Accountant position
The responsibilities of a payroll accountant are quite extensive. These include calculation of salaries, calculation of advance payments, deduction of funds for vacation, dismissal, and issuance of various compensations. In addition, the specialist must be able to draw up relevant documents, draw up reports, and additionally provide certificates to company employees upon their requests. In addition, it must take into account innovations that have appeared in legislation. There are a variety of nuances in the work of an accountant related to hourly wages, weekends or holidays. Therefore, he must take everything into account and execute it in a timely manner.
Requirements
Accountants are hired for positions only if they have a higher education. Regular courses are not enough here. In addition, work experience in a similar position must be at least three years. An important point is the knowledge of a computer, standard and specialized programs, as well as office equipment.
Responsibilities of a payroll accountant must be listed on your resume. They should be listed as a separate item. It's important to take a little more time to list your strengths on your resume. This will help management make a positive decision when selecting a specialist. After all, it is in the resume that the existing abilities, abilities, and acquired skills are written down. It is important to indicate that you have the necessary knowledge of tax legislation, PBU and other regulatory documents.
General provisions
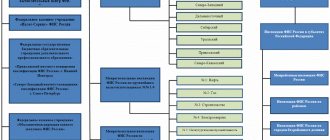
An accountant involved in payroll accounting should be classified as a specialist. Therefore, the decision to hire or fire a given employee is made by the director of the company on the basis of an order. To get a position, you need to be a specialist with a higher professional education. In addition, work experience in a financial structure must be three years or more. The responsibilities of the payroll accountant include reporting to the chief accountant.
The payroll specialist must work on the basis of:
- standards;
- design materials, if clarifications related to work specifics appear;
- organization charter;
- rules existing within the company;
- orders and various requirements signed by the company’s management;
- instructions.
The accountant must know:
- requirements, orders, basic materials of financial and control authorities regarding the organization of their activities;
- reporting rules;
- legislation related to finance, taxes and business activities;
- system, profile and specialization of the enterprise;
- existing regulations, instructions, job responsibilities of a payroll accountant;
- rules for performing operations, document flow for accounting;
- the procedure for processing payments and their forms;
- system of acceptance and registration of funds, as well as material and other assets;
- the procedure for settlements with debtors and creditors in accordance with regulatory documents;
- taxation system for legal entities and individuals;
- rules for writing off missing amounts and debts from accounting accounts;
- a system for maintaining inventory activities, as well as recording economic assets;
- deadlines for drawing up balance sheets and reports;
- production organization and management system;
- occupational health and safety.
Responsibilities of a Payroll Accountant
The payroll area is the area of activity of the accountant. It carries out operations for accounting wages, calculating personal income tax, calculating insurance premiums, generating reports to government bodies and other operations directly related to wages.
Job responsibilities
The responsibilities of a payroll accountant relate to the area of activity related to the payment of employees in the performance of their labor functions. The list of accountant’s job responsibilities comes down to performing the following operations:
- acceptance of primary documentation on the basis of which accruals or deductions will be made for employees. Such documents include time sheets, temporary disability certificates, personnel orders, writs of execution, employee statements, etc.;
- processing of primary documentation with their implementation and calculation of wages in the program, as well as checking the correctness of the calculation of certain components of wages and deductions in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- drawing up relevant correspondence on analytical payroll accounting accounts, as well as creating synthetic accounting registers for the purpose of summarizing and analyzing the information received;
- calculation of personal income tax, which must be withheld from employee salaries and transferred to the tax authorities;
- calculation of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance, Social Insurance Fund in accordance with the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- generation of salary reports to government bodies, including the transfer of statistical information, calculations in form 6-NDFL, certificates in form 2-NDFL, information on the average number of employees, form SZV-M, calculations of insurance premiums, etc.;
- proper storage of documentation relating to employee payroll and the provision of any benefits or allowances;
- providing government agencies with the information they request regarding accruals and deductions for employees’ wages, including during desk or on-site inspections.
Competent performance of job duties by a payroll accountant is only possible if he has all the necessary theoretical knowledge and practical skills in this field of activity.
Rules for calculating salary advances 2018
What should an accountant know?
A payroll accountant performs his duties competently if he has in-depth knowledge of the following issues:
- regulatory legislation of the Russian Federation regarding the calculation of salaries to employees, including those working in different modes;
- a list of primary documentation on the basis of which wages and various benefits are calculated;
- rules for recording all transactions carried out in synthetic and analytical accounting accounts;
- legal regulation and rules for the preparation of reports related to wages, as well as the timing of its submission to the relevant government bodies;
- features of the functioning of the enterprise, which affect the work activities of employees and the rules for calculating wages for them;
- various mechanisms and formulas for checking the correctness of wage calculations;
- legal regulation of the company’s activities as a whole, its taxation system;
- occupational safety and health regulations at the enterprise;
- document flow mechanism and nuances of storing documents, including employee wages.
The amount of knowledge the payroll accountant has has a direct impact on how the payroll accountant handles his or her responsibilities. In addition, there are certain requirements for this position, according to which a person is hired for this job.
Requirements for the position of accountant
As with any position, the accounting profession has requirements, non-compliance with which can negatively affect a person’s employment.
The requirements for the position of accountant are as follows:
- the candidate must necessarily have an appropriate education - higher or secondary specialized education;
- it is desirable that the employee has a qualification category established using the Professional Standard “Accountant”;
- the employee must have knowledge not only in the field of payroll, but also in other areas of accounting;
- The accountant hired must be able to work with office equipment, and especially with a personal computer, and also have a good understanding of various accounting programs and legal systems.
Additional requirements may be imposed on the candidate depending on the specifics of the enterprise's activities. Let us note that the accountant must perform his duties in accordance with the job description as the main document-guideline for the performance of labor functions.
Basic provisions of the position of accountant
For a payroll accountant, functional responsibilities must be recorded in the job description, which is one of the main documents when applying for a job. It is developed by personnel department employees or the chief accountant, and approved by the management of the enterprise.
The job description contains a certain list of points, including:
- general provisions for the position of accountant;
- knowledge that an employee must have;
- functional responsibilities that he will perform;
- employee rights when performing work;
- responsibility for all actions taken.
An accountant must be familiar with the job description under his personal signature before being hired. The document is drawn up in two copies: one remains in the personnel department of the enterprise, the second is transferred to the employee.
Source: https://okbuh.ru/zarplata/obyazannosti-buhgaltera-po-zarabotnoy-plate
Job responsibilities
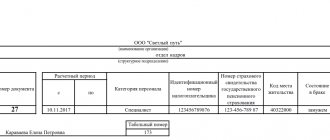
The job responsibilities of a payroll accountant include a range of specific tasks. At the end of the month, you need to check your timesheet (a document that records working hours). This is necessary in order to make an assessment and prepare for the calculation.
The accountant receives and checks sick leave, deals with payroll, contributions to extra-budgetary funds, and personal income tax. He calculates vacation pay, benefits, and makes final payments upon dismissal of employees. This specialist also carries out reconciliations with regulatory authorities (PFR, Social Insurance Fund, Federal Tax Service), takes part in inspections, and provides the necessary information. He registers the relevant transactions and transactions and posts them to the required account in a specialized program.
In small organizations, the responsibilities of a payroll accountant include not only accrual, but also transfer of taxes and contributions, and payments to employees. In large organizations, payments are handled by separate specialists. Also, in small companies, the accountant may be assigned the duties of a personnel officer.
In addition, it is important to take part in improving the types and methods of accounting, while using modern equipment and information technology, using new sources and knowledge acquired in advanced training courses. It should also assist in conducting an economic analysis of the enterprise's activities, relying on accounting records in order to identify the company's existing reserves and improve document flow in general. All of the above covers the responsibilities of a payroll accountant. There should always be order in the company's budget. It is necessary to additionally monitor the safety of accounting documents and prepare them in the appropriate order for the archive. After which you need to properly deposit them in accordance with the requirements. It is also necessary to promote the introduction of advanced computer technology, maintain and store accounting databases, and make amendments to them regarding reference and regulatory information.
Job description of a payroll accountant
Any employer in the process of conducting business is obliged to calculate and issue wages and other types of remuneration to staff.
In this case, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as the LNA. The position of payroll accountant is common in enterprises of all forms of ownership and types of activity.
Perhaps only an individual entrepreneur working alone does not need such a specialist.
The main responsibilities of an accountant include calculating earnings, sick leave, vacation pay, and business trips. In addition, it is often necessary to calculate taxes and contributions from the company’s payroll and reflect transactions in accounting. Many employers who do not have a personnel department in the company entrust the payroll accountant with the tasks of processing the hiring and dismissal of personnel.
Accountant job description
Job responsibilities of a payroll accountant include:
- Calculation and accounting of salaries, sick leave, vacation pay, compensation, additional payments, allowances, bonuses, allowances, and other types of incentive and/or motivational remuneration.
- Participation in the development of the enterprise's LNA, including regulations on business trips, remuneration, bonuses, etc.
- In accordance with the data provided, recording the hours of employment of employees, reconciling actual output with personnel documentation.
- Calculation, accrual in accounting with the payroll and payment to the state of taxes, fees, such as personal income tax, contributions for compulsory health insurance, compulsory social insurance (VNiM), compulsory medical insurance, injuries.
- Drawing up and submitting reports on personal income tax, mandatory insurance contributions, and injuries.
- Accounting for settlements with accountable persons of the organization.
- Accounting for settlements with posted employees of the organization.
- Setting deadlines for depositing salaries and monitoring their compliance.
- Preparation of statements for payroll calculations and transfer of data to the cashier of the organization.
- Set of accounting data for the preparation of annual accounting reporting forms.
- Drawing up statistical reporting forms on the number of enterprises.
- Participation in the development of measures to increase the productivity of employees of the organization.
- Execution of instructions and orders of the organization's management, including the chief accountant.
- Improving your qualification level by participating in various courses, seminars, etc.
- Monitoring changes in Russian legislation.
- Perform other functions as required.
How to draw up a job description for a payroll accountant
The exact list of the calculator’s functionality is determined in the job description. Such a document is developed by the enterprise independently, since no unified forms exist. The content is communicated to the specialist at the stage of admission to the company. To confirm that the information has been communicated, the employee must personally sign the document.
The structure of the job description is as follows:
- General provisions - here it is indicated that the position of a salary accountant belongs to the category of specialists and reports directly to the manager, and then to the chief accountant of the organization. Separately, the requirements for education, experience, qualifications and abilities, knowledge of the legislative framework of the Russian Federation are given. A responsible person is appointed to perform the functions of the accountant in the absence of the latter.
- Rights - this section of the instructions lists the basic rights of a specialist, including the right to timely receipt of explanatory information, requests, creation of normal working conditions, participation in training, etc.
- Responsibilities are the most important section of the instructions. It is recommended to provide the specialist’s work responsibilities in as much detail as possible in order to avoid later labor conflicts. Introduce responsibilities taking into account the specifics of the enterprise's activities.
- Liability - as a rule, this section provides types of liability for violations in compliance with the labor regulations of the enterprise and legal norms, for improper performance of established work duties, for causing material damage to the organization, etc.
- Working conditions – here are the legislative documents regulating the work of a specialist. Usually this is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, orders of the head of the company, safety rules and labor regulations, etc.
The personnel officer of the enterprise develops the instructions. The document is approved by the manager.
If the company does not maintain job descriptions, it will not be possible to bring the employee to disciplinary action on legal grounds. In addition, in the event of inspections by the State Labor Inspectorate (state labor inspectorate), the employer will be fined according to stat. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences.
Job description of a payroll accountant - example
Below we have provided a sample job description for a payroll accountant for a small business. The document contains the main types of duties, rights and responsibilities. Finalize the conditions taking into account the specifics of the enterprise and do not forget to convey the content to the specialist before he starts work.
() Job description of a payroll accountant
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Source: https://raszp.ru/spravochn/dolzhnostnaya-instrukciya-bukhgaltera-po-raschetu-zarpllaty.html
Rights
A payroll accountant has certain rights. He may demand from the company management appropriate conditions for the performance of his functions. It is important for an accountant to know about existing projects, decisions, and requirements that directly affect his activities. In addition, you can make suggestions for improving the work that is the responsibility of the payroll accountant. The specialist also has the right to request documents or information from the unit at the request of the company management. Among other things, such a specialist is obliged to improve and maintain his skills, take additional classes, and look for innovations on forums and websites. It is important to get acquainted with new regulatory documents or changes in them, to participate in all kinds of conferences, meetings, events that help improve the skills and knowledge of an accountant.
Accountant responsibilities
Systematically improve your skills by attending accounting courses and seminars. 2.11. Pay wages to employees of the enterprise on the basis of statements. 2.12. Monitor compliance with cash discipline and settlements with accountable persons. 2.13.Prepare data for drawing up a balance sheet and operational summary reports on income and cash expenses. 2.14.Carry out other assignments of the chief accountant (his deputy). 3. Rights The accountant of the settlement group has the right to: 3.1. Get acquainted with the draft decisions of management relating to his activities. 3.2. Make your own proposals aimed at improving the work related to the responsibilities provided for in this Job Description. 3.3.On instructions from management, request from departments of the enterprise information and documentation necessary to perform his job duties.
Responsibility
A payroll accountant is a specialist. Such a professional maintains a huge number of documents, monitors, records and updates specialized accounting programs. This means, like any employee, he bears a certain responsibility.
The payroll accountant is responsible for the proper performance of official functions (the responsibilities were briefly listed above). If offenses are committed in the course of activities, the specialist may be held accountable in accordance with administrative, criminal and civil legislation. In addition, he is responsible for material assets, maintaining trade secrets, enforcing discipline and maintaining order in general.
Performance evaluation
The payroll accountant's duties, rights and responsibilities are specified in the job description. In addition, it is important to understand that the work of a payroll accountant can only be assessed by the chief accountant and the director of the organization. They control such issues as the specialist’s compliance with established standards, timely submission of reports, calculation of payments, their issuance, correct accounting and compliance with document flow. Now you know what responsibilities a payroll accountant has; they are briefly outlined in the article.
Types of accounting
Accounting is, first of all, an information system that collects information, processes it and transmits financial information about a business entity to meet the needs of a wide variety of users.In a market economy, based on the requirements for the volume and content of information from external and internal users, accounting is divided into: financial and managerial (production).
The purpose of financial accounting is to meet the needs of external users who are not part of the enterprise's employees. The task of management accounting is to prepare information for internal users, which include personnel and specialists managing the business entity.
Consequently, financial reporting data characterizes mainly the results of the enterprise’s economic activities and therefore the main users of such financial reporting information are external users.
Management accounting extends financial accounting and is applied primarily to the internal operations of a firm. Its purpose is to provide information to managers responsible for achieving specific production goals.
Accounting information created and prepared for management's use is subject to different rules than information intended for use by external users not directly employed by the firm. Management accounting is an internal matter of every enterprise.
As for management accounting, the volume and quality of information does not necessarily have to correspond to accounting principles, since they are mostly confidential.
Despite the many differences between financial and management accounting, in practice there are also a number of similarities. First of all, it should be noted that the vast majority of financial accounting indicators are also reflected in management accounting. A number of basic principles of financial accounting are also applicable to management accounting. It must also be borne in mind that the management and managers of an enterprise cannot always be guided solely by subjective opinions and assessments.
In addition, operational information data collected for management accounting purposes can be used to draw up financial documents, since the collection of primary information is carried out according to uniform rules and procedures.
In general, the great similarity between them is that financial and management accounting data are equally used both for making management decisions and for developing strategic plans for enterprises in order to occupy a worthy niche in the market.
And yet it should be noted that the presence of a close relationship between financial and management accounting does not make it possible to draw an absolute, clear boundary between them.
The fundamental provision of accounting at any stage of development of society, on the basis of which a strict accounting system is a principle.
In accordance with the Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On Accounting”, the basic principles of accounting are the following:
- application of the double entry method in accounting;
- continuous accounting;
- use of monetary valuation, funds and their sources;
- ensuring the reliability of information;
- accrual
- prudence (caution) and a number of others.
The listed principles can be presented in a more expanded form as follows.
The use of the double entry method means that each business transaction of an enterprise is reflected in the accounting accounts twice. Once on the left side of one account and a second time on the right side of another account. This principle ensures equality of results of the enterprise's economic activities.
The continuous principle of accounting assumes that business transactions as they occur are recorded in primary documents and are reflected in accounting continuously until they are completed.
Monetary valuation represents a principle that is a universal indicator as a measure of information in accounting and reporting. According to the NAS, accounting in the republic is carried out in the national currency - sums.
The principle of reliability assumes that there cannot be errors or inaccuracies in accounting information. It should correctly reveal the essence of the information. Each information must be confirmed by primary documents that have legal force. It should be noted that sometimes information may be relevant, but unreliable in essence, which can lead to an incorrect reflection of the fact of business transactions.
The accrual principle means that a business's income and expenses are reflected in its books and financial statements as they occur. This means that information users have the opportunity to obtain information not only about transactions performed in the past with payment or receipt of funds, but also obligations for the expenditure of funds in the future. In accordance with NAS, financial statements, except for the cash flow statement, are prepared on an accrual basis. As a result, in practice, the use of the cash method is excluded, according to which income is recognized only when money is received for goods, work and services without preliminary accrual, i.e. moment of shipment of products (goods).
The cost principle is a method that expresses valuation at historical cost. At the same time, in cost accounting, monetary expressions are used both for fixation and reflection in financial statements. This principle is most often used to account for current operations and phenomena.
The going concern or going concern principle states that the business entity will continue to operate indefinitely and there is no expectation of liquidation of the business in the near future.
The principle of caution (prudence) suggests that in accounting and reporting, the valuation of assets should not be overestimated, and liabilities, on the contrary, should not be underestimated. This principle allows us to reflect in accounting the variability of the market situation and the associated risk of the economic activity of the enterprise and its owners. As a result, the principle of prudence excludes the possibility of creating hidden reserves, deliberate understatement or overstatement of assets and liabilities, which can lead to distortion of financial statements and loss of their reliability.
An important principle in a market economy is the principle of comparability. This means that information about the activities of an economic entity should be comparable with similar information about the activities of other enterprises, and this should also make it possible to compare data on the activities of the enterprise for a number of reporting periods. This principle provides a basis for users to compare the financial statements of different enterprises and evaluate their financial condition in order to make decisions about the possibility of investing in a particular enterprise. In these conditions, it is very important that the financial reporting information should be neutral, i.e. free from any distortions: the lack of neutrality of information can lead to the adoption of a biased decision in relation to a given economic entity.
A very important principle of accounting is the principle of matching income with expenses of the reporting period. According to the principle of correspondence, expenses of a reporting period must correspond to the income received for a given reporting period. If it is impossible to establish a relationship between individual types of expenses and income, expenses must be distributed between several periods according to a certain distribution system. For example, deferred expenses, reserves for future expenses, depreciation charges, etc.
The matching principle, like the accrual principle, provides a process whereby all income as received, as well as expenses, are accounted for in the same accounting period. There is probably no need to prove that all receipts for the sale of products, work performed, services rendered and their cost for the corresponding year 2004 cannot be taken into account in 2005.
Finally, the principle of the predominance of economic substance over form represents that economic events must be taken into account and presented according to their essence and reality, and not just their legal form.
In modern conditions of a market economy, accounting occupies a responsible place in the management system. At the same time, accounting performs a number of functions, the main ones being: informational; control; ensuring safety; analytical.
The most important of the listed functions is the information function, which, with the deepening of market relations, becomes very important when the role and importance of timely and reliable information about the state and financial position of the activities of an economic entity seriously increases.
Information obtained through accounting is a source for various users who, based on the analysis of the information received, make management decisions.
The main advantage of accounting is that it forms and summarizes information about the state and movement of the enterprise’s property and the sources of their formation, about economic processes and achieved results. The presence of such information allows operational and statistical accounting in order to predict the development prospects of the enterprise.
The peculiarities of a market economy place increased demands on accounting information, which without any doubt must be timely, reliable and objective. It must be effective for users and of high quality, and ultimately, accounting information must characterize the financial condition of the enterprise.
The control function of accounting in the context of the functioning, various forms of ownership and expansion of business entities increases even more. Accounting is entrusted with great tasks to implement effective control over the use of enterprise assets. Ensuring control over the implementation of planned development programs and achieving high economic indicators is the most important control function of accounting.
As a result, accounting, by comparing actual indicators with data from established norms and standards, can make appropriate adjustments.
In practice, three types of control are used: preliminary, current and subsequent.
Control carried out during business transactions and before making management decisions is called preliminary control. All kinds of contracts, projects, programs, estimate documentation, business plans, etc. are objects of current control. At the stage of preliminary control, actions are carried out as a result of which it is possible to prevent the commission of illegal business transactions, deter officials from unauthorized actions, ensure the rational use of material and financial resources, prevent the preparation of incorrect documents, etc.
Current control refers to the performance of specific operations directly during the performance of business operations. At the same time, such control has the goal of identifying deviations from the main parameters of business activities and standard indicators of the enterprise. As a result, current control promptly prevents possible theft and loss of material and monetary resources.
Subsequent control has the goal of verifying the feasibility and legality of completed business transactions for a specific period of activity. Such control ensures the identification of shortcomings in the work of officials, abuses and violations, which makes it possible to mobilize the internal resources of the enterprise to further improve its activities. As usual, internal control bodies carry out subsequent control after business transactions are completed, using information from primary documents, accounting registers (books, journals) and financial statements.
Ensuring the safety of property. It is known that enterprises of an economic entity, regardless of their size, capacity, or specific profile, have a certain set of property values. Their correct and effective use is one of the functions of accounting. Along with this, one of the most important tasks of accounting is also to ensure the safety of the enterprise’s property, creating barriers to possible abuse, theft and unwanted losses. It is a self-evident fact that in order to achieve security objectives, the necessary conditions must be created at the enterprise: the presence of weighing instruments, measuring containers that meet the technical and sanitary conditions of an equipped warehouse, and others.
The presence of various forms of ownership in the market today, the value of the safety function is of exceptional importance, because the increase in the number of owners, investors and especially foreign ones requires a clear organization of accounting.
Ensuring the function of preserving property is achieved at the enterprise by conducting a periodic inventory of valuables and objectively reflecting its results in accounting.
The analytical function of accounting is expressed in the fact that, on the basis of objective and reliable accounting data, an analysis of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise is carried out. Analysis is the process of consistently studying decisions made in order to improve them. Analytical accounting indicators, most often, form the basis for long-term planning and regulation of economic activities. Analysis of the current financial condition of the enterprise allows us to assess its position at the moment.