Author of the article: Lina Smirnova Last modified: January 2020 2257
During the work process, many employees have to work extra hours beyond the established time at the request of the manager. Involvement in overtime work is a right of the employer, which he can use under certain conditions. Let's consider what is meant by overtime work, under what conditions employees are involved in it and what is the procedure for paying for it.
Stages
Let's consider the procedure for engaging in overtime work: what kind of work is classified as overtime and when it is allowed.
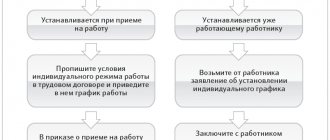
There are two main stages in attracting an employee to work overtime.
First stage:
It is important for the employer to remember that he is obliged to notify certain categories of employees by signature of the right to refuse such work. All verbal agreements with employees can lead to disputes. To avoid this, it is necessary to adhere to the position that all employee-employer agreements are documented. Therefore, the employer must:
- obtain the employee’s written consent;
- make sure there are no medical contraindications;
- notify employees under personal signature of the right to refuse to perform overtime work.
The employee notification does not have a special form, but contains information:
- Name;
- notification number and date of preparation;
- Full name and position of the specialist involved;
- the reasons why there was a need to be present at work overtime;
- the date when you need to work “extra” hours (you can specify a time interval);
- conditions - increased wages or compensation in the form of additional rest due to the employee.
The notice is signed by the head of the employing company. An employee can express his will by signing in the “Agree” or “Disagree” field.
A sample written consent to engage in overtime work can be viewed here.
Second phase:
The employer issues an order requiring overtime work and must familiarize the employee with it. The unified form of such an order has not been approved, so the employer draws it up in free form. The order must indicate:
- the reason for involving the employee in overtime work;
- work start date;
- surname, name, patronymic of the employee;
- his position and details of the document in which the employee agreed to be involved in such work.
This is also important to know:
Overtime work of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2020: how it is paid, should not exceed...
A sample order for overtime work can be found here.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
If a collective agreement or local regulation establishes the amount of additional payment, then it is possible to indicate this amount in the order. The amount may also be determined by agreement of the parties. The employee must be familiarized with the order and signed.
When inviting employees to work overtime, it is worth remembering that the duration of such work should not exceed four hours for each employee for two consecutive days and 120 hours per year. To do this, the employer is obliged to ensure accurate recording of the duration of overtime work for each employee.
In the working time sheet, overtime work is indicated either by the numbers “04”, and next to it the number of hours worked in excess of the norm is indicated. If standard daily records of hours worked are maintained for employees, on days of overtime work it is recommended to reflect separately standard and excess working hours in two lines. And if summarized accounting of working hours is used, overtime is reflected at the end of the accounting period.
What applies to overtime work?
According to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the normal working time is 40 hours per week. However, for some categories of workers, reduced working hours are established, which is normal for them (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These include, in particular:
- minor workers - from 24 to 35 hours per week depending on age;
- disabled people of group I or II - no more than 35 hours per week;
- employees whose working conditions at their workplaces, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, are classified as hazardous working conditions of the 3rd or 4th degree or hazardous working conditions - no more than 36 hours per week;
- women working in the Far North (Article 320 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- teachers (Article 333 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- health workers (Article 350 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This is also important to know:
Reducing the working week according to the Labor Code: payment features
That is, for these categories of workers, overtime will be considered work that exceeds the reduced working hours established for them (daily work, shift).
Important! If an employee is late at work on his own initiative, such work is not considered overtime.
When can you be required to work overtime?
By order of the employer, an employee without his consent can be involved in overtime work (Part 3 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- to prevent a catastrophe, industrial accident, and eliminate their consequences;
- to eliminate the circumstances due to which centralized systems of water, heat and gas supply, transport and communications do not function;
- in the event of a state of emergency or martial law and in other emergency situations that threaten the population (fires, floods, etc.).
To engage in work on these grounds, the consent of the trade union organization is not required, since these circumstances are extraordinary.
If you refuse to perform such work, a corresponding act is drawn up, and the employee is subject to disciplinary action.
With the written consent of the employee, you can be required to work overtime in the following cases (Part 2 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- if necessary, perform (finish) work that has begun, which, due to an unforeseen delay due to technical production conditions, could not be performed (finished) during the working hours established for the employee, if failure to complete this work may result in damage or destruction of the employer’s property or create a threat to life and people's health;
- during temporary work on the repair and restoration of mechanisms or structures in cases where their malfunction may cause the cessation of work for many workers;
- to continue work if the replacement employee fails to appear, if the work does not allow a break.
In other cases, involvement in overtime work is allowed only with the written consent of the employee and taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization (Part 4 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 14, 2006 in case No. 4-B06-31).
Who should not be required to work overtime?
The following are not allowed to work overtime:
- pregnant women;
- workers under the age of 18 (with the exception of minor athletes, as well as creative workers of the media, cinema organizations, television and video crews, theaters, theatrical and concert organizations, circuses and other persons involved in the creation or performance of works (Art. 348.8 and 268 Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons with whom a student agreement has been concluded (Article 203 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- other categories of workers in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
This is also important to know:
What is an irregular working day in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: who is established, schedule, payment
Women with children under three years of age may be allowed to work overtime with their written consent and provided that overtime work is not prohibited for them for health reasons in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts . A similar procedure is established for people with disabilities. Both of them must be informed, against receipt, of their right to refuse overtime work.
By virtue of Art. 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the same procedure for attracting overtime work is provided for:
- mothers and fathers raising children under the age of five without a spouse;
- workers with disabled children;
- workers caring for sick members of their families in accordance with a medical report.
In addition, fathers raising children without a mother, as well as guardians (trustees) of minors can be involved only with written consent (Article 264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What additional work is not overtime?
An important nuance is that the initiative for overtime work must come from the employer. If a particularly zealous employee decides to stay at his favorite job of his own free will, his additional work will not be taken into account and paid according to the legal requirements for overtime work (Rostrud Letter No. 658-6-0 dated March 18, 2008).
Work performed during irregular working hours is not recognized as overtime.
IMPORTANT! Overtime work cannot be a permanent practice at the enterprise; it can be resorted to only if necessary and from time to time.
Overtime pay
The procedure for paying overtime hours is regulated by Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In contrast to the previously existing rules of payment for hours worked in excess of the norm. It is possible for the employer to approve specific amounts of payment for overtime work in an employment or collective agreement, but not lower than those established in Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which defines the minimum threshold of payment for excess hours of work.
Overtime work is paid at an increased rate. For the first two hours of work at one and a half times the rate, for the next hours - at 2 times the rate. This is the minimum threshold provided for by the Labor Code, below which you cannot pay, but above it you can. This kind of provision can be enshrined in a collective agreement, regulations on wages and other regulations for the enterprise.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
In addition to increased pay for overtime hours, as an alternative, it may be possible to provide additional hours of rest in an amount not less than those worked in excess of the norm. The written consent of the employee must be obtained for such a replacement, and the time for using such compensation must be agreed upon by both parties. At the same time, the Labor Code does not define the maximum duration of rest time provided as compensation for overtime worked. More specifically, this can be stated in a collective or labor agreement or other local acts of the organization. Experts in the field of labor law recommend that the type of compensation for overtime worked be specified directly in the employee’s written consent to overtime work. If these are additional hours of rest, then it is recommended to write down their number here.
Payment for overtime hours on a shift schedule
Special methods for calculating overtime for shifts have not been established. This raises questions when calculating.
Example 1 (continued)
The employee worked 15 shifts (12 hours) and on his day off, on the last day of the month, he replaced another employee for 1/2 of the shift. In total, he worked 186 hours at a rate of 176 working hours per month. The rate per shift is 2,400 rubles.
Tariff for 1 hour: 2,400 / 12 = 200 rub.
200 × 1.5 = 300 rub. (first 2 hours)
200 × 2 = 400 rub. (subsequent hours)
The question is how to count these hours. The last day of the month was a day off for the employee, that is, overtime is already on schedule - that’s 4 hours, of which 2 are 300 rubles each. and 2 for 400 rubles. How should 6 hours of replacement be counted? 2 for 300 and 4 for 400 or all 6 for 400? There is no clear answer to this question in the laws.
Within the meaning of Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the requirements are the same for any type of overtime payments. If there are no internal company standards, it is better to prefer the option: 6 to 400. This will coincide with the conclusions of the courts in salary disputes.
Thus, the additional payment for overtime will be:
2 × 300 + 8 × 400 = 3,800 rub.
Overtime pay for cumulative accounting
To understand this issue, you should adhere to clause 5.5 of the Recommendations on the use of flexible working time regimes in enterprises, institutions and organizations of sectors of the national economy, approved by Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor No. 162, All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions No. 12-55 of 05/30/1985. These Recommendations are valid to the extent that they do not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 423 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated October 15, 2012 No. AKPI12-1068).
This is also important to know:
Reducing the working week according to the Labor Code: payment features
In accordance with the document, it is necessary to determine the number of working days in the accounting period and pay for the first two hours, falling on average on each working day of the accounting period, in no less than one and a half times the amount, and for the following hours - in no less than double the amount.
When recording working time in aggregate, overtime hours are calculated at the end of the selected accounting period (month, quarter, half-year, year). At the same time, on some days an employee may work more, on others – less, the main thing is that during the accounting period he works the established norm of hours. Exceeding this norm is considered overtime.
Important! The time when an employee was absent from work for a valid reason (for example, sick or on vacation) is excluded from his standard working hours.
Overtime calculation
Now we know what is considered recycling. Next, we will consider the question of how to pay for such work. All overtime is paid in accordance with Article 152 of the Labor Code: for the first two hours, no less than one and a half times, for subsequent hours, no less than double. That is, the law establishes only the minimum amounts of additional payments, but specific figures need to be fixed in a collective agreement, local regulation or employment contract.
On a note
If you need to call an employee to work on a weekend or holiday, then such work must be paid exactly as work on a weekend (holiday).
Please note that the specific procedure for calculating the hourly wage rate of a salaried employee must be fixed in the employment contract with the employee or in the wage regulations adopted by the organization.
Don’t forget: the employee has the right to receive additional rest time for overtime work instead of increased pay. In this case, the duration of the leave cannot be less than the overtime period. However, there is one caveat: even if an employee is given additional rest time, this does not mean that he does not need to be paid for overtime work. In this case, overtime hours must be paid in a single amount, because the time off only compensates for the increased pay.
Key points on overtime work
To avoid troubles with inspection authorities, the employer is recommended to:
- request the written consent of employees and the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization;
- check whether, according to a medical report, the recruited employees are not contraindicated from working overtime;
- compensate for work beyond normal working hours;
- reflect in a collective agreement or other local regulation the procedure for attracting employees to overtime work, providing additional days of rest and the mechanism for calculating monetary compensation for overtime (for example, will increased overtime pay include bonus payments);
- keep an overtime log and use it to monitor that employees do not overwork more than 120 hours per year.
General information about processing
Let us recall that overtime work is work outside the normal working hours (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The regulations here depend on the schedule the specialist works on. If it is a "standard" scheme, with a certain number of hours per day, then the overage may be determined daily. If summarized accounting of working time is used, then overtime is determined for the accounting period. Usually this is a month, but the law allows the use of longer time periods, up to a year (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Primary documents for payroll accounting