalent: part of the salary can be in kind, Art. 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows this, regulating that its share should not exceed 20%; Thus, according to accounting, “transfer of finished products to payroll” occurs, and postings take place in 5 stages: revenue from finished products (debit 70, credit 50-1), writing off the cost of production (debit 90-2, credit 43), accrual VAT (debit 90-3, credit 68), profit or loss from transfer to salary account (debit 90-9 or 99, credit 99 or 90-9, respectively).
Withholding personal income tax
Many employers are concerned about the issue of withholding personal income tax from wages. Not all accountants are familiar with the issues of the advance payment system, which is why controversial issues arise.
Personal income tax is withheld from the full amount due and paid to the employee for the entire month worked. The tax rate is 13%. The rate has not been legally changed to date.
6-NDFL from December salary is sent in January. Find out about the new bonus payment deadline here.
Personal income tax is not collected from the advance payment. But at the same time, preliminary payments can be reduced due to deductions made. After all, the advance is determined taking into account withholding tax in the amount of 13% of the full salary amount. Therefore, the first part of the salary is paid taking into account the deduction.
What kind of advance cannot be?
There is no clear and specific calculation method, but there are types of advance payments that are considered violations:
- a small advance, 10-15% of the amount, is considered unlawfully reduced;
- “floating” payment amount. An organization cannot set only an upper limit; this allows it to change the amount of the advance payment, which is contrary to the law;
- no advance payment. There is no other option for calculating wages other than twice a month at regular intervals.
As you may have noticed, there is no specific answer to the question of what part of the advance is from the salary. Everything is determined by the accrual methodology chosen by the employer, the actual time worked, and the availability of various additional payments and incentives.
Previous article: Authenticity of sick leave Next article: What does an offer mean?
When is the advance paid?
The date separating the payment terms is chosen by the enterprise arbitrarily. The law does not give strict instructions in this regard, however, there are recommendations from Rostrud, the Ministry of Social Development of the Russian Federation and the Federal Service for Labor and Employment, based on the logic of things.
Since remuneration for labor must be paid for the time actually worked and occurs twice a month, it is quite logical to divide the month approximately in half and choose the 15th-16th as the payment date.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! With this choice of payment dates, it is recommended to divide the salary into approximately equal parts.
However, in the absence of strict legal requirements, the entrepreneur has some freedom in choosing dates for salary payments. You just need to take into account some nuances:
- it is allowed to divide payments not necessarily into 2 parts, you can split the salary into smaller shares, paying it three or four times a month, then the logic for setting dates will be different;
- if the gap between the advance and pay is more than 15 days, then according to the law, the employee theoretically has the right to complain about the delay in wages, suspend work and even go to court;
- the selected time periods must be recorded in the internal documents of the organization.
NOTE! The time for paying the advance must be a specific date, not a period. It is impossible to schedule advance payments, for example, from the 5th to the 10th, and paydays from the 25th to the 30th. Thus, the requirement to comply with the frequency of payments is violated.
If the appointed date coincides with a weekend or holiday, the employee will receive the required advance payment the day before.
Taxation
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 223, art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated February 5, 2020 No. 14-1/OOG-549, the first part of the salary (advance payment) is not subject to:
taxation;- deduction of insurance premiums.
Previously, employers hedged their bets and multiplied the advance by a factor of 0.87, but now this cannot be done.
All contributions are deducted from the last payment when the employer takes into account:
- actually worked time for the whole month;
- not only compensatory additional payments for the second two weeks, but also incentive bonuses for the entire month (bonuses, northern bonuses, etc.).
Advance share of salary
What amount or share will the first payment of part of the salary be? The law does not answer clearly here either. Of the documents, this issue is indirectly addressed only by the somewhat outdated, but not yet repealed, Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers No. 566, which states that the amount is established by the organization and should not be lower than the tariff rate.
In modern entrepreneurship, various methods of calculating the advance interest are used, all of them are legal, the choice is up to the employer.
- Payment for actual working hours. The advance is paid on a set date in an amount corresponding to remuneration for the number of days or hours worked. However, it may vary monthly. This method is recommended in the letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-1/10/B-660; it must be mentioned in internal documents.
- Fixed percentage of the salary amount. It is more convenient for calculations, since it will be the same at constant wages. It is attractive for employees because they always know how much they can count on by a certain date. If the monthly payments are divided in half, it is convenient to pay half of the due remuneration. A level of 40% is also acceptable; a smaller share is not accepted.
- Fixed amount. An entrepreneur has the right to pay not a share of the salary, but a part of it in the form of the same amount, and recalculate the rest in accordance with the time worked. With this method, the advance payment will remain unchanged, and subsequent payments may differ under different remuneration systems (they will be the same for a fixed salary, but may change for hourly or piecework wages).
How to calculate the amount?
To calculate the advance, formulas are used that vary depending on the type of wage (tariff rate, salary or piecework wage). It is also important to take into account the system by which the organization makes calculations:
- for the time actually worked by the employee;
- as a percentage of salary.
In the second case, the employer also does not have the right to pay an advance less than the employee actually earned in 2 weeks, so the interest rate should be set around 50%. Since 2016, when changes were made to Part 6 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employers began to prefer the first calculation option.
Previously, the advance amount was allowed to be adjusted by a factor of 0.87 in case the employee who received the advance did not work the rest of the month in full, and thus there would be nothing to deduct 13% from, since personal income tax is calculated only from the final amount (Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the Ministry of Labor, in Letter No. 14-1/OOG-549 dated February 5, 2020, spoke out against reducing the amount of the first payment.
According to the tariff rate or according to the piecework system for the time actually worked
Often, employers calculate wages based on an hourly or daily rate. In this case the formula is used:
Advance = (Tariff rate + Compensation payments) x Actual time worked.
If an hourly rate is established, then the standard working time is established in hours. Accordingly, the daily rate takes into account working days in the month.
For example, employee A.A. Shamovsky The hourly rate is set at 150 rubles per hour. According to the local act of the organization, he receives an advance every 19th day of the month.
In July 2020, the working month was 184 hours, respectively, half of the working month is 92 hours, which he fully worked. No additional payments were established for Shamovsky this month.
Thus, his advance will be:
150 x 92 = 13,800 rubles.
If an employee is paid a salary based on the products he produces (piecework form of payment), the organization must still make payments 2 times a month.
The advance is calculated from the work performed by the employee in the first 15 days of the month:
Advance = Piece price x Number of units completed per half month.
Vilenkina D.M. receives piecework wages. 1 unit of products produced by it is 135 rubles. In half a month she completed 83 units. The advance will be:
135 x 83 = 11,205 rubles.
When paid for actual time worked
Salary for actual time worked is calculated according to the following formula:
Advance = (Salary + Compensation payments) / Standard working hours per month x Actual hours worked.
Olkhovskaya A.V. receives a salary of 28,734 rubles. In April 2019 there were 22 working days, so half of the working month will be 11 days. She was not awarded any compensation. Thus, the advance will be:
28,734 / 22 x 11 = 14,367 rubles.
What percentage of the salary and how much of the salary is it?
If the employer calculates the advance based on the interest rate established by the local act (or employment contract), then the calculation formula will change:
Advance = (Salary (or rate) + Compensation payments) x Interest rate.
As a rule, employers set 40, 43.5 or exactly 50%.
This method has disadvantages:
- The time actually worked by the employee is not taken into account;
- the organization and the employer may be held liable for paying the employee less than he earned.
Payment procedure
Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain instructions on the amount of the advance payment, which should be considered an advance payment. Therefore, the procedure for calculating and determining the amount must be developed by the employer.
The total amount is reflected in writing in the employment contract. But it would be smarter to determine phased payments. In this case, you can write in the documentation that the first payment will be 35% of the amount of earnings. The second payment will be made in the amount of 65% of the full salary.
These actions are necessary for the employee. They will help determine the amount that the employee can count on at each stage of payments.
It is worth remembering that 35% was given as an example. The employer can determine for himself how much he will pay for labor for each half-month worked.