In the age of active development of electronic technologies, it is difficult to surprise someone with new gadgets and devices. Society is rapidly moving forward, gradually getting rid of a layer of bureaucratic problems and obstacles, which information technologies help to combat.
Dear readers!
Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call. It's fast and free! Today, the functionality of personal electronic signatures is expanding, allowing their use on a wider range of issues, the number of areas of their application is growing, which is an important step towards the formation of an information society.
What is meant by an electronic signature (what is an electronic signature - electronic digital signature)
An electronic digital signature refers to computer data that in one way or another certifies ownership (authorship), and in some cases, the integrity of the file to which it is attached in the prescribed manner. For example, if the corresponding file is an accounting document, then an electronic signature can certify the fact:
- signing of this document by an accountant or other authorized person;
- no changes to the document after its signing.
Both possibilities, in many cases, make signing documents using an electronic digital signature more preferable than traditional certification with pen and stamp. The main thing is that the digital signature actually performs the specified functions.
What is an electronic signature called according to law?
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 2 of the Law “On Electronic Signatures” dated 04/06/2011 No. 63-FZ (this legal regulation regulates how the electronic signature is used and where one can obtain an electronic digital signature), the type of signature in question is called an “electronic signature”. But unofficially the terms “electronic signature” and “digital signature” have also become widespread. To a certain extent, this is due to the fact that in the provisions of the previous source of law regulating the use of the corresponding details of an electronic document, the term “electronic digital signature” was used. We are talking about the Law “On Electronic Digital Signatures” dated January 10, 2002 No. 1-FZ, which became invalid after Law No. 63-FZ came into force.
In order to ensure formal requirements for documents when interacting with government agencies, it is therefore desirable to use the concept of “electronic signature”. Within the framework of communications within the company, with individuals, you can use any convenient term.
How does EP work?
In appearance, what is commonly called an electronic signature looks like an ordinary USB drive. In reality, this is not the electronic signature itself, but only a tool for its formation. A sort of modern analogue of a regular pen. The drive contains a set of files:
- Encryption program.
- Unique private encryption key.
- A certificate confirming the identity of the owner of the electronic signature, with a public key, which is used to decrypt the signature.
The device is connected to the computer, then a simple workplace setup is performed. After this, the signature is ready to use. Typically, documents are signed with an electronic signature in the application through which they are sent. For example, in an electronic document management service, a personal account on the website of a government agency, or an accounting program through which reports are sent.
The process of creating an electronic signature seems incomprehensible and complicated from the outside. In fact, it can be described in a few lines. At the moment of “signing” the electronic signature document, the following happens:
- the document file is converted into a long set of characters - a hash;
- the hash is encrypted using a private key - this is an electronic signature;
- The electronic signature is attached to the document, and along with it - a certificate, which contains information about the owner of the signature and the key for decrypting the hash.
On the receiving side, the following happens:
- the owner of the certificate is verified - this way you can be sure that the signature belongs to an authorized person;
- the hash of the electronic document that was received is calculated;
- using the public key, the electronic signature is decrypted - now we know what the hash of the sent file was;
- hashes are compared - they must be the same.
Why is such a check needed? It will show that the document is complete and authentic. If the attacker decides to correct it after signing, the file hash will change. When checked, it will not match the one encrypted in the electronic signature. This will mean that the file is not genuine. Therefore, documents signed with electronic signatures are considered protected from unauthorized access. A reliable encryption algorithm allows you to transmit information over the Internet without fear. After all, even if the document is intercepted, it will not be possible to make changes to it unnoticed.
| ☑ The system has only one vulnerable spot - the storage medium (flash drive). Once in possession of it, the attacker will be able to create genuine electronic signatures. To protect against this, the user can change the standard factory password of the storage device to a unique one. |
How is an electronic signature (“imprint” of the digital signature and its encryption) regulated according to GOST?
The use of electronic signatures is strictly regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation. Law No. 63-FZ, which explains the essence of digital signatures and also reveals how to obtain an electronic digital signature, can be supplemented by various GOSTs.
For example, electronic digital signature verification is carried out on the basis of GOST R 34.10-2012. The most important requirement for an electronic signature according to the relevant GOST is the stability of its “imprint,” that is, the sequence of computer data that is attached to the file. In fact, resistance to attempts by one person to unauthorizedly sign for another. This standard assumes the use of digital signatures with an encryption depth of up to 512 bits. Deciphering such an electronic signature is practically impossible using commercially available computer equipment.
Reliable encryption of the digital signature is the main condition for the corresponding signature to perform both of the above functions: verifying the fact that a document was signed by a specific person, as well as the absence of changes in the document after its signing.
The most decryption-resistant type of digital signature is a qualified signature. Let's study its features, as well as where you can make an electronic signature of the appropriate type.
Qualified electronic digital signature (CED): what is it?
Law No. 63-FZ defines 3 types of electronic signatures:
- simple,
- reinforced,
- reinforced qualified.
See also “What is a non-qualified electronic signature”.
A simple digital signature performs only one of the above functions - it certifies the fact that a document has been signed by a specific person. However, its resistance to decryption is, as a rule, not too high. An example of a simple digital signature is the password to a person’s email, from which he sends his messages, “in a simple way” certifying the fact that they belong to him. Email passwords rarely exceed a dozen characters, which is incomparable with the 512-bit encryption depth according to GOST R 34.10-2012. In addition, someone else may accidentally or intentionally recognize them.
In turn, the enhanced digital signature is encrypted much deeper than the e-mail password - in principle, 512-bit encryption characterizes the enhanced signature. Finding out it, like a password for an e-mail, is extremely difficult, since it is a sequence of computer data: firstly, well encrypted, and secondly, not intended to be presented in a text form understandable to humans.
The qualification of an electronic signature is a guarantee of its maximum resistance to decryption from the point of view of a particular state standard. In the case of Russian digital signatures, their qualification is compliance with the requirements of GOST R 34.10-2012. Only those electronic signatures that meet the requirements of this standard can be recognized as qualified.
ConsultantPlus experts explained how a legal entity can obtain an enhanced qualified electronic signature. Get trial access to the K+ system and upgrade to the Ready Solution for free.
It is not at all necessary that a regular enhanced signature will be less protected from hacking than a qualified one. It is quite possible that the encryption standards that are implemented in an unqualified digital signature, developed, for example, by a private research center, will be even more stringent than according to GOST R 34.10-2012.
The use of enhanced qualified digital signature may be prescribed by separate regulations. For example, to send reports to government agencies, Russian companies must use the EPC. In turn, those types of CEPs that are adapted for working with specific documents, for example, tax reporting forms, are not suitable for organizing the exchange of documents between enterprises.
Anyone can use a simple electronic signature - for example, through their e-mail or mobile number. In order to use the enhanced one, you will need to use one of its mandatory components - a certificate. Let's take a closer look at its features.
What types of digital signature are there?
There are three main types of electronic signature:
- Simple electronic signature (SES).
A simple digital signature is a password from an e-mail or an SMS code for logging into mail (or another messenger). Legally significant actions using a simple digital signature are carried out in an extremely limited list of cases: it is believed that it is not reliable enough (which is not surprising - after all, a password and even an SMS code can be intercepted).
- Enhanced unqualified electronic signature (NES), which requires a certificate.
A strengthened unqualified digital signature is one that involves placing the private key on a secure medium - the same eToken. Even if it can be intercepted, it can only be literally stolen. If the owner of the digital signature keeps the media with him, he can be sure that no one will sign for it.
“Strengthening” the digital signature is carried out through the use of certain technological procedures aimed at ensuring the security of the private key on the medium. These procedures, in the case of an unqualified signature, are carried out in accordance with different standards - Russian or foreign. In turn, these standards can be enshrined both in legal acts - federal laws, GOST, and in industry or corporate regulations.
- Enhanced Qualified Electronic Signature (CES), which also requires a certificate.
The concept of an electronic digital signature: electronic signature file, key and certificate
Verification of an enhanced electronic signature file ("imprint") is possible only with the use of a special certificate - a document that verifies that the digital signature verification key belongs to a specific person. That is, the fact of signing an electronic document by a specific person.
EDS certificates are usually issued for a specific period - usually 12 months. Afterwards you need to receive them again or confirm your right to use the certificate. In some cases, the user’s access to the relevant document may be suspended - for example, if there is a suspicion of violation of the rules for working with digital signatures on his part.
If suddenly a person ceases to own an EDS certificate or the validity period of the certificate expires, then the electronic signatures of this person are invalid until the corresponding document becomes active again.
In practice, the corresponding certificates are most often represented by documents that are part of software packages for organizing document flow. Let's consider how to obtain an electronic signature for legal entities.
Where to get an electronic signature CEP
Where can I get a qualified digital signature? In order to obtain this signature, you must contact a certification center that is accredited by the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications. The list of relevant CAs is available on the department’s website. Using it, you can find out where to obtain an electronic signature for a legal entity closest.
To issue an electronic signature, it is necessary to submit to a certification center - regular or accredited - a set of documents, the composition of which is determined by the legal status of the applicant. Let's consider what the corresponding set should be if the digital signature is issued by an organization.
Advantages of using and scope of application of digital signature
The use of digital signature for a legal entity opens up great opportunities for optimizing the workflow:
- increasing the efficiency of document flow within the company;
- strengthening protection and increasing confidentiality of information exchange;
- no need for additional data verification;
- significant reduction in time for sending documents;
- improving the procedure for sending reports to specialized bodies;
- participation in document flow at the international level.
A modern digital signature is used by legal entities in the following areas of activity:
- registration of a new organization via the Internet without the participation of a notary in confirming papers;
- electronic trading - as organizers or suppliers;
- participation in government procurement on a website designated for this purpose (in accordance with Federal Law 223);
- transmission of reports in electronic format - accounting and financial documentation, tax returns, data to the relevant funds;
- posting information on the websites of Roskomnadzor and Rosimushchestvo;
- electronic declaration for customs goods.
How to obtain an electronic digital signature for legal entities
First of all, it is worth noting that Law No. 63-FZ does not fundamentally prohibit issuing an electronic signature directly to a legal entity as an independent subject of legal relations. In this sense, an electronic digital signature for a legal entity can be analogous to an organization’s seal. But in practice, the corresponding mechanism, when an electronic signature is issued only to a legal entity, has not yet been developed in Russia. One way or another, the actual user of the electronic signature becomes a person, and in the case of a legal entity, he has certain powers that are associated with the subsequent use of the issued digital signature. Most often, this person is the head of the organization.
The strengthened signature is produced by the certification authority and transmitted to the director of the company on a medium through which the established signature encryption mechanism can be implemented - for example, this could be an eToken key. Simultaneously with the digital signature carrier, the manager receives a set of software necessary for organizing data exchange with those business entities to which documents certified by an electronic signature are supposed to be sent.
How can a person who is not the head of the company obtain an electronic digital signature for a legal entity? In principle, any of its representatives can register an electronic digital signature for an organization (Clause 3, Article 14 of Law No. 63-FZ). In this case, the internal administrative act of the company must determine the employee responsible for working with electronic signatures when the company enters into legal relations in the field of state and municipal services, as well as in other cases provided for by law. If such an administrative act is not adopted, then the director of the organization is appointed by default as the responsible person in this case. An employee (not a manager) who receives an electronic digital signature is issued a corresponding permit from the manager (for example, an order granting the right to sign certain documents). Such a document usually needs to be attached to the package of documents for obtaining an electronic signature for an employee.
Where to get an electronic signature key The key, like the certificate, is included in the software product that is supplied by the certification center to the customer. The use of digital signatures without the specified components is practically impossible, so they are one way or another at the user’s disposal.
What is an electronic signature key certificate
About the certificate: what is it?
An EDS key certificate
is a document that contains information about the owner. The public key encrypts data about the owner’s status, details and powers. The certificate confirms that the key belongs to a specific person responsible for its use. The document has an electronic digital or paper version. The electronic key certificate is issued at the certification center. All information about certificates is stored in a unified federal register. The CA guarantees that the provided data is true, confirms the identity of the owner and protects the digital key from hacking.
Electronic digital signature (EDS)
- an analogue of the handwritten version of the owner’s signature. Used in document management and when working with electronic financial management systems. The electronic signature constitutes an electronic certificate issued by a certification center. It encrypts data about the owner entered into the unified registry database. EDS is applicable when working with courts, stock exchanges, when submitting documents to tax services, etc.
The digital analogue of a real signature is divided into qualified and unqualified types. Depending on the profile, the electronic certificate has a level of access to work with certain resources. The qualified option has the highest degree of protection, due to which it is used in real estate transactions, finance and for signing documents. Signing by a qualified type of contracts or agreements is accepted in courts, at stock exchanges, and at auctions. A qualified certificate has a broader scope because it provides a greater degree of protection.
Information about certificates is stored in the databases of the Unified Register of ESIA. Certification centers that have passed certification have the right to enter data. All CAs are divided into accredited and non-accredited.
Why do you need a certificate?
A handwritten signature has legal force, as it is confirmed by a person present. In electronic document management, a qualified certificate serves as a guarantee of a transaction, since it contains all the information about the participant in the process and confirms that the digital signature belongs to the owner.
The key prevents forgery or fraud in signing documents. It is encoded using cryptography and is divided into open and closed. The coding is so complex that it completely eliminates hacking. Only the owner of a token with a signature can enter data into the document, indicating his consent to the transaction or transfer of information.
Public and private key
The public key is available to persons participating in the document flow or transaction. The private key is known exclusively to the owner and cannot be determined using the public key. The certificate issued for them legalizes both keys and ensures their interaction with the system. Through it, the start and end dates for the operation of the keys are approved.
The document is signed with a public key. At the time of checking the information, a signal goes from the public key to the private key. The signature is checked for compliance with those entered into the database about the owner. If the information matches, the owner's identity is confirmed. In this case, the transaction or act of signing is considered legal.
Certification authorities: which CAs can issue enhanced certificates
Centers that have received certification from the Unified Federal Center have the right to issue an electronic signature. There are from 20 to 50 such establishments in each region. Certification gives them the right to collect and work with information about citizens, issue certificates and create signatures. Information received from citizens, legal entities and organizations is entered into the Unified Register, where it is used to identify the owner of the signature. In total, there are more than 400 certification centers in Russia.
What is an accredited certification center
An accredited certification center (CA) is an organization that has gained access to the Unified Register and has the right to collect and store key information. It has the right to create a qualified electronic certificate and distribute cryptography licenses. The organization has access to software that provides coding and management of the electronic signature structure.
The organization maintains servers from which digital signature users receive information and access to the legislative framework based on signatures. The CA serves the signature owner by updating the expiration date of the digital signature certificate and eliminating errors in the operation of the token.
At the CA you can renew, cancel or order a new signature. To sign documents electronically, you must have a qualified electronic certificate. This is exactly the service that CAs provide.
The certification center issues exclusively qualified certificates. Obtaining a certificate from a CA guarantees the authenticity and security of the electronic signature key. To work with codes, special software is used to protect the original data. A certificate from the center guarantees the prevention of forgery and hacking, for which a unique encryption system is used.
You can get acquainted with the list of certified certification centers on the websites of the Federal Tax Service and the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications. A special section by region lists operating organizations. Here you can also check data on closed and deprived of licenses organizations, find out to whom rights and powers were transferred after closure.
Composition: what does the ES certificate consist of?
An electronic signature has the form of an alphanumeric code or a graphic image. When working with certificates, specialized software is used to ensure information encryption. To obtain a signature, the future owner must provide reliable information about himself by submitting documents to the certification center.
Components of a signing certificate:
- standards to which the key complies;
- details of the certification center that issued the certificate;
- direction of use of digital signature;
- full information about restrictions and tolerances in the field of application;
- start and end dates of the certificate;
- information about the owner (SNILS, full name, registration, benefits, etc.);
- for individuals or legal entities - TIN;
- name of the organization (including irrelevant ones);
- address of the organization or legal entity;
- contact information of an organization or person (phone number, e-mail, zip code, etc.);
- addresses of certificate revocation list distribution points.
Before receiving, a detailed check of the specified data is carried out. Only after confirmation is an electronic certificate issued to the person. The media with the key is produced and transferred. To create and sign a legal document, the owner needs to install specialized software.
The official portals of manufacturers' programs contain instructions on how to use electronic signatures in their programs (Microsoft Office, Acrobat Reader and others). The signature script is applied through the software installed on the PC. Once the DS has been applied, the document cannot be changed by third parties.
Obtaining an electronic signature: how to order an electronic signature via the Internet
How to issue an electronic signature for legal entities via the Internet?
First of all, we note that interaction between certification centers and their clients can be carried out both in an offline format - when the digital signature customer comes to the CA office, and online. At the same time, the beginning of interaction between the CA and the client can begin online: many certification centers offer, in order to speed up the procedure for issuing electronic signatures, to provide basic information about customers via the Internet. Afterwards, they initiate preparations for the production of the digital signature and actually issue it, having verified the authenticity of the documents brought to the office by the customer at the appointed time. If necessary, CA specialists provide clarification on issues that arise. For example, they explain where to obtain an electronic signature for a legal entity to organize further work with digital signature and digital signature.
Thus, interaction between the CA and EDS customers does not occur entirely electronically - one way or another, the originals of title documents are needed. But modern certification centers know well how to make an electronic digital signature for a legal entity with a minimum of formalities, and online channels can be used for this.
What is digital signature
At first, digital signatures were used exclusively by legal entities, because its presence greatly simplified the work with documents. Today, an individual has the right to receive this signature. Possessing it, almost any person has the opportunity to use all the benefits of the information society for personal purposes.
Why do you need an electronic signature? It is used to identify and confirm the originality of documents received electronically. At the legislative level, the issue of their application is regulated by 44-FZ, which came into force on January 1, 2014.
Electronic document management: what electronic signature is used in the organization
It is worth noting that in order to organize document flow within an organization, as well as when exchanging documents between a company and other business entities, it is not necessary to use an enhanced qualified digital signature. This can be any signature, including a simple one, unless, of course, regulations or an agreement require the use of a different signature option (Clause 1, Article 4 of Law No. 63-FZ).
An example of using a simple digital signature for a legal entity is organizing the exchange of various documents using intracorporate mail. This type of communication, in principle, can be carried out during the interaction of the company with partner organizations - but subject to the conclusion of a separate agreement with them regulating the procedure for exchanging files and certifying them using a simple digital signature.
If partners want to increase the security of business correspondence, it makes sense to get a digital signature that is enhanced. We noted above that its unqualified version can provide the highest resistance to decryption of digital signatures, so it may be useful for company managers to consider the corresponding software and hardware solutions as a priority.
For clarifications from the Ministry of Finance, see the publication “The Ministry of Finance reminded which electronic signature should be used in the primary account.”
Where it is more expedient to order an electronic signature - in an accredited or regular CA - will depend on what specific documents are supposed to be certified by electronic signature. If the main recipients of the files being sent are government agencies, then it probably makes sense to contact accredited structures.
Qualified electronic signature, or CES
Qualified EP is quite similar to NEP. It is also created using cryptographic software. But only special organizations () that have been accredited by the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications can issue these types of signatures. The software used in the process of creating CEP must have an FSB certificate.
Where is it used?
The application of CEP is much wider. It is used when participating in various tenders as a supplier and customer; it can be used to carry out document flow within the company and with partners. It is also used to submit reports to various government agencies.
Legal force
CEP automatically gives legal documents to documents. force based on legislation. There is no need to enter into an additional agreement for this. This greatly simplifies the use of CEP in EDI.
Who is responsible for issuing electronic signatures at the enterprise?
How can an enterprise organize the supply of employees, if required, with their own electronic signatures?
First of all, we note that an employee of an enterprise whose competence is working with electronic signatures is obliged to ensure the confidentiality of the relevant software tools and not allow anyone to use the digital signature without his consent (Clause 1 of Article 10 of Law No. 63-FZ). This formulation obviously indicates that a person authorized to use an electronic signature has the ability to delegate the use of an electronic signature to other persons. It may also be noted that Law No. 63-FZ does not establish restrictions on the number of electronic signatures issued for one legal entity.
Thus, you can organize the supply of EDS to employees of an enterprise:
- by issuing local regulations, according to which an electronic digital signature issued, for example, in the name of the general director, will be transferred, in cases where this is necessary and permitted, to a replacement trustee;
- by issuing an electronic digital signature for a legal entity for each employee of the company who needs to use the appropriate signature.
It should be borne in mind that the law may provide for cases in which the implementation of the first option will be illegal. For example, if we are talking about transferring the right to use the digital signature of the chief accountant for the purpose of signing primary documents. The fact is that in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 7 and paragraph 2 of Art. 9 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, these operations must be carried out by the chief accountant himself. Within the meaning of the provisions of the law, the use of digital signature by a third party may be considered a forgery of the signature of the chief accountant.
In the first case, the digital signature will most likely be issued by the director himself or those persons to whom he delegates these powers. In the second case, the certification center will issue the digital signature, provided that the applicant can confirm his authority in terms of the subsequent use of the electronic signature.
The feasibility of obtaining an electronic signature
Before you start the hassle of filling out an application for an electronic signature, you should be aware of whether it is really necessary to obtain it. The advantages of owning an electronic signature are obvious. But what does the other side of the coin look like?
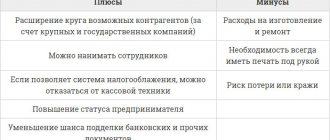
- Economic efficiency. Digital signatures in the arsenal of an individual or legal entity impose certain financial obligations on him. Money will be needed both to obtain a signature (one-time) and to pay for the annual certificate. In addition, you should take into account possible additional costs for the program itself for working with electronic signatures.
- Profit of digital signature for an ordinary citizen. The practice of using digital signatures by individuals suggests that this service is needed only by those who regularly apply to the Federal Tax Service, Rosreestr and MFC, while trying to reduce personal visits. Perhaps for an ordinary Russian, whose territorial representations of these bodies function without exhausting queues, obtaining an electronic digital signature does not make much sense.
- Digital signature for businessmen. At the initial stage of doing business, you can do without an electronic digital signature. But if there is even a small staff subordinate to the manager, the organization plans to take part in auctions, tenders, and submit reports electronically, then digital signature will make life much easier. The costs of an electronic signature for businessmen are somewhat more expensive, but they pay off due to significant savings in time and effort and the opportunity to participate in profitable corporate auctions.
How to take into account the costs of purchasing an electronic signature ?
How to issue and where to obtain an electronic signature for the chief accountant
What could be the procedure for obtaining an electronic signature by the chief accountant of an enterprise? In this case, it is better to use the first option - when a separate signature is issued for the employee. This is due precisely to the fact that many documents in the company must be signed by the chief accountant.
The chief accountant of the company, if a decision is made to vest him with the appropriate powers and issue a separate digital signature for him, will have to present to the certification center the same documents as the director - but only instead of the order presented by the director, he needs to show a local administrative document about vesting the accountant with the necessary powers to use digital signatures.
Possibility of checking digital signature
To verify the authenticity of any electronic signature on a received document, special utilities are provided. They can be installed on your computer, which is advisable for regular use, or used online. When registering an electronic digital signature at the Certification Center, inquire about the opportunity to receive such a program (most likely, you will be offered it as part of the provision of services).
To check the digital signature, it is copied from the document and placed into the program. Some verification programs have the ability to examine digital signatures not one at a time, but to process large amounts of documentation, which is very convenient and significantly saves time.
How to create an electronic signature for free
Obtaining an electronic digital signature for legal entities is almost always carried out on a paid basis. This is due at least to the fact that the digital signature key carrier, for example eToken, is a technological product that has a certain cost. In this case, the tariffing of CA services may depend on:
- on the purpose of the digital signature (for example, electronic signatures for reporting are usually cheaper than those intended for trading);
- on the number of certificates issued by the CA (as it increases, each certificate may cost less);
- on the manufacturability of the software and hardware infrastructure for working with digital signatures implemented at the enterprise.
With a long-term and trusting relationship between the CA and the customer, it is quite possible to obtain electronic digital signatures with discounts or on special conditions.
Types of electronic signature
ES, EDS, CEP
Before the adoption of Law No. 64-FZ, another legal act was in force - Law No. 1-FZ of January 10, 2002. It included the concept of an electronic digital signature (EDS). Subsequently, the word “digital” disappeared from the name of the signature, but the abbreviation EDS took root and is still widely used. Therefore, electronic signature and digital signature are similar concepts, although the second is outdated.
Types of digital signature for legal entities
- Simple . Most modern people are familiar with it. An example of a simple electronic signature is a login/password for authorization in email or other services. Or codes that are requested by payment systems when making payments via the Internet.
- Reinforced unskilled . This is a more secure electronic signature, since it is encrypted using a special program and a cryptographic key.
- Reinforced Qualified (CEP) . Differs from an unqualified signature due to stricter government regulation. Firstly, only an encryption program approved by the FSB is suitable for generating EPC. Secondly, you can obtain such a signature strictly from certification centers (CA) accredited by the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications.
| ☑ In the vast majority of cases, digital signature for a legal entity means a qualified signature. Therefore, we can say that electronic signature (EDS) and CEP are equivalent concepts. |
Results
The use of specific types of digital signature by an enterprise - simple, enhanced or enhanced qualified - depends on the addressability of the documents processed by the company. To use enhanced digital signatures you will need: a key, a certificate and special software supplied by certification centers.
You can learn more about the use of electronic signatures in the articles:
- “How to make a simple electronic signature?”;
- “When is a qualified electronic signature required?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.