Every citizen of any country in the world pays taxes, which are the basis for the formation of the state treasury. He can do this on his own behalf (by transferring so-called “direct” fees to the state treasury) or by making indirect payments.
There are many reasons for tax classification. We will consider the interpretations that are most common in Russia. We will try to reveal the essence of such phenomena as direct taxes, “tax agent”, “offshore”, and talk about what other interesting terms mean.
Object and subject of taxation
What is the object of taxation? These phenomena usually include certain types of actions (as well as events or conditions) that give the state a legal reason to calculate tax. For example, this could be a real estate purchase and sale transaction, the importation of goods into the country, or the ownership of any property.
What is the subject of taxation? This, in fact, is the material (fixed in certain quantities) basis for performing those actions that form the object of taxation. That is, in the case of a real estate purchase and sale transaction, this is an apartment, a house, a plot of land; when importing goods into the country, this is, in fact, what is being transported (food, clothing, electronics); if we are talking about owning property, this is her specific type (housing, car).
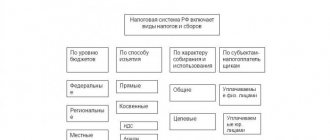
Having decided what the object and subject of fees are, let’s study the concept of direct and indirect taxes. This method of classifying encumbrances is generally accepted among Russian lawyers.
Facts about direct taxes
What taxes are considered direct? In the interpretation generally accepted by Russian lawyers, this type of collection is carried out by government bodies from property (its market value in the established currency) or the income of citizens. The entity that receives the revenue subject to taxation is called the actual payer. Almost all countries in the world have encumbrances of this type. Direct taxes include a variety of types of fees. Which of them are most common in Russia? This is personal income tax, corporate income tax, gift tax, property tax, inheritance tax, oil, gas, coal production, etc.
One of the key criteria that determines the essence of the term “direct taxes” is that the subject of payments makes contributions to the treasury consciously - himself, or by entrusting the transfer of funds to a special agent (more on them a little later). Or, at least, being aware that such and such an amount for such and such a reason must be transferred to the state budget.
Another important characteristic of direct taxes is personification. The state knows who owes the budget and how much, and on what basis this debt arose. In some cases, authorities provide the opportunity to pay direct taxes through several channels at once - as long as the subject of the encumbrance fulfills his obligations to transfer the required amount.
Terminology: what is a direct tax
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation gives the following definition of tax in paragraph 1 of Art. 8: this is a mandatory, individually gratuitous payment levied on organizations and individuals in the form of alienation of funds belonging to them by right of ownership/economic management/operational management for the purpose of financial support for the activities of the state and/or municipalities.
At the same time, in economic theory, tax law and taxation, it is traditional to divide taxes into direct and indirect. However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not answer the question of what direct taxes are and does not separately list the types of direct taxes.
As a general rule, the state levies direct taxes directly on the income and property of the taxpayer.
The essence of a direct tax is that:
- it is taken from income or property;
- it is paid by the obligated person at his own expense.
This is its main difference from an indirect tax, which acts as a kind of surcharge on the price or tariff and is paid at the expense of the buyer.
For more information, see “Direct and indirect taxes: what is the difference (examples).”
Classic examples of direct taxes in relation to Russia include:
- personal income tax;
- unified social tax (it was replaced by insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds);
- corporate income tax;
- property tax (land, transport, etc.).
Taxes: real and personal
Direct taxes are usually divided into two types. The first is the so-called “personal” fees. They are taxes that are levied on the income or property of citizens and organizations, based on individual monetary indicators. That is, it takes into account the actual amount of revenue (salaries, rent, etc.), the value of property owned by a specific person - an individual or a legal entity. Direct personal tax is, in fact, tied to a person’s passport or TIN (or OGRN of an organization). In this case, the state is not very interested in a specific subject of taxation, but rather in the entity that is obliged to pay contributions to the budget from the revenue received.
The second main type of fees that belong to direct taxes are “real” payments. They are levied not from a specific subject (individual or organization), but from a certain type of property belonging to it - land, real estate, securities, etc. When calculating the amounts payable to the state treasury, the external characteristics of the objects of taxation are taken into account. If this is, for example, a house, then its area plays a decisive role. As a rule, there is no calculation of the potential income that a particular property can bring to the owner.
And therefore, every year a property tax is charged - direct, subject to mandatory payment. Although it is relatively small in Russia (in many other countries of the world such fees are calculated based on the market value of the property and can amount to significant amounts).
We learned that direct taxes are divided into several types, determined their essence, and found out why they are called that. Next in line is the study of a completely different type of fees. Namely, taxes related to indirect ones. Let's try to study their main features.
Story
Direct taxes represent historically the earliest form of taxation. Direct taxes are mandatory and every citizen is required to pay them.
Direct taxes are divided into:
- real taxes;
- personal taxes.
Direct taxes include:
- income tax;
- corporate income tax (corporations, organizations, etc.);
- inheritance and gift tax;
- property tax;
- mineral extraction tax;
- etc.
Direct taxes are imposed directly on income and property. There is a direct connection between the subject and the state: the taxpayer immediately feels tax pressure. A distinctive feature of this tax is the relatively complex calculation of its amount.
Direct taxes - income tax; property tax; personal income tax. Income tax - tax is imposed on the income received by the taxpayer. Organizational property tax - tax is imposed on movable and immovable property that is taken into account on the balance sheet as fixed assets.
The object of direct tax is the income (wages, profits, interest, rent, etc.) and the value of property (land, house, securities, etc.) of the taxpayer, who simultaneously acts as both the collector and the final payer of the tax.
Facts about indirect taxes
Indirect fees include amounts payable to the state treasury on the basis of surcharges established directly by the taxpayer to the principal value of an asset. The most common types of this type of monetary encumbrance are excise taxes, customs duties, and VAT.
Fees of this type are called indirect because they are actually paid not by the subject of the transfer of fees, but by some third party. As a rule, the buyer of the goods. VAT, duties and excise taxes are costs that are included by the entrepreneur in the selling price of the goods (we can say that they are on a par with the costs of transport, loading, purchasing from the manufacturer, advertising, etc.).
This is where direct and indirect taxes differ: in the case of the former, the payer deliberately transfers funds to the state, and when paying the latter, third parties do it for him. Which, in turn, may not be aware of this (after all, the nuances of calculating VAT, as well as determining its share in the cost of goods - as a rule, information is closed to buyers).
In Russia, not only those entrepreneurs who are engaged in trade are required to pay VAT, but also those who provide services. True, the law defines a fairly large number of services, the provision of which is not subject to this type of indirect tax. In order to have reliable information on this matter, an entrepreneur should arm himself with the latest Tax Code of the Russian Federation and read Article 164 - it reflects all the nuances associated with taxation of business through VAT.
The importance of indirect taxes for the state
Most countries in the world, including Russia, use indirect taxes as one of the main tools for budget formation. Economists say the main advantage of this type of fee is the speed of transactions: as soon as the product is sold (or, for example, crosses the border), the tax is transferred to the treasury as soon as possible.
Another advantage of indirect fees from the point of view of budgetary policy: VAT and other types of encumbrances, as a rule, are tied to consumer goods. That is, their trade turnover will be carried out in almost any economic situation. This means that the budget will always receive funds collected as part of indirect fees. Their value, by the way, can be regulated by the state by introducing recommended or mandatory VAT rates.
In what proportions is the ratio of direct and indirect taxes reflected in the country's budget? It all depends on the specific state. It is known that indirect taxes still predominate in Russian budget revenues: customs duties, fees for the import of goods, payments for the use of natural resources. If we talk specifically about taxes on profits and income, then their share in the structure of revenue of the Russian Federation budget is now about 3%.
Difference between direct and indirect taxes
Both types are tax liabilities. The differences are presented in the table.
| Criterion | Tax | |
| Straight | Indirect | |
| Who is the taxpayer? | FL, YUL | A consumer purchasing products manufactured by a sole proprietor or legal entity. |
| How is the relationship with the state? | Payments are made directly to the state. | Taxes are calculated through intermediaries, who are the owners of organizations or manufacturers. |
| What is the object of taxation? | All property of the taxpayer (real estate, transport), his income, categories of minerals. | Manufactured goods, services provided, work performed intended for sale. |
| What affects the amount of tax? | The amount of income received from various types of activities, the current financial situation, etc. | Price for goods produced or services provided, tariff rates, categories, etc. |
| How do they depend on financial activities? | Direct dependency | No dependency |
| How is the calculation carried out? | Complex, involves division into several categories. | Simple, carried out using special formulas. |
| How does participation in price formation take place? | The price depends on the specific production. | They influence the reduction or increase in the cost of goods, services, and works. |
| What is the degree of openness? | Open payments | Closed payments, consumers have no idea about the amount of taxes paid to the state treasury. |
The basis of the state tax system is the ratio of two types of fees. From the point of view of the optimal ratio, it is necessary that their shares be equal. Then all participants will not be disadvantaged, regardless of the changes that occur. In addition to the fact that the amount of taxes must correspond to the income level of each participant, it is necessary to take into account the development of the country from an economic point of view, as well as take into account all the needs that are relevant in a particular time period.
The modern taxation system in the Russian Federation involves a mixture of direct and indirect taxes. Thus, by equalizing them, stabilization occurs and equilibrium of different market segments is achieved.
It should be noted that the tax fees that were payable by individuals for 2016-2017. less than for enterprises. Indirect taxes are almost twice as high as direct taxes. This distinctive feature is typical only for economically developed countries.
Offshores, tax benefits
In some cases, certain groups of individuals and organizations are exempt from paying taxes. This could be, for example, if they operate in “offshore zones” - the territories of states that guarantee a zero (or extremely low) tax rate for foreign firms. But even in countries that are not “offshore”, there may be a certain kind of privileges called “tax immunity”. This phenomenon implies the freedom of citizens or organizations from transferring payments to the budget for one reason or another, determined by law.
One of the most common criteria for classifying fees in favor of the state treasury is the administrative level of the taxable entity. Based on this, local, regional and federal types of encumbrances are distinguished. The most interesting thing is that at each level both indirect and direct taxes can be levied. In the Russian Federation, the system of fees to the budget operates, as many experts note, within the framework of fairly strict regulations. Let's look at how taxation is structured at each level.
Local taxes
Local taxes are payments made by individuals and organizations that go to local administrative structures (municipalities). The amount of payments, accordingly, is regulated by local authorities - state councils, city halls. Although, as Russian lawyers note, in our country this system is so centralized that the role of municipalities in determining the amount of tax deductions is actually reduced to a minimum.
In the Russian Federation, local fees include, first of all, land tax. But there are other important types of fees. This is a tax on citizens’ property, on advertising, on donations (inheritance), as well as various types of licensing encumbrances. Municipal fees are paid by entities that have permanent registration in specific cities, regions, and rural settlements.
Regional taxes
The administrative level of government in Russia next to municipalities is the subject of the federation, that is, the region. Fees of this type include: real estate tax, on the property of legal entities, on sales, on business activities related to gambling. This also includes, similar to what happens at the municipal level, licensing encumbrances - but of a regional nature. It is also customary to include transport and road taxes among fees at this level. Regional fees are required to be paid by residents of specific federal subjects.
Types of direct taxes
Direct taxes can be divided into 2 groups – taxes on income and property. These mandatory payments are paid by the taxpayer himself - the recipient of the income or the owner of the property. From the point of view of classical theory, the main difference between direct taxes and indirect taxes is the inability to redistribute the tax burden to other economic entities.
However, not for all payments this difference between direct and indirect taxes corresponds to traditional ideas
Income taxes include personal income tax and corporate income tax. These payments are indeed practically impossible to shift to other persons.
As for the “property” group of direct taxes, the situation here is somewhat different. The owner of a property, land or vehicle can rent it out. Thus, the costs of taxes on the ownership of these objects will actually be borne not by the owner of the property, but by the tenant.
Consequently, this group of direct taxes to a certain extent has the properties of indirect taxes.
Federal taxes
Federal taxes are collected at the highest level of government and with the direct participation of relevant authorities. These include a variety of types of encumbrances - both direct taxes and indirect ones.
These are VAT, excise taxes, encumbrances based on the profits of legal entities, personal income tax, contributions to social funds, customs duties, etc. Federal direct and indirect taxes are required to be paid by absolutely all citizens and legal entities registered in Russia.
The concept of tax and types of taxes in the Russian Federation
Definition 1
A tax is a financial obligation of an individual or legal entity to the state, which must be fulfilled within the time limits established by law.
Taxation resolves issues of income distribution between the state, legal entities and individuals. Taxes reflect the obligation of legal entities and individuals to take part in the creation of financial resources of the state and, acting as an instrument of redistribution, help eliminate emerging violations in the system of distribution of financial resources, restrain or stimulate the development of a certain form of activity.
In modern conditions, taxes are an effective and important part of the government’s financial policy.
Basic principles of taxation:
- uniformity - a comprehensive, unified approach of the state to persons paying tax, from the point of view of the unity and universality of taxation rules;
- certainty - the taxation procedure is strictly established by the relevant legislation, so the deadlines for paying taxes and their amounts are known in advance.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework Direct and indirect taxes of the Russian Federation 420 rub.
- Abstract Direct and indirect taxes of the Russian Federation 230 rub.
- Test work Direct and indirect taxes of the Russian Federation 230 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Note 1
Taxes are the main source of revenue for the state budget; they are the main instrument for the redistribution of finances between members of society.
Fiscal policy is the deliberate use of the government's tax and spending functions to achieve the government's macroeconomic goals. In the fiscal taxation system, there are two types of taxation – direct and indirect.
About double taxation
The situation in question arises if a person who is a citizen of one country pays taxes in it - direct and indirect. And he does the same thing, for the same reasons, while in another state. For example, if we open a business in Germany, then, on the one hand, we are obliged to pay taxes to the German treasury, and on the other hand, transfer the corresponding amounts to the Russian budget. Regarding indirect fees, when we purchase goods in a Berlin supermarket, we pay VAT for it in the same way. Tax rates in Russia and Germany, as a rule, differ.
This state of affairs is unfavorable for citizens and entrepreneurs. Therefore, in the world practice of diplomatic relations between different countries, it is customary, whenever possible, to draw up agreements to avoid double taxation. There is also a unilateral method to avoid this phenomenon - the issuance of national laws allowing citizens doing business abroad not to pay taxes of the same types in their home countries that are assessed in another country. Or make concessions, in turn, for foreigners (for example, the authorities of many European countries allow foreign citizens who make purchases in German stores to return the paid VAT when leaving the state by filling out a special application at customs - if, of course, the receipts have been preserved).
Tax collection methods
In what ways does the state burden tax payers to the treasury? There are four main methods by which taxes are collected - direct and indirect. They are common both in Russia and in the world.
Firstly, this is taxation of the so-called “progressive” type. By applying it, the state obliges citizens to transfer amounts to the treasury at a rate, the value of which increases in relation to the increase in the tax base. That is, for example, if a person earns 10 thousand dollars a month, then he is obliged to pay personal income tax in the amount of 12%, and if his salary is 50 thousand dollars, then he transfers 15% to the budget.
The “progressive” taxation method is adjacent to the “regressive” method of taxation. In turn, with it, the rate decreases as the income base increases.
There is taxation of the so-called “proportional” type. With it, the rate does not depend on the size of the tax base. This regime is sometimes referred to as a “flat scale” of fees. The most popular tax in Russia, which is calculated in this way, is personal income tax of 13%.
There is so-called “equal” taxation. It represents the collection of identical and, as a rule, fixed amounts from citizens, regardless of income level. This type of taxation is usually used less frequently than the previous three. But in our country it also exists (below we will give several practical examples to prove it).
Popular types of fees: Personal income tax
Perhaps the most common direct tax in Russia is personal income tax. All individuals residing in the territory of the Russian Federation and receiving personal income in one form or another are required to pay it. These can be both citizens of Russia and subjects of foreign states. It is possible that personal income tax payers will be persons who do not have a passport of any country.
The object of taxation is the receipt of income through entrepreneurial activity, hired work, or the sale of something. Not only cash revenue is taken into account, but also income in kind (at market price or state-determined value).
The standard personal income tax rate in Russia is 13%. For non-residents of the country the rate is significantly higher - 30%. The most interesting thing is that citizens of the Russian Federation can also be classified as having this status in cases where they live abroad most of the time. In turn, foreigners receive resident status if they live in Russia for more than 183 days within 12 months.
In many foreign countries, an analogue of personal income tax is returned if the income of citizens is below a certain level. In Russia, there is no mechanism that exactly replicates such a scheme, but there are many other grounds for the return of paid fees. Such procedures are called “tax deductions” in the Russian Federation.
Question - Answer Economics part 7
Question 151
Which of the following is a factor that influences both macroeconomic demand and macroeconomic supply?
Choose one answer.
| production cost level |
| market price level + |
| state procurements |
| income of the population |
Question 152
A contractionary fiscal policy presupposes
Choose one answer.
| increasing the level of taxation and reducing government spending + |
| constancy in the level of government spending and tax revenues |
| lower taxes and higher levels of government spending |
| higher taxes and higher government spending |
| reduction in tax revenues and government spending |
Question 153
What is the combination of a crisis decline in production with inflation called?
Choose one answer.
| inflationary spiral |
| offer shock |
| stagflation + |
| hyperinflation |
Question 154
What is the mixed type of macroeconomic regulator based on?
Choose one answer.
| on the synthesis of market and state management of the national economy + |
| on state management of the national economy |
| on market management of the national economy |
Question 155
Which of the following applies to direct taxes?
Choose one answer.
| land tax |
| all of the above are true + |
| income tax |
| Personal income tax |
Question 156
What is the name of the method and mechanism for organizing and streamlining the national economy?
Choose one answer.
| macroeconomic regulator + |
| government regulation |
| mode of production |
| control mechanism |
Question 157
What is the name of the policy of “automatic” manipulation of government spending and taxes through built-in stabilizers?
Choose one answer.
| discretionary fiscal policy |
| non-discretionary fiscal policy + |
Question 158
What types of government loans are allocated by location?
Choose one answer.
| interest and winnings |
| short and long term |
| internal and external + |
| large and small |
Question 159
What is the name given to the policy of deliberately manipulating government spending and taxes?
Choose one answer.
| discretionary fiscal policy + |
| non-discretionary fiscal policy |
Question 160
Which of the following are characteristics of a market regulator?
Choose one answer.
| ability to implement major structural changes |
| poor response to consumer expectations |
| generation of external effects + |
| the ability to predict and plan final results |
Question 161
What is the name of the graph depicting inequality in the distribution of income in a society?
Choose one answer.
| Lorenz curve + |
| Phillips curve |
| Laffer curve |
| production possibilities curve |
Question 162
What is the central idea of Keynesian government regulation?
Choose one answer.
| reduction of taxes on private businesses |
| aggregate supply growth |
| increase in employment due to growth in effective demand + |
| deficit-free budget |
Question 163
Which of the following is one of the main objectives of tax reform?
Choose one answer.
| achieving budget balance |
| all of the above are true + |
| improvement of the investment climate |
| performing tax administration |
Question 164
Which of the following refers to the maximum permissible functions of the state?
Choose one answer.
| providing the economy with money |
| non-market sector management |
| regulation of social relations + |
| regulation of externalities |
Question 165
What types of government loans are distinguished by types of profitability?
Choose one answer.
| internal and external |
| large and small |
| short and long term |
| interest and winnings + |
Question 166
Which of the following is a function of market prices?
Choose one answer.
| information function |
| all of the above are true + |
| distribution function |
| stimulating function |
Question 167
Which of the following is not a way to improve the efficiency of budget policy?
Choose one answer.
| closed formation of budgets at all levels for the population + |
| clear delineation of spending powers between budgets of all levels |
| placement of government orders on a competitive basis |
| deficit-free budget |
Question 168
Which management system is characterized by direct management of enterprises from the center?
Choose one answer.
| for traditional economics |
| for a mixed economy with minimal state functions |
| for a mixed economy with maximum permissible functions of the state |
| for administrative command system + |
Question 169
Which graph illustrates the relationship between changes in the income tax rate and changes in budget revenues?
Choose one answer.
| Laffer curve + |
| Philips curve |
| budget line |
| Lorenz curve |
Question 170
Government debt is the debt that a government has accumulated as a result of borrowing money to finance past
Choose one answer.
| defense spending |
| budget deficits + |
| government spending |
Question 171
Under what conditions does a government budget surplus exist?
Choose one answer.
| if government revenues exceed expenses + |
| if government debt is reduced |
| if taxes are reduced |
| if government spending increases |
Question 172
What is the government's spending and tax policies called?
Choose one answer.
| monetary policy |
| cheap money policy |
| fiscal policy + |
| policy based on the quantity theory of money |
Question 173
Which of the following is a consequence of the crowding-out effect that results from increased government spending?
Choose one answer.
| reduction in future production potential |
| reduction in private investment spending |
| all of the above are true + |
| increase in interest rate |
Question 174
Expansionary fiscal policy implies
Choose one answer.
| reduction in tax revenues and government spending |
| higher taxes and higher government spending |
| constancy in the level of government spending and tax revenues |
| increasing government spending and reducing taxation + |
| increasing taxation and reducing government spending |
Question 175
Under what conditions does a government budget deficit exist?
Choose one answer.
| if taxes are reduced |
| if government spending increases |
| if government debt is reduced |
| if government spending exceeds revenues + |
Popular types of fees: property tax
Listing the types of direct taxes adopted in Russia, one cannot fail to note various types of property fees. Owners of apartments, houses, land plots and cars living in Russia pay the treasury for what they have. It does not matter whether a person uses his property or not, whether he uses his possessions for commercial purposes or does not do so - he is obliged to transfer amounts to the treasury. If we are talking about real estate, then the tax, in accordance with current legislation, is defined as 0.1% of the cadastral value of the property. Regarding vehicles, the amount of the fee depends on the engine power in hp. With. and is established by separate legislative acts.
Direct taxes in the Russian Federation
Definition 2
Direct taxes are taxes that the state imposes on the income of individuals and legal entities (wages, any types of profits and interest), property (real estate, transport, land plots). These fees are paid to the state treasury by citizens themselves.
Direct tax is the earliest historically established form of taxation. Direct taxes are divided into real and personal taxes.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Types of direct taxes levied on legal entities:
- on property;
- for business;
- at a profit;
- to the ground;
- for mining;
- to water sources.
The amount of direct taxes is determined by the size and level of income of the citizen. The amount of contributions increases with salary growth. The calculation is complex and involves division into several categories. The amount of tax directly depends on the specific production.
Types of direct taxes levied:
- Personal income tax is a national income tax. The main type of direct taxes. Calculated as a percentage of the total tax of legal entities and individuals minus expenses (documented), in accordance with the law.
- Property tax. The tax is established on the property of individuals or organizations. The object of taxation is the property of the organization that is on the balance sheet of the enterprise (fixed assets, residual value).
- Property tax. A tax imposed on movable and immovable property, cash income in the form of interest on a deposit and in the form of rent.
- Tax on property received by gift and inheritance.
- Vehicle tax. It is a regional tax, levied on registered vehicles. The objects of taxation are: motor scooters, motorcycles, cars, buses, mechanisms and self-propelled vehicles on caterpillar or pneumatic tracks, helicopters, airplanes, sailing ships, yachts, motor ships, jet skis, motor boats, towed vessels, boats, motor sleighs, snowmobiles, other aircraft and water vehicles registered in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation in the prescribed manner.
- Corporate income tax. A tax levied on the profits of an organization (bank, enterprise, insurance company, etc.). When calculating tax, an organization's profit is determined as income from the organization's activities minus the amount of established deductions and discounts.
- Water tax. Paid by individuals and organizations that carry out special and specific water use.
- MET - mineral extraction tax. Federal tax levied on subsoil users.
- ECXH – single agricultural tax. It exists as a replacement for paying property and corporate income taxes and insurance premiums.
- STS is a simplified taxation system. A special mechanism for collecting taxes and fees, replacing the payment of individual taxes with the payment of a single tax with a simplified reporting and accounting system.
- UTII is a single tax on imputed tax. The tax introduced by the legislation of municipal districts, districts, cities of Federal significance, is used in conjunction with the general taxation system, and can only apply to certain types of activities. Replaces the payment of some taxes and fees, simplifying and reducing interactions with fiscal services.
- PSN – patent taxation system. A special tax payment regime in which a tax return is not submitted; the tax is calculated when paying for the patent.
- Gambling tax. Taxation of income received from organizations and enterprises conducting gambling.
- Land tax. A tax paid by individuals and organizations that own land plots on the right of perpetual use, the right of ownership, the right of lifelong inheritable possession.
Payments to social funds
Direct federal taxes common in Russia are transfers to extra-budgetary funds: the Pension Fund, the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and the Social Insurance Fund. They are carried out on a quarterly (and in some cases, annual) basis by entrepreneurs and legal entities in relation to two cases: either when it comes to paying wages to employees, or when there is a need to make so-called “fixed” payments to the funds.
In the first case, approximately 30% of the amount earned by an employee of the company in accordance with the employment contract is subject to payment to the Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and Social Insurance Fund. In the second, the amount of payments is determined by individual legislative acts, and from year to year can vary greatly (both up and down). By the way, in this case, contributions to the Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and Social Insurance Fund can be classified as a rare type of “equal” taxation. Regardless of the income level of the entrepreneur, the amounts for all individual entrepreneurs registered in Russia will be the same.
Popular types of fees: corporate income tax
Let's consider another direct tax. We have considered examples of those that are characteristic mainly of the activities of individuals. Now we will talk about the type of fees that reflect the specifics of the work of organizations. Namely, about corporate income tax.
This type of fee is paid by legal entities registered in the Russian Federation and conducting business activities. The object of the levy may be the receipt of revenue or net profit through the sale of goods or the provision of services. In some cases, receipts from the rental of real estate and other property, receipt of interest payments on shares, as well as compensation (subsidies) from the state are equated to income.
The only thing that gives a company the right to legally reduce income tax is direct expenses. That is, you need to show the Federal Tax Service that the revenue is accompanied by significant costs. Direct costs include a variety of types of costs, but most often the purchase price of goods at the factory, transportation costs, and staff salaries fall into this category.
The standard corporate income tax rate in Russia is 20%. In many cases, special regimes for collecting payments to the budget are used: UTII, simplified tax system, etc.
What are direct taxes
This type is a variation of the method of collecting funds from the population to replenish the budget. This taxation applies to profits, as well as property of both individuals and legal entities operating in the country.
The main distinguishing feature of a direct tax is the payment of a statutory fee directly by a citizen, an enterprise, as well as an authorized body (also called a tax agent). Due to this, the subject from whom the collection is carried out is the payer directly.
The detailed classification of direct taxes is carried out similarly to all other types of budget obligations.
For example, in Russian legislation, the established taxation system provides that all revenues to the country’s budget are divided into three types:
- Regional;
- Federal;
- Local.
Direct taxes themselves are divided into several groups, which are:
- Fees that are levied on the income a person receives;
- Fees imposed for the possession of certain properties.
In addition, taxes paid on the profit and income of an individual are determined by one source and object, the taxation of which is carried out. To be precise, income tax is taken from the profit received, but income tax is taken from the person’s salary.
At the same time, property fees do not have similar parameters, because the object subject to taxation is not a source of income, but you must pay for it in any case.
You can see what types of taxes are included in the tax system of the Russian Federation in this video:
Main types of direct taxes
The use of such adjustment methods is carried out in interaction with the tax rate, as well as various benefits. Due to this impact on the economy, the state has the opportunity to create the necessary balance between the interests of the state and market participants.
Thus, a better environment is created for the development of one type of industry and at the same time the dulling of others. For these purposes, the following types of taxes are applied:
Structure and features of personal income tax
All individuals without exception are subject to such a fee. Due to this, it is of interest to both representatives of various organizations and ordinary employees.
It is also often called income tax due to the fact that its amount is based on profit. This capacity may include a salary, bonus or other income of a citizen. The main operations that form the structure of this income are:
- Interest and dividends received by a person;
- Income received from rental housing;
- Pension;
- Compensations paid in accordance with the current employment contract.
There are exceptions when personal income tax is not required to be paid. Such situations arise by court decision or in the following cases:
- If this concerns the compensation paid for the price of the employee’s food;
- If the company makes a payment to its sole owner;
- When a citizen withdrew his funds from the initial capital of any organization or enterprise;
- In case of payments to foreign citizens, payment of personal income tax is also not required.
What to do in case of overpayment of personal income tax and whether such overpayment can be offset - read here.
Income tax
This type of fee is a direct tax, the amount of which depends on the final outcome of the functioning of a particular enterprise. In fact, it is a fee based on the profit actually received by a specific organization.
To determine how much the company earned during the required period, the initial amount is subtracted from the total amount. The resulting difference is taxed. It must be paid:
- Without exception, all legal entities. Persons working in the Russian Federation;
- Foreign companies that are recognized as tax residents of Russia and carry out their activities on its territory.
Additionally, there is a group of people who should not pay this type of fee. These are:
- Citizens applying special tax regimes;
- All participants .
It is paid only if the object of taxation itself exists. If it is absent, therefore, there is no need to pay.
Property tax
This type of financial fee belongs to the regional type. Therefore, each subject can determine the optimal tax option based on the range provided for by current legislation and its own needs.
In addition, at the regional level, the specifics of tax payments, possible benefits and much more are regulated. The main thing is that the regional laws adopted do not contradict federal legislation.
The need to pay this fee applies to all organizations recognized as taxpayers in the Russian Federation. At the same time, they must have their own property that is subject to taxation.
There are also a number of organizations that are exempt from paying this type of tax. These are:
- Organizers of the Olympic and Paralympic Games, as well as all contractors working for them;
- FIFA;
- All types of football associations.
The object of this taxation is all property that is on the balance sheet of a company registered in Russia that carries out permitted activities. How to calculate corporate property tax - read the link.
The main types of direct taxes in the Russian Federation.
Land tax
This type of collection is classified as local. At the same time, all funds received from its fees are sent to the local budget.
The objects of this taxation are all companies or organizations that have a piece of land that meets the legislative criteria for assigning a tax. Moreover, if the site is part of a mutual fund, the need to pay a fee falls on the management company.
You can read how to correctly fill out a land tax return in this article.
Important! Companies that have land for free use or use it on the basis of a lease agreement are not recognized as taxpayers.
Transport tax
This type of collection is also regional and all funds collected through it go to the regional budget. It is paid by everyone who owns a vehicle.
Legal entities that have one or more vehicles on their balance sheet must calculate and pay the tax themselves.
The amount to be paid to individuals is based on the data that the Federal Tax Service receives from the State Traffic Inspectorate. It is calculated based on the number of vehicles, as well as their parameters and tax rate.
Water tax
All companies using water resources owned by Russia to conduct business must pay the appropriate tax. This also applies to those using groundwater.
Therefore, the objects of taxation today are those legal entities that carry out the following type of activity:
- They collect water resources for their needs from objects (rivers, lakes or other bodies of water) located on the territory of Russia;
- They use water areas for their own purposes;
- Water is used for purposes other than those intended for hydropower.
Persons who are not subject to the need to pay water tax are legal entities (organizations and companies), as well as individuals who use certain water resources solely on the basis of agreements on the provision for their use (paid or free of charge) of reservoirs located in the state.
For the gaming business
This type of financial collection also applies to taxes received by regional budgets. The funds obtained in this way are the income of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Objects of taxation are companies and organizations legally engaged in gambling.
In this type of business activity, the collection of tax on gambling occurs for three types of income at once:
- Winning;
- Bet;
- Payment for organizing gambling.
Worth knowing! This type of taxpayer includes companies that conduct card games, various table games, install slot machines and accept bets (applies to bookmakers). All of these activities are taxable.
For mining
This type of tax is paid by all companies engaged in mining in Russia. Moreover, their activities must be carried out on the basis of a license issued by the state.
All legal entities engaged in mining must register no later than 30 days from the date of receipt of the state license.
When the development of a site with natural resources does not take place on the territory of the Russian Federation, documents are drawn up at the legal address of the organization itself.
Properties and characteristics of direct taxes.