Organization of military records
The main documents regulating the implementation of military registration are the Law “On Military Duty and Military Service” dated March 28, 1998 No. 53-FZ, Regulations on Military Registration dated November 27, 2006 No. 719.
Purpose of accounting:
- In peacetime - ensuring that every person liable for military service fulfills his duty, fully filling the army, and preventing illegal evasion from service.
- During the war period - timely mobilization of persons liable for military service, provision of labor resources.
A labor force is being formed from citizens liable for military service who fall under category “B”. In wartime, they are drafted into the army, but are not sent to places of hostilities; they are left in structures to perform certain functions.
For the mechanism to work, the state must have up-to-date information and control the situation. For this purpose, military commissariats, with the help of organizations, keep records of all potential conscripts aged 17-27 years, those in the reserve at the same age, retired officers, etc.
The law stipulates that every young man in our country is obliged to appear at the military registration and enlistment office to undergo a medical examination in order to register for primary registration and assign a fitness category when he turns 17 years old. Initial registration is carried out from January 1 to March 31. All persons who have received a summons should appear at the military registration and enlistment office, even if they have not yet turned 17, but will be this year.
Large departments, local authorities, and organizations are responsible for the functioning of the military registration mechanism. If a potential conscript officially works or studies in an organization, records should be carried out by employees in accordance with generally accepted rules.
Who to consider?
First of all, we note that conscripts and employees liable for military service are subject to military registration in the organization in 2015. Who belongs to such persons is established by clause 1 of Art. 52 of the Federal Law of March 28, 1998 No. 53-FZ “On Military Duty and Military Service” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 53-FZ) and clause 14 of the Regulations on Military Registration, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 719 (hereinafter referred to as Position).
Conscripts are male citizens aged 18 to 27 years old, who are required to be registered with the military and are not in the reserves.
Persons liable for military service are citizens who are in reserve. These include:
- discharged from military service and enlisted in the reserves of the RF Armed Forces;
- have successfully completed training at military departments at federal state educational organizations of higher education in military training programs for reserve officers, sergeants, reserve foremen or reserve soldiers and sailors;
- those who have not completed military service due to exemption from conscription;
- those who have not completed military service due to the provision of deferments from conscription or were not called up for any other reasons, upon reaching the age of 27 years;
- discharged from military service without military registration and subsequently registered with military commissariats;
- have completed alternative civil service;
- female, having military specialties according to the application.
Women with military ranks of officers remain in the reserve until they reach the age of 50, and the rest until they reach the age of 45.
At the same time, persons who are not subject to military registration in the organization - 2020 have been identified:
- exempted from military duty;
- those undergoing military service;
- those serving a sentence of imprisonment;
- females who do not have a military specialty;
- permanently residing outside the Russian Federation;
- having military ranks of officers and being in the reserve of the Foreign Intelligence Service and the FSB.
Maintaining military records - where to start?
Each organization must have information about all men of military age, military personnel with category “B”, officers transferred to the reserve, persons who have completed alternative service or have been deferred for valid reasons. And also women with military specialties. The rules for maintaining and the procedure for military registration are established in the Methodological Recommendations for maintaining military records in organizations approved by the General Staff of the RF Armed Forces on April 11, 2008.
The organization collects up-to-date data on each military service member. This is done by an individual employee or a group of people, depending on the number of employees in the structure. With a total number of 1500 people. Responsibilities are assigned to one specialist, part-time; the position is not allocated separately. With a number of employees of more than 1500 people. A special structural unit is being created and several employees are involved in accounting. Candidates are approved by the military registration and enlistment office. Copies of orders on the appointment or dismissal of an official are also sent there.
Who is involved in military registration?
The following are responsible for maintaining documentation for registering those liable for military service at an enterprise of state or municipal ownership:
- Director of the organization.
- Head of the HR department (or his deputy).
- Clerk, secretary.
The best way to maintain records is to create a military registration table (MRT), but in small organizations this is unrealistic. It is created when the institution employs from 2000 to 4000 people who are subject to military registration. In this case, two people are allocated for this work. In small organizations, the responsibility falls on one of the HR department employees.
Regardless of the presence of a military registration table, those responsible for registration perform the following tasks.
- Maintain documentation of conscripts and military personnel from the enterprise personnel.
- Ensure that enterprise personnel fulfill military duties prescribed by the laws of the Russian Federation.
- Documentation of information about employees liable for military service.
- Interact with departments of the commissariat, state and municipal bodies on various issues.
Instructions for maintaining military records
The list of duties and powers of employees who must maintain military records is indicated in their job description. It also contains information about what knowledge an employee should have, what to follow in his work, how to collect, analyze, and systematize data, what penalties are imposed for violations committed in his work.
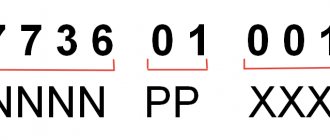
For each conscript, the following information is indicated on a special card:
- FULL NAME;
- Passport details;
- Place of registration, residence;
- Education;
- Job title;
- Family status;
- Fitness category;
- Anthropometric data;
- Reasons for deferment from military service;
- Data on completion of alternative service, attendance at military training;
- Availability of military and civilian specialties;
- Knowledge of foreign languages;
- Sports category, level of physical fitness;
- Criminal record;
- Reservation of a citizen in case of hostilities.
Information is recorded in the prescribed manner.
Workers not subject to military registration
Military records are not kept for all employees. Let's consider workers who are not subject to military registration:
- Those who have received exemption from military duty, for example, those employees who were recognized as partially fit or unfit for military service, as well as those who served in another state;
- Those undergoing military or alternative civilian service;
- Those permanently residing outside the Russian Federation;
- Having the rank of officers who are in the reserves of the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service or the Russian FSB;
- Women who do not have a military specialty.
Methodological recommendations for maintaining military records in 2020
For correct record keeping, the organization draws up an employee action plan for the year and coordinates it with the military registration and enlistment office.
The main documents for collecting information regarding each employee are:
- Certificate of registration for potential conscripts;
- Military ID for those in reserve.
These documents must be provided together when the employee is hired. An authorized employee checks that there are no inaccuracies, damage, torn sheets, or other defects. Next, a card of the established form is created for each employee, where all relevant information is recorded - marital status, education, position held, registration, etc. All information is stored in a common database, and is not visible to military registration and enlistment office employees.
In this case, the summons comes to an authorized employee, who issues it against the addressee’s signature. In the future, he is obliged to ensure that the conscript appears at the military registration and enlistment office at the appointed time. If a woman with a military specialty is hired, she is initially sent to the military registration and enlistment office for initial registration. The same applies to boys over 17 years of age.
An important function of specialists conducting military records in an organization is to assign a position to each person liable for military service for the duration of hostilities. That is, who will do what in the event of war. You can find out about this opportunity to reserve places at the military registration and enlistment office. Typically, these are strategically important enterprises that affect the livelihoods of the entire population of the country.
The authorized specialist keeps a special audit log, according to which he compares the data with those available at the military registration and enlistment office. The employee must notify the military registration and enlistment office of all changes by sending them copies of the orders.
Documents that must be in the organization
The authorized employee must have the following documentation:
- Order on the organization of military registration of citizens.
- Work plan.
- A file of personal cards of form No. T-2 and No. T-2 GS (MS) for citizens from among the conscripts, persons in the reserve.
- Check log.
- Receipts for receiving military registration documents from citizens.
- Office work.
- Other documents as required.
- Reference information on military registration, mobilization training, mobilization.
Some information is transmitted to the military registration and enlistment office in electronic form within a clearly defined time frame.
How to keep military records
- On the day of hiring, check the mark in your passport and military registration documents . On the 13th page of the passport there should be a stamp, for example, this: “I am obligated to perform military duty.” Check the data with your registration or military ID. If a person does not have documents, inform the military registration and enlistment office. Corrections, suspicious inaccuracies, fake documents are also reasons to call the military commissar.
- Copy the data from military registration documents into a personal card in the T-2 form. Fill out section II “Information on military registration”. Personal cards should be stored in a separate file cabinet.
3. Tell the employee about his responsibilities : the need to register for military service at his place of residence or place of stay, especially for conscripts.
Report calls to the military registration and enlistment office and serve summonses. The time an employee spent at the military registration and enlistment office is paid in the amount of average earnings. In the time sheet, enter the code “G” or “23”.
4 . Every year, coordinate the work plan for military registration with the military registration and enlistment office and maintain it . Save the template from the guidelines.
5. Report regularly to the military registration and enlistment office:
- Within two weeks, send letters of accepted and dismissed employees who are subject to military registration.
- Information about employees - upon request of the military registration and enlistment office, within two weeks.
- Lists of minor employees for initial military registration - the period depends on age.
6. Update personal cards if an employee got married, divorced, received a diploma, transferred to another position, or changed his place of residence. Report this to the military registration and enlistment office within 2 weeks.
Once a year, check section II of your personal card with military registration documents and military registration and enlistment office data.
For example, when an employee has reached the age limit (50 years for soldiers), the military registration and enlistment office must deregister him and make an entry on his military ID. After this, you need to put a mark on your personal card: “Removed from military registration due to age.” If a person is declared unfit for service, write: “Removed from military registration due to health reasons.”
7. Keep a check log . The form can be purchased at a specialized store or taken from the guidelines. The log is filled out by a representative of the military registration and enlistment office during the inspection.
Responsibility for violating the rules - fines in 2020
Maintaining military records is the responsibility of every organization; failure to comply with this requirement results in administrative liability in the form of fines.
The following are considered violations:
- Failure to provide information about potential recruits within the established time limits;
- Failure to provide assistance in the appearance of an employee when summoned to the military registration and enlistment office;
- Intentional or unintentional concealment of information about current data, in particular, the relocation of an employee, removal from the place of registration.
Violations by employers often result in minor penalties. The only norm is Art. 21.4 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For failure to provide information about hiring, dismissal of a conscript, persons liable for military service in the reserve, a fine of 300-1000 rubles is imposed on the management of the organization. For this reason, organizations do not keep military records or do so partially.
However, if the military registration and enlistment office sends a request to the organization to provide up-to-date information, a requirement regarding maintaining military records, all this will be ignored, the management will be subject to significant fines.
- 2000 – 4000 rub. Against a specialist, for incorrect, incomplete record keeping;
- 3000 – 5000 rub. For a company and 300-500 rubles. For officials - management;
- 10,000 – 20,000 rub. For organization, 1000-2000 rubles. On officials for failure to comply with the instructions of the military commissariat, lack of military registration at the enterprise.
For failure to provide up-to-date information or for not sending students in grades 10-11 who have reached the age of 17 to the military registration and enlistment office, educational institutions are subject to a fine. The amount of the penalty is 300 – 1000 rubles.
How many specialists keep military records?
Depending on the number of employees in the organization, the number of employees responsible for maintaining military records is determined:
- The number of staff is up to 500 people - records must be kept by 1 employee, including a part-time employee;
- From 500 to 2000 people – records are kept by 1 full-time employee;
- From 2000 to 4000 people – records are kept by 2 full-time employees.
When determining the number of responsible employees, for every subsequent 3,000 employees, you need to add one more full-time employee (
Step-by-step instruction
The principles of maintaining military records in an organization or enterprise are regulated by several legal documents:
- Federal Law No. 31-FZ of February 26, 1997 “On mobilization preparation and mobilization in the Russian Federation” (Article 9 “Responsibilities of Organizations”);
- Federal Law No. 61-FZ of May 31, 1996 “On Defense” (Article 8 “Functions of organizations and responsibilities of their officials in the field of defense”);
- Regulations on military registration, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 719 of November 27, 2006.
Responsibility for maintaining military records rests with the manager. He has the right to appoint specialists who will carry out the work. The minimum number of authorized persons is determined by the total number of employees. Up to 1500 people – 1 employee or specialist performs part-time duties, from 3000 people. And a structural unit with two or three specialists is being formed.
The order for the appointment of authorized persons is sent to the military registration and enlistment office and agreed with them. In the future, an action plan is provided regarding the adequate accounting of potential conscripts and military personnel in the reserve.
Documentation
Documents are checked for authenticity and all necessary data is recorded. Cards are issued for all men aged 17 to 27 years who are potential conscripts or military reserve personnel. They do not keep records of persons who have fitness category “D”, women who do not have military specialties.
Information is entered accordingly. In the future, it is necessary to maintain the relevance of the data, carry out explanatory work among employees regarding military service, changes, and responsibility for evasion.
Transfer of information to the military registration and enlistment office
When all the cards are compiled, the information must be transferred to the military commissariat. In the future, it is necessary to closely cooperate with the military, provide timely information about the appointment, dismissal of employees, change of residence, transfer to another position, marital status, etc. You should also report about employees who deliberately evade service. There is a fine for hiding information.
Submitting reports
To obtain sample documents and instructions for filling them out, you must contact the military registration and enlistment office. There you will also receive information about the deadlines for submitting reports. Every month, an authorized specialist must send information to the military registration and enlistment office about dismissed and newly enrolled employees. Once a year, information is submitted about persons who will turn 17 next year. There is an electronic version of reporting, special programs for maintaining military records. Management decides on the use of the software.
Military registration in the organization
Federal Law of May 31, 1996 No. 61-FZ “On Defense” clearly and unambiguously establishes the obligation of organizations and officials to maintain military records in the organization. Article 8 “Functions of organizations and responsibilities of their officials in the field of defense” of the above law states that “organizations, regardless of their form of ownership, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, carry out military registration of employees and, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, provide buildings and structures for defense needs , vehicles and other property owned by them, with subsequent compensation for expenses incurred in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.” The same article states that “officials of organizations, regardless of their form of ownership:
1) must fulfill their duties in the field of defense provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
2) create the necessary conditions for employees to perform their military duties in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.”
Thus, the most common mistake employers make regarding military records is that many organizations do not keep them. Some believe that if they are not state, budgetary organizations, then they are not obligated to do this, others do not find the resources for this (for example, additional employees in the personnel department may be required). However, the legislation directly provides for the employer’s obligation to maintain military records.
On a note! Any employer is obliged to keep military records in the organization; there is not a single legal excuse for not keeping military records (even if there are no military personnel in the organization at all)!
How to properly maintain military records in an organization is prescribed in the Methodological Recommendations for maintaining military records in organizations (approved by the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation on April 11, 2008).
Who is subject to military registration?
The following are subject to military registration in organizations (clause 14 of the Regulations on military registration, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 719):
1) male citizens aged 18 to 27 years who are required to be registered with the military and are not in the reserves;
2) citizens who are in reserve. The categories of citizens who are in reserve are established in paragraph 1 of Art. 52 of the Federal Law of March 28, 1998 No. 53-FZ.
The following citizens are not subject to military registration in military commissariats, local self-government bodies and organizations (clause 15 of the Regulations on Military Registration):
1) exempted from military duty in accordance with Art. 23 of the Law on Military Duty;
2) undergoing military service;
3) those serving a sentence of imprisonment;
4) female, without a military specialty;
5) permanently residing outside the Russian Federation;
6) having military ranks of officers and being in the reserves of the Foreign Intelligence Service of the Russian Federation and the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation.
Military registration of those liable for military service is divided into special and general (clause 16 of the Regulations on military registration).
Special military registration includes those liable for military service who, in accordance with the established procedure, are reserved for state authorities, local self-government bodies or organizations for periods of mobilization, martial law and in wartime, as well as those serving in internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and criminal authorities. -executive system, authorities for control over the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances in the positions of ordinary and commanding personnel.
The rest of those liable for military service are on the general military register.
What documents should a military registration organization have?
1) an order on the organization of military registration of citizens, including the reservation of citizens in reserve.
2) a work plan for maintaining military records of citizens and booking citizens in reserve. The specified plan, in order to ensure the completeness and quality of military registration of conscripts and reserve personnel from among those working (studying) in organizations (educational institutions) and the reservation of citizens in the reserve, is developed by organizations during the calendar year. The plan must be agreed upon with the military commissariat of the municipality.
3) a file cabinet of personal cards of form No. T-2 and No. T-2 GS (MS) for citizens from among conscripts and citizens in reserve;
4) a log of checks on the implementation of military registration and reservation of citizens in the reserves of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation;
5) receipts for receiving military registration documents from citizens (the form of receipt is established by Appendix No. 14 to the Methodological Recommendations).
6) official paperwork (a separate matter) on the issues of maintaining military records of citizens and booking citizens in the reserve in the organization;
7) other documents in accordance with the requirements established by federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government bodies and heads of organizations;
 reference information on military registration, mobilization training and mobilization.
reference information on military registration, mobilization training and mobilization.
The documents that must be regularly submitted to the military registration and enlistment office deserve special attention
<*> May be submitted electronically.
<**> They are an appendix to the list of citizens subject to initial military registration (clause 4 of the table).
Typical mistakes in military registration.
1. The organization does not require military registration documents from the employee;
2. The organization makes mistakes when maintaining a personal card for military registration;
3. The organization does not agree with the military registration and enlistment office on the work plan for the implementation of military registration and the order on the organization of military registration;
4. The organization does not send information about the hiring/dismissal of employees to the military registration and enlistment office;
5. The organization does not verify information with the military registration and enlistment office;
6. The organization lacks information/local regulations on military registration.
Violations by employers in the field of military registration are associated with insignificant liability. The only norm that provides for liability for deficiencies in military registration is Art. 21.4 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For failure by the manager or other responsible person to report to the military commissariat information about those hired or dismissed from work of citizens liable for military service under Part 3 of Art. 21.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the fine ranges from 300 to 1000 rubles. Organizations do not take such a fine seriously. Therefore, they prefer not to keep military records at all or to keep them partially.
However, when the organization receives a request from the military registration and enlistment office to submit documents, military records will have to be maintained. If the requirements of the military registration and enlistment office to submit documents in accordance with the law are ignored, penalties will follow:
- fine from 2000 to 4000 rubles. against officials for disobedience to a lawful order or requirement of an official of a body exercising state supervision (control) (Article 19.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- a fine from 3000 to 5000 per company and from 300 to 500 rubles. against officials for failure to submit or untimely submission to a state body of information (information), the submission of which is provided for by law (Article 19.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- a fine of 10,000 to 20,000 per company and from 1,000 to 2,000 rubles. or disqualification for up to three years on officials for failure to comply within the prescribed period with a legal order of the body exercising state supervision.
Thus, in the case of requests from the military registration and enlistment office and when reporting an inspection by the military registration and enlistment office of military registration, the risk from insignificant becomes quite noticeable.
For heads of educational organizations, the issue of failure by the head or other official of the organization, as well as by the official of the local government responsible for military registration work, to submit, within the prescribed period, lists of citizens subject to military registration to the military commissariat or other body carrying out military registration is also relevant initial registration with military personnel shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine in the amount of 300 to 1000 rubles. (Article 21.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). Primary registration for military service usually occurs for students in grades 10-11.
Citizens and officials guilty of failure to fulfill military registration obligations bear responsibility in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
- Author - Zvyagin Alexander Sergeevich
- 01.05.2017
- All consultations by the author
Mandatory or not accounting?
The law obliges every enterprise, organization, and institution to keep records regarding conscripts and reserve military personnel. The fulfillment of duties should be monitored by authorized bodies, military registration and enlistment offices, local authorities, and government departments. Not all structures take this responsibility for granted and do not consider it necessary to control conscripts, but this does not mean that this can be done. Such institutions are subject to fines; if they regularly violate the law on military activities, officials may be deprived of the opportunity to hold high positions for 3 years or more.
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your feedback about military registration in the organization - below in the comments, your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Igor
In our country we should do a lot of things, but not all of them do them. I have been working for 4 years at different enterprises, I have not heard of any registration, they do not hand me over to the military registration and enlistment office and they do not impose fines. There is no interest from managers, and the sanctions are insignificant. In addition, these are additional costs for maintaining specialists, or even an entire headquarters.
Andrey
Who keeps military records are government organizations and educational institutions. As a student, we were sent to the military registration and enlistment office every year. As soon as I graduated from the university, information immediately went there. They took me to serve.
Order on the organization of military registration (sample document)
A sample order is contained in Appendix 4 to the Methodological Recommendations. The document must contain the following information:
- name of company;
- date of issue of the order;
- Document Number;
- order on the organization of accounting;
- details of the person responsible for maintaining records;
- information about the deputy employee responsible for accounting in the company in the event of his temporary absence or incapacity for work;
- information on control over the execution of the order.
The order is signed by the head of the organization and certified with the company seal. A copy of the document is sent to the military registration and enlistment office.