Hello! In this article we will talk about the system of penalties for entrepreneurs and directors of organizations in case of improper registration of their employees.
Today you will learn:
- For what reasons is a fine imposed on the individual entrepreneur and director of the company if the employees are not officially registered;
- What is the responsibility of the legal entity in this case;
- What is the employer's responsibility in case of incorrect registration of migrants;
- What you need to consider when hiring foreign illegal immigrants;
- The amount of fines that are imposed on individual entrepreneurs and legal entities for inappropriate employment of employees.
Reasons for imposing fines on company management
Labor relations between employer and employee must be formalized in accordance with legal regulations.
To hire a person for a position, the employer is obliged to conclude an employment contract with him, according to which both parties to the employment relationship have certain responsibilities. Such an agreement is drawn up and signed in two copies, indicating the date of employment. If the contract is fixed-term, then it is necessary to indicate the end date of the employment relationship. One copy of the agreement is kept by the employer, the other is given to the employee.
The date of admission is very important information, which indicates that the person is officially registered and started working from a certain point.
The contract must include the following: last name, first name, patronymic of the person being accepted, his personal data (passport number and series, INN and SNILS numbers), residential address. The employee must provide documents confirming education and qualifications for the position held. The contract must indicate the type and nature of the work and the work week schedule. These are integral components of an employment contract that cannot be violated.
An employee is obliged to properly perform his job functions and comply with the daily routine at the enterprise. And the employer, in turn, guarantees constant wages that correspond to the staffing schedule, pays taxes, and provides the employee with all benefits and social guarantees.
A person can work without registration for only three days, after which an employment contract must be drawn up.
Reasons for imposing fines:
- Late conclusion of an employment contract with an employee or absence of one. This leads to the fact that the employee does not have official earnings, and therefore no personal income tax is paid to the state;
- If the contract is not concluded, the employee’s length of service is not counted and payments are not made to the Pension Fund, which will negatively affect the registration of an old-age pension;
- Medical institutions may refuse to provide free assistance to an employee of any organization due to the fact that contributions to the health insurance fund are not paid;
When a person is not officially registered at an enterprise, he loses his rights. He cannot achieve a number of payments, for example, vacation pay, sick leave payments, and final payment. And when addressing these issues to the courts, he will not be able to prove the occurrence of such moments.
The question arises of how to avoid a fine for an unregistered employee, as well as administrative and criminal liability. The main thing is to legitimize the relationship between the employer and the employee in a timely and correct manner.
Criminal liability of the employer-entrepreneur
Law enforcement officers initiate a case if a businessman causes major damage to the budget or causes serious harm to an employee. Bringing unscrupulous employers to criminal liability is carried out on the following grounds:
- Evasion of payment of insurance fees (Article 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). An act is recognized as a crime when the arrears reach 900 thousand rubles for 3 years in a row. The share of unpaid contributions must be at least 10% of the entrepreneur’s total obligations to state funds and the budget. In addition, major damage is considered to be 2,700,000 rubles. In this case, the period of the debt and its relationship with other deductions are not taken into account. The punishment for the crime is a criminal fine of 100–300 thousand rubles, forced labor for up to 1 year, arrest for 6 months or imprisonment in a correctional institution for a year. If the convicted person does not have the funds to pay the fine, his earnings (income) for a period of up to 2 years are withheld. Sanctions become tougher when the arrears reach a particularly large size. This is recognized as a debt of 4,500,000 for 3 years (20% of total liabilities) or 13,500,000 rubles for the entire period of violation.
- Delay of wages (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). If evasion from concluding an employment contract is accompanied by withholding money, the entrepreneur also faces criminal liability. Partial non-payment of labor for 3 months or more will result in a fine of up to 120 thousand rubles, disqualification for up to 1 year, forced labor for up to 2 years or imprisonment for 12 months for a businessman. If a businessman does not pay wages at all for more than 2 months in a row, the punishment becomes more severe. The fine increases to 500 thousand rubles, and the period of disqualification and detention in a correctional institution is up to 3 years.
- Neglect of labor protection rules (Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Unofficial employment is often accompanied by a violation of the procedures for training, testing knowledge, and conducting internships. Illegal workers are not fully provided with protective equipment. If, as a result of such violations, serious harm is caused to people’s health, the entrepreneur faces a fine of up to 400 thousand rubles, compulsory work for 180–240 hours, imprisonment for a year with or without disqualification, as well as correctional labor for 12 months. Much tougher sanctions are provided for crimes that lead to the death of an employee. The maximum penalty for such an act will be 5 years of imprisonment in a correctional institution.
Criminal legislation does not distinguish between Russians and foreign workers. Individual entrepreneur fines for unregistered employees are assessed according to uniform rules, and other types of punishments are applied by the court, taking into account the gravity of the act.
Responsibility for failure to register individual entrepreneurs
Typically, in practice, entrepreneurs do not enter into employment contracts with their employees. So, they are trying to save their money, thereby not paying taxes to government funds. This is a violation that entails a fine on the individual entrepreneur of up to five thousand rubles, and the entrepreneur’s activities are suspended for 90 days. Often such situations end in the closure of the individual entrepreneur’s activities; in the best cases, they will lead to losses.
If the audit reveals that the employee has not been registered for several years, and taxes have not been paid for this period, then a criminal case will be opened against the individual entrepreneur, and a demand may be made for payment of insurance premiums for the lost period in full.
The fine for such a violation for an individual entrepreneur is up to 300,000 rubles, and an arrest may also be imposed for up to two years.
A fine for an individual entrepreneur will significantly affect its financial results, so in order to protect yourself from huge losses in the future, you should draw up employment contracts in accordance with all the rules with your employees.
Fine for an unregistered individual entrepreneur 2020 for
During their work, any entrepreneurs, including individual entrepreneurs, can commit offenses in various areas of legislation: tax, labor and others. These offenses can be committed either intentionally, on purpose, or through ignorance or mistake. In all cases, this is punishable by up to a criminal article. But more often this punishment comes in the form of a fine.
- Special or intentional. Some individual entrepreneurs may deliberately violate the law, for example, in order not to pay taxes or pay them in a smaller amount.
- Random. In its activities, an individual entrepreneur, like any other entrepreneur, has to deal with a huge amount of information. Therefore, it is not difficult to make a mistake, for example due to inattention, for which, nevertheless, you will need to bear responsibility.
- Out of ignorance or lack of experience. Some individual entrepreneurs may try to optimize their finances, in particular tax payments: legislation allows this to be done, for example, by choosing a taxation system, by choosing a method for writing off goods, etc. But due to insufficient preparation of the individual entrepreneur or his accountant, an error may occur.
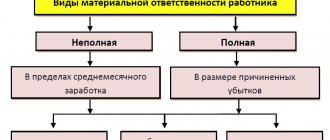
Responsibility for failure to register employees as legal entities. persons
Legal entities must also be held accountable before the law for failure to formally hire their employees and for violations in the preparation of employment documents.
If such a situation occurs, fines may be imposed directly on the director or HR inspector.
Measures for such violations may include:
- Removal of officials from work;
- Imposition of large fines on legal entities. person in the amount of up to 100,000 rubles;
- Imposition of fines on the head of an organization in the amount of up to 5,000 rubles;
- Suspension of activities for a period of 90 days;
- Criminal prosecution;
- Correctional work;
- Arrest for up to three years.
Such measures can also be determined in the event of incorrect execution of work books and employment contracts.
Employment options
Employment in practice is of two types:
- Official . In this case, labor relations are formalized by drawing up one of two documents:
- employment contract;
civil contract.
An employment contract is concluded with all employees hired for permanent activities. It comes in two types:
- urgent, that is, work is expected for a certain period of time;
- unlimited
The document must contain the following information:
- information about the parties;
- working conditions;
- the subject of the contract, that is, the labor function;
- terms of payment;
- place of work;
- start date of activity.
A civil agreement is concluded when an employee must perform certain work or services. In fact, it is a contract. In such a relationship, the employer does not have to pay pension contributions, provide certain working conditions, pay for vacation, etc. Some unscrupulous employers deliberately use such an agreement instead of an employment agreement. In this case, the employee has the right to go to court to force the execution of correct documents and payment of compensation. Sometimes employers offer limited conditions as part of formal employment. For example:
- the employee is registered for a reduced day, although in fact he works full time;
- he is officially paid the minimum wage, and the balance is paid in cash.
The legal consequences of such employment relationships are discussed in detail in the following video:
Responsibility for migrants
Incorrect registration of migrants, that is, foreign citizens, entails even greater liability for the employer.
In the following cases, the director will receive a fine for working with illegal immigrants:
- If the foreigner does not have permission for any type of activity;
- If a special permit has not been issued to attract a foreigner to work;
- If a contract has been concluded with a migrant under which he was not notified of the terms of work;
- When a foreign citizen works in a profession other than that specified in his work permit.
For such labor violations, a fine is imposed on the director in the amount of 35,000-70,000 rubles. The organization will be fined in the amount of up to 1,000,000 rubles, and the operation of the enterprise will be stopped for 90 days.
When hiring foreigners, you should ensure that they are registered. In case of delay, the Federal Migration Service may impose penalties on the employer.
When hiring a foreigner, you should pay attention to a number of points:
- Check the presence of an identity document (passport, refugee card or residence permit);
- Check the initial registration of an illegal immigrant;
- Check the availability of a patent or work permit in a particular area of the Russian Federation;
- Check documents confirming the qualifications of the position held;
- Availability of pension fund and TIN certificates.
| Grounds for imposing a fine | Amount of fine |
| When a foreigner performs work that is not specified in the permit | The size is determined by the FMS |
| If a foreigner does not have a work permit | Up to 50,000 rub. per official, up to 800,000 rubles. in legal person for each illegal worker |
| If the employer has not notified the FMS about hiring a foreigner | From 25,000 to 50,000 rubles. for the director personally, from 400,000 to 800,000 rubles. to the organization. |
| If the employer does not fulfill the obligation to register an illegal worker | Up to 500,000 rub. in legal face |
| If the employee carries out his activities in a territory other than the one for which the permit was issued | Up to 50,000 rub. per official, up to 800,000 rubles. in legal person for each illegal worker |
No matter what violation occurred, when attracting foreign labor, the fine for unofficial employment is very high.
Therefore, in order to avoid such financial losses for the organization, you should carefully study the legislative framework when registering illegal immigrants.
When auditor organizations detect violations of labor legislation, they draw up an inspection protocol, on the basis of which the amount of penalties is determined.
Is it necessary to officially register an employee with an individual entrepreneur?
Official registration of an employee with an individual entrepreneur is a prerequisite. As soon as an individual entrepreneur enters into an employment contract with a person, he actually becomes an employer. This agreement must be concluded no later than three days from the date of hiring. Within 10 days, the individual entrepreneur registers the workforce with the Social Insurance Fund, and within 30 days with the Pension Fund. An unemployed individual entrepreneur faces a fine.
What fine is imposed if illegal employees are identified?
Also, for everyone who has worked for more than five days, it is necessary to issue work books. The maintenance of books is regulated on the basis of the Labor Code and other regulations.
Important! Labor legislation is mandatory for employers to comply with.
When an employee comes to an entrepreneur, the individual entrepreneur must ask him for registration:
- passport;
- book about work activity;
- military ID. Provided to men between 18 and 27 years of age who are eligible for military service;
- TIN. If the employee is not an individual entrepreneur, then it is not necessary to have a TIN;
- medical book. Its presence is necessary for workers in the catering industry, medicine, and salespeople in grocery stores;
- a document from the Ministry of Internal Affairs stating that there is no criminal record;
- educational documents.
Referring to these papers, the individual entrepreneur draws up an employment contract. It must be in two copies. There is a standard form of the agreement, but it is possible to make changes and additions to it.
The agreement must necessarily indicate:
- FULL NAME;
- information from the passport;
- the place where the contract is drawn up, as well as the date of conclusion.
Also, the drawn up contract specifies information such as position, working hours, benefits, etc.
After the contract is concluded, it is necessary to issue an order stating that the person has been hired, as well as make an entry in the work book.
The employee is obliged to perform his functions on the basis of the job description. The individual entrepreneur must create all the conditions for performing these functions. The responsibilities of the IP also include:
- payroll;
- transfer of contributions and taxes to the relevant authorities;
- granting leave;
- sick pay.
Important! The relationship between employer and employee is regulated by the Labor Code.
Based on Article 64 of the Labor Code, an individual entrepreneur cannot unreasonably refuse a person a job. In case of any violation of their rights, a person can contact the labor inspectorate.
Conclusion
If you are an employer, no matter an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity, you are obliged to officially employ your employees, pay them their due salaries and pay taxes. Otherwise, you will be subject to criminal liability.
If you decide to save on your employees, then you will have to spend several times more money.
The employee, for his part, must demand official employment in order to provide himself with all social benefits and not receive wages “in an envelope.”
Fine for an unregistered individual entrepreneur 2020 for
First of all, a new chapter 50.1 has been introduced into the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is entirely devoted to regulating the labor of foreign workers. This means that foreigners have finally and irrevocably been equalized in legal status with Russian citizens, including in terms of guarantees. An employment contract with a foreign worker will need to include information about his work permit and documents confirming the legality of his stay on the territory of the Russian Federation.
We recommend reading: Extension of registration of houses on dacha plots
I advise you to contact them if necessary. I opened an IP here. Satisfied, everything was fast, no problems. Very nice girls in the department))) Quite a good price, many others were more expensive when I was choosing. They explained everything in detail and gave advice on many issues. It’s very convenient that they took me to the notary right away, again, a nice girl went with me))))))))) When I opened an individual entrepreneur, I didn’t need an account, now I do, right now I’m also opening it through ECLEX, they have such a service there too, again very convenient.
What is the expected fine for individual entrepreneurs for unregistered workers?
Registration first of all consists in the fact that an employment contract is drawn up between the individual entrepreneur and the employee, which serves as documentary evidence of official registration. This document contains the most important information about both the employee and the entrepreneur. It also contains a lot of other necessary data, and this includes the position that the employee will hold, his salary and responsibilities. This document must be signed by both parties, otherwise it will not have any legal force.
If, in the event of significant violations, the entrepreneur is not given a real or suspended prison sentence, then another punishment may be applied. It may consist of a ban on future business activities or a ban on working in a specific area of activity in which the violation was detected.
Fine Individual Entrepreneur for an Unregistered Worker 2020
If inaccuracies or errors are discovered in employment contracts, employees working in individual entrepreneurs may also be issued a fine . For minor offenses, such as delay in drawing up a contract by several days, inaccuracies or errors in its content, etc., it is also appointed.
In our country, quite often you can encounter a situation where individual entrepreneurs, in an attempt to save on taxes, do not enter into employment contracts with an employee. This is a direct violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation and is punishable in accordance with it. It is worth considering this issue in detail.
What fine does an individual entrepreneur receive for an unregistered employee?
The size of the sanction will depend on the losses caused by the employer to the state . Among other things, its legal status matters: whether it carries out entrepreneurial activities or is a private organization. A separate type of punishment is provided, among other things, for the employment of illegal migrants. Let's look at each of these aspects in more detail.
All entrepreneurs and organizations, regardless of their type of activity, must comply with Russian legislation. They are also responsible for the official employment of hired workers. To do this, you need to draw up a written contract with the future employee - then there will definitely be no problems with the law. But the use of labor resources without a supporting document is a fairly major violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
We recommend reading: Definition of the Main and Secondary Roads at an Unregulated Intersection
Fine for unregistered individual entrepreneur 2020-2020 for
This type of liability occurs if there has been large-scale tax evasion for an unregistered employee. Types and extent of liability for an unregistered employee If an individual entrepreneur or an official of an organization evades registration of an employee, administrative or criminal liability arises. It depends on the type of responsibility what fine for an unregistered employee must be paid. The extent of responsibility of an individual entrepreneur for an unregistered employee: According to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - penalties from 1000 to 5000 rubles.
Minimum wage and salary: when comparing, do not forget about allowances and regional coefficients. The salary of an employee who has worked his full working hours for the month cannot be less than the minimum wage. In this case, the salary is taken into account taking into account all allowances and increasing factors.