Mandatory points
An outsourcing agreement is concluded with the direct contractor (outsourcing company), which cannot act as an intermediary of services, that is, reassignment of execution is not allowed (Article 780).
The subject of the agreement is specific services (activities) of the Civil Code, Article 779. The result of outsourcing activities is not endowed with material characteristics, but has a different qualitative assessment.
Obviously, the mandatory (essential) points of an outsourcing agreement are:
- the subject of the agreement, or the service itself, which is subject to a detailed description, with a step-by-step listing of the work required by the customer;
- the start and end dates of the outsourcing agreement (Article 783), without which it will not be recognized as valid (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service ZSO No. A27-9091/2009);
- deadlines for providing interim reporting, options and deadlines for informing the customer.
Vague wording and lack of specification of the mandatory aspects of the contract are the main mistakes when concluding an outsourcing agreement.
The contract may contain additional provisions that the parties consider important. Additional points of the agreement should be discussed and a bilateral agreement reached.
If the service that is the subject of the contract eventually requires clarification, expansion of the tasks and/or powers of the outsourcer, as well as changes in control actions on the part of the customer, then an additional agreement is concluded.
The procedure for discussing, concluding and signing such a document is specified in the text of the main agreement.
What do you need to know about an outsourcing agreement?
Outsourcing agreement for the provision of services under Art. 780 of the Civil Code is not concluded with an intermediary. Art. 779 of the Civil Code indicates the focus of the contract - specific activities. It has no physical characteristics, but there is a quality assessment. The agreement must stipulate:
- detailed characteristics of the subject of the agreement;
- a list of tasks that the contractor needs to perform;
- the period of validity of the agreement (the exact terms are indicated in accordance with the provisions of Article 783 of the Civil Code), which confirms its validity;
- time when interim reporting is provided.
The main drawbacks when signing an outsourcing agreement are vague wording. In addition to specifying the terms of cooperation, additional provisions must be specified.
Rules for drawing up an outsourcing agreement
Outsourcing is most in demand in the areas of information technology, accounting and data processing, legal services and logistics.
Recently, the economic activities of organizations are increasingly being outsourced.
The outsourcing agreement requires written form (Civil Code Art. 160), notarized registration is not required.
Features of the contract and content requirements:
- The document has a number to which subsequent additional agreements and annexes can be linked. The date and place of signing the contract are mandatory.
- Full information about the parties to the agreement. Persons representing companies must be authorized to enter into transactions and sign agreements. Such powers are not vested in acting (IO) and interim acting (ACTING) managers (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region No. KG-A41/10211-03 2004/09/01).
- Subject of the transaction, or characteristics of the service with details. The lack of details and specification of tasks can lead to the fact that the necessary actions of the performer fall into the category of additional services paid for separately. The scope of work for a service without details in the contract can be interpreted by the parties differently (Civil Code Art. 783).
- Bilateral duties and rights. Streamlining interim reporting. Providing information (what and in what cases).
- Bilateral responsibility (for example, violation of reporting deadlines, lack of information) and options for assessing the quality of work (Civil Code art. 721, 783).
- Cost of the service in rubles (Civil Code Art. 314) and payment scheme (Art. 781).
- Validity of the contract (usually from 6 months) and the possibility of its extension.
- Resolution of conflict situations and disputes.
- The procedure and conditions for terminating the agreement, possible refusal to cooperate. The procedure for concluding additional agreements to this agreement.
If other documents are attached to the contract (license of an outsourcing organization (for example, audit, legal and medical services), expanded detail of work, etc.), then they fit into the text of the contract.
An outsourcing agreement is concluded between companies (LEs), so when signing it is necessary to indicate the details of the customer and the contractor. Signatures on the contract are certified by seals.
Important nuances of an outsourcing transaction
The contractor, represented by the outsourcing company, does not provide intermediary services, but directly carries out activities on behalf of the customer. The contract does not specify the manufactured product, but describes the services.
It is mandatory to record the service in as much detail as possible regarding quality characteristics and time periods for reporting, and methods of information delivery.
The conclusion of a contract must be preceded by a comprehensive discussion by the parties of all controversial issues and specification of services in a draft version.
If, due to objective circumstances, it is not possible to avoid vague wording in the text of the agreement, then the terms of additional agreements aimed at clarifying the boundaries of the executor’s powers are prescribed in a separate paragraph in the document.
AGREEMENT ____for paid services
___________ «___ «_________ 20__
Individual entrepreneur _______________________, registration certificate No. ________________, issued by ______________________, hereinafter referred to as the Contractor on the one hand, and ____________________________________________________________
passport series ___________ No. _________________ issued
____________________________________________________,
hereinafter referred to as the Customer, on the other hand, have entered into an agreement as follows:
SUBJECT OF THE AGREEMENT
1.1 Under the contract for the provision of paid services, the Contractor undertakes, on the instructions of the Customer, to select personnel from the Agency’s applicants and hire personnel to perform the services specified in clause 1.2 of this agreement, and the Customer undertakes to pay for these services.
1.2 The Contractor undertakes to provide the following services:
1.2.1 Provide: ________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Services are provided by qualified personnel. The professionalism, friendliness and honesty of the Agency's employees are guaranteed.
1.2.2. The schedule for the provision of services and other working conditions of the Agency Personnel, as well as additional data for the provision of services, data on the employee are established in Appendix No. 1, which is an integral part of the Agreement.
1.3. This Agreement was concluded for the period from “___________” ___________ 20__ to “__” 20__.
DUTIES OF THE PARTIES
2.1. Responsibilities of the Contractor
2.1.1 Provide services with adequate quality
2.1.2 The Contractor guarantees to the Customer that the Agency Personnel has the skills and qualifications necessary to fulfill their obligations under this Agreement.
2.1.3 The Contractor shall replace personnel, at the discretion of the Contractor, in the event of staff illness, or their inability to perform duties under this Agreement, during the entire term of the contract, as stated in the Additional Agreement.
2.1.4 The Contractor provides candidates for replacement of Personnel at the Customer’s request (free of charge) in the event of a motivated written justification by the Customer for the need for replacement. Replacement of personnel is carried out within seven (7) working days, and an Additional Agreement is signed.
2.2. Responsibilities of the Customer
2.2.1. Provide the Personnel with a place of work, all necessary tools, equipment, devices and consumables for the proper performance by the Personnel of their obligations under this Agreement.
2.2.2. In case of illness or other cases of inability of the Personnel to fulfill their obligations under this Agreement, accept replacement personnel provided by the Contractor and pay the cost of services in the same amount.
2.2.3. If the Personnel is forced to temporarily not work due to the temporary absence of the Customer or other reasons beyond the control of the Personnel or the Contractor, the Customer is obliged to notify the Contractor and staff three calendar days before the expected time of absence and partially pay (by agreement with the Contractor) the cost of services for the period of downtime personnel, reserving them for further work.
2.2.4. Provide the Contractor with a motivated written justification if the quality of the Personnel’s work does not objectively satisfy the Customer.
2.2.5. Notify the Contractor in writing of the refusal of services 10 calendar days before the expected date of termination of this Agreement.
What should be specified in the agreement?
The outsourcing agreement includes several main important points.
- Item. One of them is the subject of the contract. This is one of the essential conditions for drawing up an agreement. If the subject of the agreement is not defined, then such an act is considered invalid and not concluded. Most often, the subject of the contract is the provision of paid services in a certain field of activity. For example, services in the field of tax or accounting.
- Contract price. Another one of the main points.
This point should be formulated in accordance with one or another pricing principle. The rules contained in the fifth section of the Tax Code are also taken into account. Funds can be paid monthly and commensurate with the number of services provided, or they can also be paid one-time in a set amount. In case the composition of the contract may stipulate the advance payment, as well as the timing of the final payment. - Term. The third most important point is the term of the contract, as well as the procedure for accepting the result. And despite the fact that the term does not relate to the essential conditions, nevertheless, this clause of the contract is extremely important. Let us turn to Chapter 39 of the Civil Code, which talks about the provision of paid services.
There is no mention of deadlines here, but if you want to get results as quickly as possible, then deadlines still need to be mentioned. The start of the work is established, as well as the deadline for its completion.However, in accordance with the decision made by the parties, intermediate deadlines may be provided that are associated with certain types of services. By additional agreement or agreement between the parties, changes to the terms may be made.
- Rights and obligations. The responsibilities of the contractor in accordance with Article 779 of the Civil Code include the need to act strictly within the established framework of the contract and carry out activities to carry out tasks from the customer. The more detailed the contract describes the essence of the contractor’s activities, the fewer problems you will expect.
For example, the contractor undertakes to provide services in a specific area in a timely manner and, most importantly, in full. The employee's activities can be specified. It is also important to specify the responsibilities of the customer, which are also established in accordance with Article 779 of the Civil Code.The main responsibility of the customer is to pay for the services received. It is calculated in accordance with Article 781 of the Civil Code. The customer can stipulate in the contract the need to check the progress and quality of work, and only upon approval pay for the work performed in accordance with Article 715 of the Civil Code.
- Responsibility. The contract must contain a clause on the liability of the parties, which may arise in connection with violations of deadlines, as well as other significant clauses of the contract. The clause “responsibility of the parties” specifies penalties, as well as cases when the contract can be terminated by mutual consent, or by only one party.
We do not recommend completing the documents yourself. Save time - contact our lawyers by phone:
+7 (499) 938-90-37Moscow
Who has the right to outstaff
Outstaffing has been replaced by official activities to provide labor to employees, which are clearly regulated by law and are carried out in cases limited by law. Private employment agencies that have undergone special accreditation and individual legal entities can provide the labor of employees to other organizations and entrepreneurs, that is, temporarily lease personnel.
The main requirements for them are the following (clause 6 of article 18.1 of the Federal Law of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1 “On Employment of the Population in the Russian Federation”):
- presence of an authorized capital of at least 1 million rubles;
- absence of arrears in taxes, fees and other obligatory payments;
- The head of a higher education agency has at least two years of experience in the field of employment or promotion of employment in the Russian Federation for the last three years.
Organizations applying special tax regimes cannot be private employment agencies (Clause 6, Article 18.1 of Law No. 1032-1).
A private employment agency is obliged to conclude an employment contract with an employee who will be temporarily sent to work for another company or individual and make an entry in his work book.
The employment contract must stipulate that the employee will work under the management and control of an individual or organization that is not his employer. But such a condition can be included if the employee is sent (Article 341.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- to an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur to provide assistance with housekeeping;
- to a company or individual entrepreneur to temporarily perform the duties of absent employees, who retain their place of work;
- to an organization or individual entrepreneur to carry out work related to a deliberately temporary (up to nine months) expansion.
Legislators have identified three categories of workers who can be sent to work for the receiving party not only in the listed cases, but also in cases where fixed-term employment contracts are allowed. These categories include:
- persons studying full-time;
- single and large parents;
- persons released from institutions executing a sentence of imprisonment.
Other legal entities, including foreign ones, may provide workers (with their consent) to perform work:
- in an affiliated organization;
- in a JSC, if the sending party has previously entered into a shareholder agreement;
- in companies that are a party to a shareholder agreement with the sending party (clause 3 of article 18.1 of law No. 1032-1).
Differences between outsourcing and outstaffing
| (from the English “outsourcing” - “external source”, “use of other people’s resources”) | (from the English “out” - “outside” and “staff” - “staff”) | |
| Risks from concluding a contract | Absent if formatted correctly | Banned from January 1, 2020 . Outstaffing has been replaced by official activities to provide labor to employees, which can be carried out only in strictly limited cases by law. |
| Subject of the agreement | The customer transfers to the contractor the execution of business processes or functions that were previously carried out by the customer’s internal divisions. The transferred functions are non-core for the customer. For example, legal services, marketing research, call center services, cleaning buildings, preparing and delivering lunches to the office, providing transportation services, maintaining the operation of a computer network and information infrastructure, providing advertising services, providing security, searching, recruiting and training personnel, etc. d. | The contractor sends its personnel (workers) to the customer to perform labor functions. In this case, the subject of the contract is not people, but services related to this area. As a rule, non-core personnel are transferred to an outstaffing agreement, for example, technical service employees, sales representatives, insurance agents, drivers, salespeople, etc. |
| Actual place of work | The actual place of work for the employee remains the same. Outsourcing is not associated with the physical movement of personnel from the contractor’s company to the customer’s company | When outstaffing, employees work on the customer’s premises |
| Factual Guide | The tasks for the employees are set by the performer. The customer does not have any rights to manage personnel | The personnel provided are under the control of the customer. It is he: determines the range of job responsibilities of assigned employees and the scope of their work; sets specific tasks; provides means of production; teaches, etc. In this case, the contractor may not know what the workers he provides are doing. |
| Control | The customer can only evaluate the result of the service itself (clean office, properly prepared reporting, etc.), but not the process of the contractor’s employees. They are not under his control and management | The provided personnel is under the control of the customer |
| Party responsible for the final result | The performer is responsible for the final result. If necessary, the customer can make claims against him | The customer himself is responsible for the results of the work of the provided workers. He can make claims to the contractor only if he provided him with personnel untimely or in insufficient quantities. |
Types of outsourcing
There are many types of outsourcing - outsourcing companies can perform almost any non-core work.
Accounting. This look is very relevant. One of its most important forms is the transfer to a third party of everything related to the reporting and activities of the accountant. The head of the enterprise that ordered the services is responsible for the results. You can fully service the enterprise, or you can partially. This type of transaction allows you not to waste resources on creating an accounting department for the enterprise.
IT outsourcing is the transfer of those functions that are related to the maintenance of computers and other office equipment. This could be hardware or software maintenance. It is the most popular in the world, since Internet technologies are in demand everywhere.
Personnel outsourcing is suitable for large enterprises that may have a fluctuating workforce. Issues related to personnel management consume a lot of time and money. Therefore, special recruitment agencies sometimes take on work related to hiring personnel, calculating bonuses, calculating tax burden, etc. Payroll processing is usually not an outsourced service. The recruitment agency is not responsible for the availability of high-quality staff work.
Legal. This type is convenient for not too large enterprises. The outsourcing company will serve another company on tax and labor law. Outsourcing can also affect registration, reorganization, and liquidation of legal entities. Highly qualified lawyers are the key to the successful transfer of legal functions to an outsourcing company. A third-party specialist does not work as expensively as an in-house lawyer, since he does not have such a large workload.
Logistic. This type of service is otherwise called transport. A third-party company provides logistics services to those who do not need transportation as often. The competence of such a company includes transportation and warehousing. Thanks to this, many companies are freed from the need to maintain their own logistics service.
Industrial. It is needed by enterprises working with high technologies. The production process is transferred to third parties in order to be able to concentrate on the development and promotion of innovative products and services.
An outsourcing agreement has its pros and cons.
The advantages include saving time on recruiting personnel to perform the necessary functions to carry out current financial and economic activities, and the bulk of the time can be spent on developing the business and extracting maximum profits. By concluding an outsourcing agreement, the Customer organization reduces the burden of the tax burden and saves on taxes because it pays for the service performed, and not for the work of the staff themselves. An outsourcing agreement helps to quickly and efficiently resolve issues that are not key for the Customer. There is no need to additionally encourage staff with bonuses, promotions, social packages and motivate them for fruitful work.
The disadvantages include the fact that the work under the outsourcing agreement will be performed poorly and this will only become apparent after some time has passed, when the error will lead to unpleasant consequences for the life of the organization. We can only hope for the qualifications of the staff. There may be a leak of information; here we can only hope for the reliability and integrity of the Contractor. Lack of motivation of the Contractor's staff, because the Customer does not manage the process of performing the work and cannot influence its quality; he receives only the finished result.
Despite the existing disadvantages of a personnel outsourcing agreement, many companies quite often and successfully use it in their production activities. These are IKEA, NIKE, NOKIA, Kodak
If you decide to introduce personnel outsourcing in your company, then you need to go through some steps:
- Conduct an analysis of the organization’s economic activities and determine whether you need to attract additional personnel, which will lead to an increase in your profits.
- Conduct a summary analysis of the costs of a personnel outsourcing agreement and an analysis of the costs of your own staff
- After weighing all the pros and cons, we choose the best option. If all the advantages are in favor of personnel outsourcing, we decide to conclude it.
- Choosing an outsourcing company
- We sign a personnel outsourcing agreement
- We get the result of the finished work
Each stage of concluding a personnel outsourcing agreement requires careful analysis, calculation, and careful study. The future success of the company will largely depend on how you approach the conclusion of the contract. If you choose an unreliable Contractor, you may lose success in a competitive market and vice versa. Good luck!
Agency labor: what is it and why is it prohibited?
In 2020, Article 56.1 appeared in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which provides a clear definition of the concept of “agency labor,” or labor at the direction of a nominal employer, but under the direction and in the interests of another company. Such work in Russia.
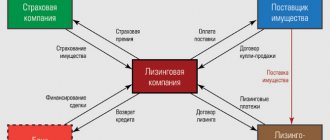
The essence of agency labor is as follows: one company or entrepreneur (contractor) transfers a certain number of workers to another organization or entrepreneur (customer). As a result, employees work for the customer, and the contractor is the employer. The contractor, in turn, enters into employment contracts with them, pays them wages and benefits, and maintains personnel records. Thus, employees work in an organization with which they are not connected either by labor or civil law relations (see the diagram below).
The state of affairs in outstaffing that existed before 2020 was unfavorable for the employee. An employee was hired to work for one company, and he worked for another. The employer did not bear any responsibility for the employee. Most often this concerned work in hazardous industries, where no payment was provided for hazardous work. Organizations with harmful and dangerous working conditions thus saved on insurance premiums for injuries. These conditions served as the reason for the adoption of a new article 56.1 in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is possible to lease employees from another company, but now outstaffing has changed and is regulated by a new one.