Arbitration managers, or, as they are popularly called, arbitration managers, are direct participants in the bankruptcy process. Despite the fact that bankruptcy cases rarely proceed without this specialist, there are many rumors surrounding their position. Moreover, sometimes these rumors seem absolutely crazy. To avoid any unnecessary insinuations on the topic of cooperation with the AU, let’s take a closer look at what their professional responsibilities are, let’s figure out who they are and who they work for. It is on the topic of the last question that many unverified rumors arise.
People believe that the manager is acting against their interests or, conversely, that most issues related to bankruptcy can be resolved with his help. Essentially, both sides are right, but this topic requires more detailed study.
Who is an arbitration manager and why is he needed?
Content
An arbitration manager is a professional participant in a bankruptcy case who, on the basis of a court decision, organizes the insolvency procedure of citizens, entrepreneurs and organizations.
After appointment by the court, the arbitration manager carries out the following work:
- informs the debtor's employees, creditors, founders and other interested parties about the beginning of the bankruptcy procedure;
- organizes and conducts meetings of creditors;
- collects information about all creditor claims;
- exercises control over the actions of the debtor in order to preserve his property;
- conducts an inventory and assessment of the bankrupt's movable and immovable property;
- monitors debt repayment;
- conducts auctions;
- collects debts from the debtor's debtors.
The results of the activities of the arbitration manager are reflected in the report in the form approved by Order of the Ministry of Justice dated August 14, 2003 No. 195. Each bankruptcy procedure has its own report form.
We must remember! The report of the arbitration manager must be published on the EFRSB website in his card. In addition, information about the results of meetings of creditors, challenging transactions, and bidding must be published.
Species diversity
Depending on what the arbitration manager does, it is permissible to classify him into one group or another. We will consider most of them, excluding only one category - financial. The fact is that this person acts upon recognition of the insolvency of an individual. He carries out restructuring, inspection, and reporting. But it has nothing to do with enterprises. Therefore, we will not mention him in the lists.
Temporary
This is the observer. The requirements for it are somewhat different. This specialist participates in legal proceedings, conducts supervision and inspection. But outside the boardroom, his functions are limited.
Administrative
In fact, this is an analogue of the position discussed today. But it does not participate in the rehabilitation process, but during financial recovery. This is more, again, observational work. He checks reporting and accounting. But he does not remove managers from their positions. Requires certain guarantors to cover its debt obligations, and then transmits information to creditors. That is, this is a kind of postponement, restructuring. And the manager himself makes sure that it is carried out on a normal schedule. Looks at expense items and checks feasibility. Otherwise, the company may try to simply get rid of assets and cash resources.
External
This is exactly what we are talking about. He occupies a leadership position and draws up a management plan a month after joining. He also constantly contacts creditors, collects a register of their requirements and wishes, and takes into account the amendments they make to the plan. Can also enter into a peace agreement with the assembly on behalf of the company. Or order the sale of property during bankruptcy proceedings. If he suddenly decides that further work will not bring the expected results. If you think about it, this is a kind of central arbitration manager; what he does is often simply not possible for others. After all, getting a company back on its feet, not just pumping all resources out of it in order to cover the debt, but actually rehabilitating it, is a task of colossal complexity.
Competitive
This position is used when resuscitation of a legal entity is no longer possible. And all that remains is to sell the property by auction, by auction. He personally monitors the execution of this task by all participants, organizes tenders and identifies the bankruptcy estate.
What are the requirements for an arbitration manager?
To obtain the status of an arbitration manager, a citizen must meet the following requirements:
- have Russian citizenship;
- have higher education;
- have worked in a managerial position for at least a year;
- undergo an internship as an assistant to an arbitration manager for at least two years;
- pass a theoretical exam according to a special program;
- be members of the SRO.
Also, the citizen should not be subject to administrative punishment in the form of disqualification or have a criminal record.
Important! To carry out his activities, the arbitration manager is registered as an individual entrepreneur. In addition, he is obliged to pay a fee for membership in the SRO and enter into an insurance contract for liability for possible damage to persons participating in the bankruptcy case.
Requirements for a manager
This person must be perfectly prepared for his task. Possess a higher education and have at least one year of experience in a leadership position. And also, not to be judged, which is logical. In addition, the person performing his duties should not have serious complaints or dark spots on his reputation.
And be a full member of the SRO. The total term must be more than three years from the date of his current appointment. The rules of the SRO, especially the payment of membership dues, must not be violated even once. And most importantly, the candidate must pass a specialized exam, which is designed to determine his professional suitability.
How is an arbitration manager appointed?
The general rules for the appointment of an arbitration manager are established in Article 45 of the Bankruptcy Law.
There are two possible scenarios:
- The bankruptcy application indicates the candidates for arbitration managers of a specific SRO. After receiving a court ruling, the self-regulatory organization sends information about them to the first court hearing.
- The application indicates the SRO without information about specific insolvency practitioners. After receiving a court ruling, the self-regulatory organization independently selects three candidates, who are given the choice of the court to appoint in a particular case.
In addition to filing for bankruptcy, insolvency practitioners can be selected at a meeting of creditors. This situation occurs when bankruptcy has already begun and creditors have decided to move to the next stage.
The court ruling must be executed within 9 days. Information on candidates for arbitration managers is delivered to the court within 5 days.
You should know! After receiving information about three candidates for arbitration managers, the judge compares their qualifications and work experience. Assesses who is suitable for conducting bankruptcy proceedings of the debtor. The selected candidate is appointed by a court ruling. From this moment he has the right to begin to perform his duties.
Example 1. The arbitration court considered the bankruptcy application of D.V. Kabanov. The court decided to start with the debt restructuring procedure. To support the SRO process, the Association “National Organization of Arbitration Managers” presented candidates for arbitration managers. The court considered that the arbitration manager Akhundzhanov E.A. complies with the requirements of bankruptcy law and has appointed him as the citizen's financial manager. A reward for debt restructuring in the amount of 25,000 rubles was also approved. (Determination of the Arbitration Court of the Belgorod Region dated 06/05/2019 in case No. A08-3517/2019).
Procedure for appointing a manager
The process of appointing a specialist for management has several stages:
- The court of the debtor declares him bankrupt. An SRO is designated to manage his affairs. It is its members who can become managers for a newly bankrupt person.
- Next, work begins at the SRO, where they must collect a list of specialists who could take on the case. Whether to include a specialist or not is a collective decision. The list consists of at least three people. The decision whether to continue cooperation falls on the shoulders of the company or individual, as well as creditors. Perhaps none of the candidates will be suitable. If this happens, you can submit your candidacy to the AU for consideration.
- After receiving a request, the list is formed within no more than 5 days. The result is sent to the court, creditors and debtor. They must approve the candidacy.
- Each side of the case can refuse one of the proposed managers, and the remaining one will begin work.
- When the parties have not used the challenge, the court will appoint the administrator who is first on the list.
What follows is an observation that will allow us to analyze the state of the market and carry out the bankruptcy procedure, maximally satisfying the requests of all parties. It will be carried out by a temporary administrator appointed by the court. Next comes the stage of financial recovery. If this does not help, the property is described and sold.
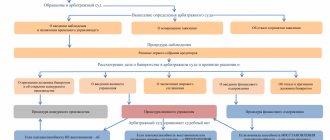
Status of an arbitration manager in various bankruptcy procedures
At different stages of the process of declaring a debtor insolvent, the insolvency practitioner has a different status.
The following types of arbitration managers are distinguished:
- Temporary manager. Appointed at the observation stage, during which the debtor’s solvency is assessed, measures are taken to preserve his property, a register of creditors’ claims is compiled and their first meeting is held.
- External manager. Involved during financial rehabilitation, which is carried out in order to pay debts according to the approved schedule and preserve the legal entity.
- Administrative manager. Approved for the purpose of external management to restore the debtor’s solvency.
- Competition manager. Appointed to support bankruptcy proceedings, during which the organization’s property is sold and debts are repaid using the proceeds.
If the debtor is an entrepreneur or citizen, the arbitration manager is given the status of a financial manager. He carries out debt restructuring and sale of bankrupt property.
Interesting! In practice, the question arises what bankruptcy procedures are not carried out by the arbitration manager. The only procedure in which the manager does not participate is a settlement agreement, when creditors and the debtor decide to resolve the issue of debts by signing an agreement. The court approves the agreement and dismisses the bankruptcy case. Subsequently, the arbitration manager is relieved of the responsibility for conducting the bankruptcy case and the debtor independently fulfills the terms of the transaction.
How to find a manager
Bankruptcy proceedings with an arbitration manager are a common occurrence. But you still need to find a good specialist. A complete list of professionals is presented on the Unified Federal Register of Bankruptcy Information. Theoretically, all the managers presented can work for the debtor, but this is only a theory. In fact, not everyone takes up the business and only if they see a benefit in it, since the interest of a specialist depends on his possible income.
The more experienced the specialist, the higher the likelihood of his professionalism. You can find out about the experience of an AU by the date of its registration: the earlier it is registered, the longer it works. But the more experienced the manager, the more expensive he is. He rarely undertakes to supervise individuals, usually specializing in legal organizations.
The arbitration court can appoint a manager. A special request is made to the SRO to provide a free candidate. In this case, it will not be the client who chooses, but it is still important to pay attention to several factors that will help you feel safe:
- The manager can be disqualified. This is possible thanks to strict control over the work of professionals. If the reputation of the specialist offered to you is bad, using his services is risky - either this person is unprofessional or neglects his duties. Disqualifying a trustee in the middle of a bankruptcy case will be very damaging. It is easier to verify the honesty of the manager in the file of arbitration cases. To do this, you need to enter the full name of the manager in the “Participant” field. Above the list of cases there will be a button “Administrative matters”. If a case of disqualification has been opened against the manager, it is better to look for another specialist.
- He withdrew himself. If the AU experienced situations where he accepted a case, but then refused, it is undesirable to use the services of such a frivolous person. You may find yourself without help at the most inopportune moment. You can easily find out about this in the EFRSB or in the card index. One statement about this is bad, but if there are more of them, you cannot hire this manager. He's irresponsible.
- Doesn't work well. The manager should not work with his sleeves down. The AU registry contains publications made by a specialist. Publications must be made according to legal deadlines, and if they are constantly violated, this is alarming. Systematic violations are grounds for administrative liability. The next step is disqualification.
In reality, you need to pay attention not only to the listed factors, but also to many other alarm bells. Then you won't have a headache if something goes wrong.
Rights of the arbitration manager
The bankruptcy law gives the arbitration manager the rights necessary to carry out his functions. In accordance with Part 1 of Article 20.3 of the Bankruptcy Law, he has the right:
- convene a meeting of creditors;
- submit applications and petitions to the arbitration court;
- receive remuneration for your work;
- attract specialists and appraisers;
- request information about the debtor’s property, its debtors and creditors;
- refuse to participate in the case at any stage of bankruptcy.
All activities of the arbitration manager are financed from the debtor’s property. After the sale of the bankrupt's property, his expenses and remuneration are paid first.
Important! The arbitration manager has the right to send requests to other organizations, government bodies and various departments. A response to a request must be provided within seven days of receipt. If it is left without consideration, the arbitration manager has the right to contact the police with a statement of violation of the Bankruptcy Law. If it is confirmed that the request was not executed without good reason, the guilty person will be held administratively liable.
Rules for changing a manager
According to the law, a specialist can be replaced if he cannot cope with basic tasks or violates the law in the process of work. The change can be made at the request of the manager himself or on the basis of a petition filed by the SRO, creditors or direct debtors.
The reason is usually a lack of knowledge about the rules of bankruptcy of a citizen or organization, the inaction of a specialist, which led to losses, as well as the identification of various violations or crimes in the process of work.
A new manager is appointed only by the court, for which new candidates are evaluated. When a specialist is removed, no remuneration is paid to him if at least one bankruptcy procedure has not been completed.
Responsibilities of the arbitration manager
The work of an arbitration manager involves serious responsibility. In this regard, he is assigned a number of responsibilities:
- take necessary actions to protect the bankrupt’s property;
- analyze whether the debtor can pay debts;
- create a register of creditors' claims;
- report administrative offenses and crimes to the competent authorities;
- inform creditors about the results of the work performed;
- spend the debtor's funds only for purposes related to bankruptcy;
- identify cases of fictitious and deliberate bankruptcy and report them to law enforcement agencies.
Due to the nature of his activities, an arbitration manager may have access to state secrets. He is obliged not to disseminate to other persons confidential information obtained in connection with the implementation of events within the framework of the bankruptcy case.
Powers of a financial manager in bankruptcy
- Informing counterparties about the beginning of the bankruptcy procedure and the stages of its implementation.
- Inventory of the debtor's property, preventing attempts to conceal and transfer property to third parties.
- Valuation of property and creation of bankruptcy estate for sale. If the owner does not agree with the announced amounts, the financial institution is obliged to invite a third-party appraiser.
- Organizing bankruptcy auctions, taking all measures to sell property at the highest price.
- Directing the proceeds to pay off priority claims for the bankrupt.
- Transfer of illiquid funds (unsold property) to creditors in payment of debt. Anything not accepted will be returned to the debtor.
- Collection of debts from bankrupt debtors and redirection of these funds to pay off claims.
Arbitration manager Bankruptcy of individual entrepreneurs Bankruptcy of individuals
Fin. the manager is not just a controller, he is vested with the right to dispose of the client’s property, receipts of funds and expenses. Its tasks include identifying fictitious (deliberate) bankruptcy, shadow accounting, hidden accounts, donations. He can stop transfers of funds, cancel accounts, prohibit transactions or challenge any of those already carried out within three years before the bankruptcy. At the same time, he acts in the interests of the client and does everything to carry out the process as profitably as possible within the framework of the law.
What expenses does the arbitration manager bear?
The insolvency process entails significant costs. All of them are financed by the debtor.
Costs include:
- manager's remuneration (fixed and additional percentage);
- publication of messages on the EFRSB website, in the Kommersant newspaper, local media;
- concluding contracts with external specialists;
- postage;
- purchase of office supplies;
- travel expenses;
- purchase of inventory items;
- protection of the debtor's property.
All expenses associated with organizing the bankruptcy process are recognized as current and are paid off first.
You should know! To pay current expenses for the debtor, a special account is opened at the bank. Before each meeting of creditors, the arbitration manager prepares a cash flow statement and provides it to creditors. If any expenses are unreasonable, creditors have the right to file a complaint in court against the actions of the arbitration manager.
Violation of the debtor's rights
If a judicial representative exceeds his powers , then it is necessary to write a complaint against him to the court of which he is a member, as well as a statement to the prosecutor's office. If your rights are violated, you must respond immediately. You will have a great chance of tipping the scales in your favor, regardless of whether you are a plaintiff in court or a defendant.
Responsibility of the financial manager
If you see that your manager exceeds his authority, makes mistakes, does not protect your interests or infringes on them in any way, you can write a complaint against the financial manager at any time.
This is also important to know:
How bankruptcy of a non-profit organization with debts is carried out
The manager may be held liable for any violations (even the smallest ones). For the first time, this is an administrative liability in the form of a fine of up to 50,000 rubles. If mistakes are made again, the specialist will face disqualification for up to 3 years.
Involvement of an assistant arbitration manager and other specialists
If an arbitration manager is involved in a complex bankruptcy case that entails a large amount of work in searching for property, collecting debts from the debtor’s debtors, valuation, accounting, security, he has the right to attract an assistant and other specialists.
The following specialists are involved:
- lawyer;
- security company;
- appraiser;
- accountant;
- surveyor;
- engineer;
- excavator operator;
- other specialists.
To attract assistants, the arbitration manager must justify that he is not able to complete all the work himself. For example, to protect the debtor's property, a special permit is required. With a large volume of debt collection in favor of the debtor, it is necessary to do a lot of work in preparing documents.
We must remember! An application for the involvement of specialists is submitted to the arbitration court. Creditors have the right to express their opinion on whether they agree or disagree with the arbitration manager’s proposal. If the additional costs for assistants are justified, the court makes a ruling in favor of the manager. It usually indicates who he has the right to attract as specialists and what the maximum remuneration for their work is. The costs of assistants are financed by the debtor.
Example 2. The arbitration court is considering the bankruptcy case of PKF Stor LLC. The debtor is in bankruptcy proceedings, K.V. Lazarev has been approved as the bankruptcy manager. The arbitration manager applied to the court to recognize the costs of hiring specialists as necessary. The court considered it necessary to engage the following to ensure the activities of the bankruptcy trustee:
- appraiser with payment for services in the amount of RUB 2,231,977;
- security organization with payment for services in the amount of 7,184,265 rubles;
- a specialist in construction and installation works with payment for services in the amount of RUB 2,088,345;
- cadastral engineer with payment for work in the amount of 307,000 rubles;
- other specialists.
(Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the West Siberian District dated September 19, 2018 in case No. A75-246/2015).
Why do we need a self-regulatory organization of arbitration managers?
To carry out his activities professionally, the arbitration manager must be a member of the SRO. A self-regulatory organization is understood as a structure that unites arbitration managers in order to regulate their activities.
The SRO performs the following functions:
- controls the activities of arbitration managers;
- submits candidates for arbitration managers to the court for the purpose of their appointment in a specific bankruptcy case;
- establishes standards of professional activity;
- collects contributions to the compensation fund.
Thus, in relation to its participants, the SRO acts as a protector, organizer of training, and regulator of activities.
No disqualification or criminal record
The law establishes a one-month period for such exclusion from the date of discovery of non-compliance with the requirements. The self-regulatory organization of insolvency practitioners may itself establish additional membership criteria. In addition, members are required to pay membership fees, otherwise they will be expelled and lose the right to carry out their activities. The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for an expanded list of requirements for managers in the event of bankruptcy of credit institutions and strategic enterprises. Each individual organization independently establishes a list of documents required for submission by candidates and requirements for their execution.
The decision to admit or refuse admission to the ranks of arbitration managers is made within thirty days from the date of submission of the application and package of documents and comes into force only if the person documents all of the above conditions, after which, within three days, the accepted person is included in the consolidated state register of arbitration managers or register of members of a self-regulatory organization. From this moment, a member of the organization can be approved by the arbitration court as an arbitration manager in a bankruptcy case, and in the judicial act on approval, in addition to the surname, name, patronymic of the manager, his number in the register, as well as the taxpayer identification number, will be indicated.
Within ten days from the moment of inclusion in the register, the person is issued a document on membership in the organization, but even before receiving such a document, the arbitration manager can carry out his activities under the control of the arbitration court, after appropriate approval of his candidacy.
Is it possible to appeal the actions of the arbitration manager?
Creditors who believe that the bankruptcy manager is violating bankruptcy laws have the right to appeal his actions.
A complaint can be submitted to the following authorities:
- to an arbitration court considering a bankruptcy case;
- in an SRO, of which the manager is a member;
- to the Rosreestr Office of the subject in which the manager is registered;
- to the tax authority;
- to law enforcement agencies.
Most often, the complaint is filed with the arbitration court hearing the bankruptcy case. If it is justified, the manager is removed from his duties.
Example 3. The arbitration court is considering the bankruptcy case of Bar-Bogunay LLC. From January 30, 2017, bankruptcy proceedings were initiated against the organization, A.V. Shukhatov was approved as the bankruptcy manager. Member of the society Andreyanov A.Yu. filed a complaint with the court against the actions of the bankruptcy trustee, since he was improperly performing his duties. In particular, the manager sold non-residential premises owned by the debtor without holding an auction. With Tuzov I.V. a compensation agreement was concluded in the amount of 10,615,015 rubles. The court considered the actions of Shukhatov A.V. unlawful and removed him from the position of bankruptcy trustee (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the East Siberian District dated January 31, 2020 in case No. A33-15936/2016).
Reward
There are no wages as such. But the candidate claims a reward of up to 7% of the amount of debts returned. Therefore, he is personally extremely interested in the successful closure of obligations. And he will try to make every effort to do this. Considering the source of his income, it becomes clear that he will first of all respect the position and interests of creditors. After all, it is their interests that will bring him money. It is also clear that the larger the debt, the greater the benefit. But the work is also more difficult. After all, what does an arbitration manager mean? This is a person who must not only find funds to repay the debt. But to some extent, earn them when the company has resources, but no money. Create the right strategy.
What responsibility does the arbitration manager have?
For failure to perform or improper performance of his duties, the arbitration manager may be held administratively liable. The initiator may be Rosreestr, whose powers include conducting scheduled and unscheduled inspections.
Improper performance of duties may be expressed in the following actions:
- failure to publish mandatory information on the EFRSB website;
- failure to hold a meeting of creditors;
- sale of the debtor's property without auction;
- failure to take measures to challenge the debtor's transactions;
- other violations of bankruptcy laws.
If violations are detected, the arbitration manager is invited to draw up an administrative protocol. The case is then sent to court to impose an administrative penalty.
Unlawful actions of the manager are qualified under Part 3 of Article 14.13 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and are punishable by a fine of 25,000 to 50,000 rubles. In case of repeated misconduct, the arbitration manager may be disqualified, i.e. deprived of the right to engage in his activities for up to three years.
Example 4. The Office of Rosreestr for the Kirov Region applied to the arbitration court with an application to impose an administrative penalty on the arbitration manager Prasol S.B. under Part 3 of Article 14.13 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The managers committed the following violations:
- the debtor is not paid a monthly amount in the amount of the subsistence minimum;
- the financial manager's report has not been sent to the creditor;
- the financial manager's reports do not contain mandatory information about the debtor;
- the meeting of creditors was not informed of information about the valuation of property;
- information about the involved specialists is not provided;
- a law firm was hired without the consent of the creditors;
- unreasonable postage costs have been incurred;
- creditors are not notified of the start of the sale of property;
- Mandatory information has not been published on the EFRSB.
By a court decision, the arbitration manager was imposed a fine in the amount of 25,000 rubles.
(Resolution of the Second Arbitration Court of Appeal dated September 7, 2020 in case No. A28-3310/2020).
Status and functions of the arbitration manager at the stage of observation and financial recovery
Depending on the stage of the process, the manager performs different duties aimed at achieving the goals set for him at each specific stage, and has different statuses assigned by the arbitration court:
- A temporary manager approved to carry out the monitoring procedure (Article 2 of Law 127-FZ). One of the key responsibilities of the manager at this stage is to conduct an analysis of the financial condition of the debtor enterprise, the results of which determine its solvency, the possibility of satisfying the financial claims presented to it, assess the chances of terminating the bankruptcy procedure and restoring the normal functioning of the enterprise, and also identify signs of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy (if any). The rights of the temporary manager are determined by Art. 66, and duties - Art. 67 of Law 127-FZ.
- An administrative manager approved to carry out the financial recovery procedure (Article 2 of Law 127-FZ). At this stage, the manager exercises control over the activities of the enterprise and adjusts it in accordance with the developed financial recovery plan. In addition, he creates a register of creditors' claims and controls the timing of repayment of the company's debts. The full list of rights and obligations that the manager has at this stage is determined by the provisions of Art. 83 of Law 127-FZ.