Where can I get money?
It is difficult to accurately answer the question of how much it costs to open a publishing house. For example, in 2010, investments in the publishing of one book, according to experts, amounted to 5-10 thousand dollars. Every year this amount changes, and not only because of inflation: in order to estimate the volume of investments, it is necessary to conduct your own research.
Due to the high risk, banks do not issue loans secured by the publishing business. There are three financing options:
- own funds;
— a loan secured by property or other business;
- investments.
Keep in mind that at the initial stage, investors in your project may be more interested in the image side: a publisher is prestigious. The issue of profit can be raised only after several successfully implemented projects.
There is an alternative way - find a larger publishing house, use its material resources (printing and post-printing equipment) and your idea (texts, materials).
Publishing house business plan
In addition to the authors of the concepts contained in the business plan, financiers who have an understanding of the peculiarities of the credit market, the availability of free capital, and the risk of the business take an active part in its creation. The core team of specialists in developing a business plan consists of economists, statisticians, and marketing specialists.
1.3. Structure and scope of a business plan
A business plan is currently being developed by almost every enterprise, regardless of the form of ownership, scale of activity, territorial location, type and range of products.
There are many guidelines for developing a business plan. However, there is no strictly regulated form and structure of a business plan. As a rule, it contains sections that reveal the main idea and goals of the business; characterizes the specifics of the enterprise's (publishing house's) products and how they satisfy market needs; an assessment of the market is given and a strategy for the company’s behavior in certain market segments is established; the organizational and production structure is determined; a financial project for the business is formed, including a financing strategy and investment proposals; the prospects for the development of the enterprise (publishing house) are described.
A business plan is a long-term document that is drawn up for three to five years. For the first year, the main indicators are given by month, for the second - by quarter, and starting from the third, you can limit yourself to annual indicators.
This document should be written in simple, understandable language; its length of 20-25 pages is considered normal. Additional information is provided in the appendix.
The most typical structure of a business plan is:
- Business Plan Summary
- Description of the company and designed products
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Production plan
- Organizational plan
- Risk Plan
- Financial plan
- Investment plan
1.4. Sections of a business plan
1.4.1. Summary
This section is usually compiled after the development of the business plan is completed. It is an advertisement for the project and should be written in such a way as to arouse the interest of a potential investor or lender. This section contains all the information, data, indicators characterizing the activities of the company. The main attention in the summary is paid to the volume, range of products, possible regions of their sales and market segments. In addition, the following may be presented here:
- company structure;
- the essence and method of implementation of the project;
- total cost of the project and funding requirements;
- possible sources of funding;
- level of project profitability.
1.4.2. Description of the company and designed products
This section in the business plan gives a general idea of the enterprise (publishing house) so that potential investors, partners, sponsors and interested organizations can assess its internal capabilities in all respects: financial, production and sales, creative, personnel, management. Information must be supported by certain qualitative indicators.
It is especially important to emphasize those positive aspects of the publishing house that can favorably influence the implementation of the project, i.e. reveal all its potential.
At the first stage, a brief description of the area in which the publishing house operates or intends to enter is given; it is indicated who is the main buyer of his book products or potential consumer. The date of registration of the project, as well as the details of the organization, are noted. If a publishing house has been operating for several years and needs to expand its funding, it is necessary to describe its history and list the largest profitable contracts and operations. If the publishing house has suffered losses or setbacks in recent years, they should be mentioned and indicate what management intends to do to overcome the difficulties encountered and improve the situation.
Separately, it should be said about the upcoming changes in the management of the company, if any are expected in connection with the implementation of the new project. When calculating the property of a publishing house, the age and value of fixed assets and inventory items are determined; debt repayment periods and the state of fixed production assets.
At the next stage, the characteristics of the products being produced or planned for production are given. A potential investor or sponsor, first of all, wants to find out what the publishing house is going to produce and sell, what is the degree of security of the product, its advantages and possible disadvantages. Therefore, it is necessary to consider in detail the range of books and textbooks, their distinctive features that allow obtaining a useful effect. The most important issue is to describe the beneficial effect of achieving the final goal of the release. It is advisable to note new or even unique qualities of the books offered, and indicate the reasons for buyers’ interest in them. You can also focus on the fullest satisfaction of consumer needs.
It is important to pay attention to the targeted use of financial resources. It should be emphasized the difference between the range of book products that is already available on the market and the one that the publishing house is going to produce. It is necessary to provide brief functional characteristics of the products, and if necessary, draw up brochures and annotations, and provide a summary of the publications.
It is advisable to describe books and textbooks according to the following scheme:
- The essence of publications.
- The main features of publications: what need they satisfy; how they are implemented; how variable is the demand for them; what group of buyers are they available to; what are the fixed costs associated with production; who should carry out printing training (information about the printing house and its capabilities).
- Analysis of books and textbooks: at what price will the consumer buy publications; what are their differences from similar publications of competitors; what are the advantages and what are the weaknesses; the expected life cycle of publications; design possibilities; proposed sales areas; prospects for replacing these publications with others.
- Production conditions. Here it is necessary to show what changes in the publishing house may occur if the production of these books (textbooks) is mastered. Here are some of them:
- — increasing requirements for the qualifications of workers and the emergence of a need for new employees (possibilities should be provided for hiring workers with the required qualifications and appropriate professional level);
- — the emergence of a need for retraining (retraining) of existing personnel;
- — change in the range of materials used and their suppliers;
- — updating the technology of editorial and publishing preparation and, as a consequence, the emergence of a need for new equipment and personnel.
1.4.3. Market analysis
The purpose of this section is to obtain sufficient information about the competitiveness of a given project with appropriate justification. Market assessment includes:
- Determination of the main characteristics of the market
- b) degree of market saturation;
- c) trends in changes in capacity and saturation in the near future;
- a) principles of segmentation and the most promising market segments;
- b) the main criterion for the attractiveness of a product for a typical buyer of a given market (price, quality, design).
3) Determination of the most promising markets and the level of projected sales
- a) selection of the most promising markets;
- b) forecast of sales volume for the next year and in the near future;
4) Organization of sales of products in a competitive environment.
1.4.4. Marketing plan
The publishing house's marketing strategy is based on research and assessment of the book market. The marketing plan includes such elements as a distribution scheme for goods, pricing, sales volume, advertising, methods of sales promotion, organization of after-sales customer service, and formation of public opinion.
This section answers the questions:
- How will you sell your product - through your own stores or through wholesale organizations?
- How will you determine prices for goods and what level of profitability are you ready to achieve?
- How will you advertise and how much money will you allocate for it?
- How do you plan to achieve constant growth in sales volumes by expanding the sales area or by searching for new forms of attracting customers?
- How do you organize the service, how much money will it cost?
- How do you intend to achieve a good reputation for your products and the company itself in the eyes of the public?
1.4.5. Production plan
The production plan is developed on the basis of the marketing plan. The main part of this section of the business plan is to provide information on ensuring the production of products from the production side, to develop measures to maintain and develop production.
This section of the plan provides a diagram of production flows in the enterprise. This diagram clearly shows:
- where and where all types of raw materials and components will come from;
- how they will be processed into finished products, what are the stages of the production process;
- what methods will be used to control product quality;
- where and how these products will be supplied from the enterprise;
- what documents does the entrepreneur use?
- This process flow chart reflects production efficiency.
1.4.6. Organizational plan
This plan determines the main directions of personnel policy.
The organizational plan reflects:
- organizational structure of the publishing house;
- personnel requirements (number, activity profile, qualifications);
- system and forms of remuneration and material incentives;
- characteristics of management personnel;
- the need to attract external experts.
1.4.7. Risk Plan
This plan provides data on the types of risk, as well as the stages at which risks and their level are determined. Then measures are developed to reduce the level of risk.
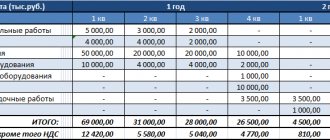
1.4.8. Financial plan
This section is based on calculations of indicators obtained in previous sections of the business plan, and is intended to summarize them and present them in monetary terms. The business plan provides for the calculation of the project’s potential and its financing schedule; it can also serve as an operational plan for the financial management of the project.
Several documents are developed as part of the financial plan:
- Forecast of product sales volume.
- Balance of cash expenses and receipts (cash flow analysis).
- Income and cost table (profit and loss forecast).
- Consolidated balance sheet of assets and liabilities of an enterprise.
- Break-even (profitability) chart.
referat911.ru
Underwater rocks
Book publishing is considered a high-risk business. A certain amount of time passes from the start of production of a book to its publication. During this period, reader tastes may change. In addition, the publishing house is highly dependent on authors and staff. If texts or other materials are not ready on time, the publisher loses valuable time and the attention of a fickle reader.
The main risk— the inability to calculate demand —applies to both books and magazines.
Printing house publish a book
The classic way a printing house works is to receive an original layout of a future publication from the customer, send it to the printer and immediately deliver the finished edition to the client.
The first and most logical step for printing houses was to include pre-press processing in their list of services. To do this, it was enough just to hire a publisher, a proofreader and a layout designer on its staff, and now the printing house could not only print, but also prepare the book for printing.
The next step is more difficult. Establish relationships with book distributors.
Large publishing houses, monopolistic giants, have long and productively worked with similar giants that dominate the book trade. You can't get through there. But regional bookselling chains, single stores, and Internet sites remain, because more and more books (and not only books) are now sold on the global network.
Many ambitious printing houses have long done this, and now an author who wants to publish at his own expense can count not only on printing, but also on a full range of services, from proofreading his manuscript to organizing meetings with readers.
Required Personnel
Forming your staff should begin with finding good editors . If in the grocery business the most important thing is the director of product sales, then in a publishing house absolutely everything rests on the editors! They are the ones who select the manuscripts that will eventually be published.
It is these specialists who must imagine who will be able to read this or that “masterpiece” and how to correctly convey information about the book to the reader. The cover must be appropriate, the price must be affordable, and the right sales channel must be selected.
The product sales director is the second most important person. Because there are situations when a book becomes a bestseller in a kiosk at a bus stop, but is not sold at all in large stores!
Very large companies have more than 500 employees, but to become a good publishing house you don’t need to have so many people under your command! Here's an example:
- “Mann, Ivanov and Ferber” - this publisher operates without any staff at all. The three founders of the company are involved exclusively in the process of creating the book at the level of merchandising and the overall concept. The rest is done by contractors!
Features of publishing
The creation and publication of books and other printed literature performs educational, social and intellectual functions. To successfully implement an idea in this area, you need to have many knowledge and skills:
- be well-read and understand good books;
- have experience in the publishing market;
- constantly look for and establish contacts with promising young authors;
- understand which projects are worth taking on;
- clearly represent the target audience, its tastes and wishes;
- be able to convey the product to the consumer;
- understand the law (publishing, copyright, advertising), etc.
And although experienced entrepreneurs talk about the difficulties of this business and the numerous disadvantages of the project, the level of entry is still not too high. And if at least one of the books you publish becomes a bestseller, then the success of the whole business is guaranteed.
It is also worth noting the fact that many publishing houses in our country began not with an attempt to make profitable investments, but with the opportunity to release to the market the literature that was in short supply. For example, the owners started their business out of a desire to compensate for the lack of high-quality specialized printing products on the shelves in the business sector.