The reasons for the bankruptcy of an organization in most cases are the financial crisis in the country and the subsequent unprofitability of the company, depriving the owners of the opportunity to pay off debts and loans.
Bankruptcy is one of the legal measures that allows you to get out of an unprofitable business.
The concept and essence of enterprise bankruptcy
The official definition of the concept of bankruptcy of an enterprise is given by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”.
According to the law, bankruptcy of an enterprise is a state of inability to fully satisfy the claims of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) fulfill obligations to make mandatory payments.
The essence of enterprise bankruptcy is as follows.
If an organization is unable to pay off its debts on its own, it either transfers the property it owns to creditors to sell it and cover the debt, or agrees to introduce a set of special measures in its respect, the purpose of which is to restore solvency.
Not every organization facing financial difficulties can go through bankruptcy status.
It is important to comply with the key criterion - the amount of debt must exceed 100 thousand rubles, and payments for obligations should have been made three months ago. If these conditions are met, the enterprise will be declared bankrupt by the arbitration court.
The debtor company does not need to wait for creditors and the tax service to go to court - it can independently demand bankruptcy proceedings.
The essence, types and causes of bankruptcy of companies
Bankruptcy or insolvency of a company or enterprise has many definitions. Thus, according to general business practice, bankruptcy is considered the failure to fulfill financial and other obligations of a company to its counterparties and partners.
In a legal sense, insolvency (bankruptcy) is the inability of a debtor recognized by an arbitration court to fully satisfy the demands of creditors for monetary obligations and (or) to fulfill the obligation to make mandatory payments (Federal Law No. 127 of 2002). That is, the priority here is the cause-and-effect relationship between insolvency and bankruptcy.
Bankruptcy probability assessment
As a rule, the prerequisites for bankruptcy arise long before the official introduction of this procedure. To determine the main signals of the possible onset of trouble in an organization, it makes sense to turn to the business life cycle model.
This model is based on the idea that an organization (company, firm, business) develops and ceases to exist along a path that consists of several successive stages or cycles. The application of this concept in company management makes it possible to predict problems characteristic of the organization at one or another stage.
Table 1. Company life cycle and associated reasons for possible bankruptcy:
| Stages | Character traits | Possible reasons for bankruptcy |
| Birth | The stage of creation and the beginning of the organization's activities.
|
|
| Youth | The stage of rapid growth, the period of the rebirth of the organization.
|
|
| Maturity | The stage of obtaining maximum financial return is the optimal point of the life cycle curve.
|
|
| Aging | The stage of slowing down growth rates is the aging of the organization.
|
|
In a more general understanding and from the point of view of the formal definition contained in legislative acts (in particular in Federal Law No. 127 “On Insolvency, Bankruptcy”), there are various causes and types of bankruptcy:
- real bankruptcy, which is characterized by the complete inability of an enterprise to restore its financial stability and solvency in the coming period due to real losses of capital used and business assets - financial causes of bankruptcy of enterprises;
- technical bankruptcy, in which insolvency is caused by a significant delay in receivables. Sometimes such bankruptcy is called a technical default, when, for example, a company cannot ensure payment of financial obligations, especially those related to the circulation of securities - bills, bills of lading, dividends on shares or bonds. In addition, so-called “cash gaps” also lead to technical bankruptcy or default. These are cases where a company generally has the ability to pay current obligations, but because there is a time lag between the receipt of income and the payment of debts, it faces the risk of defaulting on its obligations.
Bankruptcy legislation
- criminal bankruptcy, which is an instrument of dishonest acquisition of property. This type of bankruptcy includes willful bankruptcy, sham bankruptcy, and bankruptcy misconduct.
In addition to legal definitions of the causes of bankruptcy, there is also their economic and functional classification.
These reasons include, first of all:
- business bankruptcy, which is associated with ineffective enterprise management, use of resources, and marketing strategy;
- the root cause of bankruptcy of enterprises is the bankruptcy of the owner, which is caused by the owner’s lack of investment resources that are necessary for expanded or simple reproduction in the presence of normal labor resources, fixed assets, marketing policy and demand for manufactured products;
- bankruptcy of the production model, when, under the influence of the first two factors or due to outdated equipment, due to high competition, the enterprise produces uncompetitive products, and without partial or complete repurposing of production it is impossible to correct the situation;
- bankruptcy caused by “unfair management”. This type includes management actions associated with evasion of fulfillment of their obligations, or associated with criminal actions (inaction) of top management.
All of the above general causes of bankruptcy rarely exist separately in practice. When a real business goes bankrupt, as a rule, there are several reasons from the above list of factors. In each specific case, the share of one or another cause of bankruptcy is determined by the conditions in which the company finds itself and how its management or owners react to them.
Reasons for bankruptcy of an enterprise
The causes of bankruptcy of an enterprise are divided into external and internal.
[1]. External reasons
In the Russian Federation, external reasons have taken a dominant position. Political and economic instability, as well as the instability of financial mechanisms during inflation, became significant impetus for the aggravation of crisis situations in Russian enterprises.
External causes of bankruptcy include:
- a sharp increase in the cost of production resources;
- increased international competition;
- various demographic data - population size and level of financial well-being, demand for products and services.
Some of the reasons can cause unpredictable bankruptcy, and some gradually bring the enterprise to this state.
[2]. Internal reasons
Internal reasons, in turn, are divided into objective and subjective.
Let's start with the objective ones:
- lack of working capital as a result of ineffective production and commercial activities or ill-conceived investment policies;
- increase in production costs due to a decline in production capacity;
- release of work in progress in quantities exceeding the norm;
- delays in payment from customers;
- low efficiency of the marketing component;
- obtaining loans on unfavorable terms, which increases costs and reduces the ability to self-finance;
- ill-conceived expansion of production.
Subjective ones include:
- failure to anticipate signs of bankruptcy;
- a sharp drop in sales;
- decline in production;
- reduction in the quality and cost of manufactured products;
- disproportionately high costs;
- low level of product profitability;
- long production cycle;
- high level of debt together with unfulfilled payments.
Causes and types of insolvency of organizations
First, let's note the types of bankruptcy:
- Failure where the organization is not at fault. In this situation, the collapse of the enterprise occurs due to reasons that do not depend on the actions of the company. These are natural disasters, political and economic instability, the ruin of a connecting organization that had obligations to pay a given company, and various other external reasons.
- Fictitious insolvency. Occasionally, companies go to the length of falsifying their own insolvency. They do this while sticking to the goal of not paying off their debts. Enterprises hide their property, which is criminally punishable.
- Insolvency due to negligence. This type of company bankruptcy occurs more often than others. This type of bankruptcy occurs as a result of the ineffective activities of the company. A timely analysis of the company’s condition and timely stabilization measures can determine the prerequisites and prevent bankruptcy due to negligence.
Signs of enterprise bankruptcy
The question arises: what are the signs and procedure for establishing bankruptcy of an enterprise?
Diagnosis of bankruptcy of an enterprise is carried out taking into account obligations in terms of the amount of funds.
The initial sign of approaching bankruptcy can be considered a delay in the provision of financial statements by an enterprise, which is confirmed by frequent changes in balance sheet indicators.
In some cases, a legal entity may attempt to force its own insolvency, which is referred to as willful or willful bankruptcy. It is caused by deliberate actions or inaction of management.
If, in fact, the organization is able to repay the debt on all obligations to creditors at the time of applying to the arbitration court, but declares the opposite, such a circumstance is a direct sign of premeditation of bankruptcy.
In order to accurately identify signs of this type of company insolvency, it is necessary to carefully study all of its production activities.
Signs of deliberate bankruptcy of an enterprise are also determined by the security indicator for current assets.
If, as a result of calculation, this indicator exceeds or equals one, the company has all the signs of real bankruptcy. If the indicator does not reach one, there are no signs.
Knowing all the signs and procedure for establishing bankruptcy of an enterprise, it is possible to determine its intentionality and bring management to administrative or criminal liability.
Types of enterprise bankruptcy
The legislation provides for the following types of enterprise bankruptcy:
[1]. Real bankruptcy . Real bankruptcy is the absence of an enterprise's ability to restore its solvent status.
This type of insolvency is declared by the arbitration court. The main reason may be ineffective management of the company, leading to capital losses.
[2]. Temporary (or conditional) bankruptcy . The reason is that the value of the asset is too high.
High-quality and qualified enterprise management can contribute to the restoration of solvency.
[3]. Intentional (intentional) bankruptcy . Achieved by deliberately bringing the enterprise to a state of insolvency through the theft of its funds.
Intentional bankruptcy is a punishable offence.
[4]. Fictitious bankruptcy . Bankruptcy, the application for which was initially fabricated. The goal may be to obtain a deferment from debt repayment.
If the bankruptcy application is fictitious, the management will be held accountable.
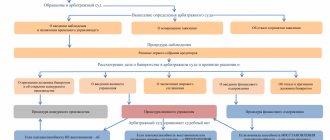
Enterprise bankruptcy procedure
The bankruptcy procedure for an enterprise begins with the execution of an application, which expresses the requirements for issuing bankrupt status to the debtor.
The initiator of filing an application can be either the debtor himself or the creditors to whom he has obligations.
The arbitration court is analyzing the validity of this request. To achieve this, a set of measures is carried out to determine possible fictitious or deliberate insolvency.
Let's look at how the bankruptcy of an enterprise is diagnosed using the example of a standard organization.
Bankruptcy itself consists of several successive stages:
[1]. Observation . At this stage, the real level of solvency of the company applying for bankruptcy status is determined.
The analysis is carried out by government agencies and ensures the complete safety of property belonging to the future bankrupt. This stage of bankruptcy lasts about three to four months;
[2]. Financial recovery . This procedure is aimed at saving the organization from subsequent liquidation.
To achieve this, a set of measures is being taken to restore solvency and pay off debts.
The arbitration court approves a special repayment schedule for debts subject to the restructuring procedure.
Management is prohibited by its actions from increasing the enterprise's debt. Financial recovery may take about 2 years;
[3]. External control. If credit institutions have appropriate requirements, the court may appoint external management of the debtor company.
The term of performance of duties in the position of external manager cannot exceed 18 months.
When implementing external management, the organization gets rid of fines and penalties for obligations.
[4]. Competition proceedings . The last, but no less important stage.
The goal of this stage is to sell property at auction in order to pay off all debts. A bankruptcy trustee is appointed.
The tender period again cannot exceed 18 months.
Managing the bankruptcy of an enterprise is a rather labor-intensive and time-consuming process. For this reason, the law provides for a simplified bankruptcy procedure.
Beginning of bankruptcy proceedings
After finding out the cause of bankruptcy and making the appropriate decision, it is advisable to proceed with the procedure itself. It begins with filing an application on the topic of recognizing the debtor enterprise as economically insolvent. It is important to note that it can be filed both by the company itself, which has decided to declare itself as such voluntarily, and by the creditor. Next, the arbitration court considers the validity of the application. It is important to know that the insolvency procedure involves a number of stages. Let's look at the first two:
- Observation takes place immediately after the cause of bankruptcy of a bank or organization is established. This stage is necessary to ensure the safety of the debtor’s property complex, carry out an analysis of its financial condition, create a register of creditor claims and organize the first meeting of creditors. It must be borne in mind that the observation period cannot be more than 7 months from the date of acceptance of the application from the company or creditor.
- Financial recovery should be viewed as a procedure designed to save the company from liquidation. First of all, it is aimed at covering debts and restoring solvency. To achieve this, debts are restructured and a repayment schedule is drawn up, which must be approved by the arbitration court. At this stage, the manager does not have the right to make decisions that could lead to an increase in the company's debt. He undertakes to coordinate his own actions and ideas with the meeting of creditors. It is worth considering that this stage can drag on for up to two years.
Simplified bankruptcy procedure
Simplification of the bankruptcy procedure allows this process to be carried out in a reduced time frame while minimizing any loss of funds.
The initial stage of the simplified procedure is the liquidation of the company as a legal entity.
The publication of this fact occurs after all changes have been made to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
After 2 months, the procedure for drawing up the so-called liquidation balance sheet is carried out, after drawing up which the liquidator, in accordance with the law, has the obligation to notify the credit institution that all the factors of bankruptcy of the enterprise have emerged, as well as to submit a statement of claim to the arbitration court in order to declare the company bankrupt.
The court will analyze the suitability of this application. The analysis will be based on relevant documents, and if the evidence is convincing, the court will make a decision to declare the organization bankrupt.
After recognition, a bankruptcy procedure will be carried out, lasting about six months.
The remaining stages of bankruptcy of an enterprise are simply skipped, thanks to which the entire procedure is carried out in a short time.
Simplified insolvency procedure
From the above we can conclude that the bankruptcy procedure of a company is a very complex and lengthy process. However, currently there is a simplified option that allows you to implement all the necessary items in a short time, as well as with minimal financial losses. The simplified procedure for economic insolvency begins immediately after the cause of bankruptcy of the bank, organization is identified and the appropriate decision is made by the creditor or the structure itself.
To begin with, the legal entity is liquidated. After making certain entries in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, an official message regarding the liquidation of the enterprise is published in the media. Two months after publication, it is advisable to draw up an interim liquidation balance sheet of the structure, after which the liquidator of the company, due to the direct indication of Part 2 of Article 224-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy),” undertakes to notify creditors that there are signs of economic insolvency, and also to file a arbitration judicial body statement of claim to declare a company bankrupt.
Forecasting bankruptcy of an enterprise
Assessing the likelihood of bankruptcy is an integral part of the borrower's credit analysis activities. There are generally accepted methods for predicting the bankruptcy of an enterprise:
- qualitative - based on the analysis of available data on already bankrupt companies and compares them with data from a company about which there are assumptions about impending bankruptcy;
- quantitative – assessment of the organization’s financial data and operating with a list of ratios.
Here are the most popular models for predicting enterprise bankruptcy using the qualitative method:
- Altman's two-factor model is extremely simple and does not require a huge amount of information. It was developed based on an analysis of 19 American companies. It is based on taking into account the possibility of termination of the company's financing;
- Altman's five-factor model – used for publicly traded companies. 95-97% accurate.
- Taffler's four-factor model is another model for PAO. The coefficients of this model give a clear picture of the possibility of insolvency in the future and financial condition in the present;
- Springate's four-factor model is based on Altman's model. Of the 19 indicators, 4 are taken and assigned their own “weight” in the final forecast;
- The Chesser model of insolvency was derived from a study of 37 successful and 37 unsuccessful cases of company financing. In three out of four cases, it accurately determines the probability of paying off debt obligations;
- The Beaver indicator system does not use integral indicators and does not take into account the weight of coefficients, but gives no less accurate forecasts.
Forecasting the possible bankruptcy of a company is a standard practice used by creditors to protect their investments.
Bankruptcy is a consequence of the emergence and increase of insolvency
In 2012, a Law on Bankruptcy appeared, based on the provisions of which it can be concluded that one of the signs of economic insolvency is the inability to make payments, which already has or is just becoming sustainable. It turns out that in order to determine the concept, types and causes of bankruptcy, it is necessary to find out how the financial situation of the debtor has evolved and when exactly insolvency occurred, recognized by the court dealing with economic affairs as a legal fact with consequences established by the Law.
The assessment of the ability to carry out financial transactions is carried out in accordance with Council of Ministers Resolution No. 1672, dated 2011. The analysis of the company's condition is carried out on the basis of the Instruction, the purpose of which is to standardize the procedure for calculating solvency ratios and study the financial situation of business entities, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Economy No. 140/206 (2011).
When analyzing and assessing solvency to identify the causes of bankruptcy of enterprises, you may encounter difficulties associated with the lack of financial statements in full or doubts about their reliability. It is worth remembering that one of the fundamental principles of financial and economic analysis is to operate exclusively with verified facts. Therefore, there may be a need to determine the degree of compliance of the data from the debtor’s accounting records with the information of its accounting, confirming the actual presence of these assets and liabilities. The correctness of their reflection in the relevant documentation is of great importance.
The research is carried out using methods of formal, logical, arithmetic, normative and mutual verification, which in the vast majority of cases is possible only through economic examination.
A decrease in the ability to make payments and the financial stability of a business entity occurs due to a decrease in the liquidity of assets, a reduction in sources of financing (and therefore an increase in the share of borrowed funds) and a disproportionate change in the value of assets/liabilities.
The latter, when carrying out business activities, is usually due to expenses, which is understood as a decrease in the volume of assets or an increase in the number of liabilities, leading to a decrease in equity capital. Moreover, this situation should not be associated with the transfer of financial resources to the owner of the property or their distribution among the participants.
Based on this, the reasons for the bankruptcy of organizations are identified, the activities of the debtor are examined - all significant points relating to the recognition of a person as economically insolvent are determined.
Preventing enterprise bankruptcy
The Bankruptcy Law clearly establishes that the management of the debtor enterprise has the obligation to do everything in its power to ensure the prevention and prevention of the need for such procedures as bankruptcy and liquidation of the enterprise.
In practice, the following ways to prevent bankruptcy of an enterprise are used:
- Providing all necessary financial assistance to the debtor by creditors and other persons can significantly improve the financial condition of the enterprise and the risk of bankruptcy will decrease;
- Prevention of bankruptcy in enterprise management, namely a qualitative change in the composition and structure of management bodies;
- Collection of existing receivables significantly reduces the risk of bankruptcy of the enterprise;
- Attracting any type of investment, including foreign;
- Assistance in achieving mutually beneficial relationships with existing creditors for debt restructuring;
- Carrying out reorganization as a preventive measure against bankruptcy of an enterprise, and so on.
Preventing enterprise bankruptcy is the most important activity of an organization.
The use of all measures together makes it possible to overcome the existing difficulties.
Consequences of enterprise bankruptcy
The consequences of bankruptcy of an enterprise are divided into (1) negative and (2) positive.
The negative ones include financial losses for creditors, the need to fire hired workers, money and time costs, and the weakening of the corresponding link in the national economy.
Despite the many negative consequences of bankruptcy, there are also positive aspects to this process:
- The emergence of the opportunity to organize a new, more reliable, thoughtful and effective business;
- Payment of all tax obligations;
- Removal of unqualified management unable to effectively manage;
- Maximum possible satisfaction of creditors' requirements.
Dismissal of personnel in case of bankruptcy of an enterprise
Let us consider in more detail the dismissal of all existing employees in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise.
Mass dismissal of personnel must occur without violating current legislation.
To this end, the HR department must quickly prepare all documents and carry out a number of actions.
Dismissal algorithm:
- Notifying the employment service about bankruptcy and dismissing the entire staff due to this circumstance. The notice is provided in writing two months in advance for partial dismissal, and three months in advance for complete dismissal;
- Notification of each employee. It is considered completed if the employee signs the notification;
- Notifying the state of the possibility of early termination of employment. An employee signature is also required. Those who agree receive compensation;
- Creating an order to terminate relations with personnel. Everyone reads the text of the order and signs it;
- Preparation of personnel documentation;
- Issuance of work books.
The causes and consequences of enterprise bankruptcy affect both creditors and debtors.