- Statistical data
- Profitability
- Expenses
- How to calculate profitability
Transportation of various goods using road transport is considered one of the few types of business activity that, in current conditions, can be started from scratch. This opinion is motivated by the success of the domestic economy and the rapid growth of gross domestic product (GDP). These factors, superimposed on the long distances characteristic of Russia and the fairly high profitability of cargo transportation, make it possible to predict rapid and successful business development.
Having decided to start a business in the field of road transport of goods, many novice businessmen first of all ask questions such as:
- The efficiency of this type of business.
- Categories (types) of road freight transportation.
Statistical data
According to Rosstat, the “contribution” of road freight transportation to Russia’s GDP is more than 8%. In addition, more than 15 million people are employed in this sector of the economy. It is also interesting that in the structure of road freight transportation, the share of small and medium-sized businesses during the reporting period (2015-2016) amounted to more than 80%.
According to Rosstat, the “contribution” of road freight transportation to Russia’s GDP is more than 8%
The positive dynamics of development of this market segment allows us to conclude that the situation in it is favorable for successful business in any region of Russia.
Road freight transportation
Numerous options for road freight transportation can generally be divided into 4 groups:
- Satisfying the needs of the population related to the transportation of large cargo (furniture, household appliances, etc.). The weight of transported cargo, as a rule, does not exceed 7 tons.
- Transportation of goods according to orders from industrial enterprises. Provides for the organization of cargo transportation both within Russia and abroad (international transportation).
- Servicing retail outlets and enterprises (delivery of goods within settlements, between them and along interregional routes). This type of cargo transportation requires refrigerators.
- Transportation of associated (consolidated) cargo. This type of activity requires the organization of a serious logistics service.
Classification
There are several other ways to classify road freight transport. They can be:
- bulk - transportation of large quantities of identical products;
- small - moving a small amount of cargo that differs in size and characteristics;
In addition, there are transportations:
- Standard oversized cargo.
- Large cargo. For this type of transportation, special low-loader trawls are used.
Road freight transportation is also classified according to:
- industry characteristics - agricultural, postal, public utilities, catering, etc.;
- territorial basis - suburban, urban, intra- and inter-district, technological (within one enterprise), etc.
Profitability of road freight transportation
Cargo transportation is a specific type of business activity that is directly related to the presence of a bank account. The absence of an account significantly reduces the financial capabilities of both the transport company and the individual entrepreneur, since:
- It will be impossible to enter into agreements with legal entities.
- This will discourage some individuals who prefer to pay into a business bank account (preferably through a reputable bank).
In addition, having a current account will require financial reporting from a business entity, including payment of taxes. This, in turn, will determine the taxation system, which depends on the market segment:
- Providing services to individuals - allows for reporting according to a simplified scheme until the number of cars exceeds 20 units.
- Cooperation with industrial enterprises will require reporting using a common system.
- When working as an intermediary, when the transportation of goods is carried out by other enterprises or individuals, the choice of taxation system does not matter and can be any.
In general, profitability is a quantitative assessment of the efficiency of using the current costs of an enterprise. The level of profitability is calculated as a percentage. At the same time, the analysis of its components makes it possible to evaluate the activities of a business entity as a whole, as well as by type of activity, separate divisions, etc.
When organizing the work of a motor transport enterprise or carrying out individual entrepreneurial activities in the field of cargo transportation, it is necessary to initially plan the level of profitability, which, based on regulatory documents, cannot exceed 35%.
More on the topic: Motor transport + cross-docking = delivery speed
Business in the field of cargo transportation is no different from any other type of entrepreneurial activity. In the same way, when forming a pricing policy, you need to take into account both actual and future costs. At the same time, increasing the efficiency of transportation is possible only by reducing its cost.
Freight costs
As a rule, all costs are divided into groups:
- Direct costs, which include everything that is necessary to directly carry out the work:
- provision of fuel and lubricants;
- scheduled vehicle repairs;
- wages of workers;
- contributions to social funds.
In addition, direct costs are:
- permanent;
- variables.
For example, if a driver receives a constant monthly salary, then this refers to fixed expenses, and if he works on a contract basis (piecework), then this refers to variable expenses.
- Indirect costs, which include:
- overhead costs (driver meals, payment for communication services, cost of office supplies, etc.);
- costs for routine maintenance and repair of vehicles.
As a rule, the increase in indirect costs is directly related to the amount of wear and tear (mileage) of vehicles.
How to calculate the profitability of cargo transportation
In modern market relations existing in the field of cargo transportation, great attention is paid to determining the level of their efficiency. As a rule, motor transport enterprises and organizations carry out several types of freight transportation. This can be intracity, intercity or suburban, as well as other types of cargo transportation, and each of them has its own level of profitability. Ultimately, their relationship with each other determines the efficiency of the motor transport enterprise as a whole.
In modern market relations existing in the field of cargo transportation, great attention is paid to determining the level of their efficiency
When monitoring the economic activity of a motor transport enterprise, it is necessary to remember that the average level of profitability does not give a clear picture. It is necessary to consider both the overall efficiency of the enterprise and the profitability of each type of cargo transportation separately. At the same time, it may well be that while the profitability of some types is high, others will turn out to be unprofitable.
Analyzing the activities of a motor transport enterprise, profitability is determined by calculation:
- By balance sheet profit (total profitability of the enterprise).
- Certain categories of transportation.
- Operation of certain types of vehicles
- Separate route.
Profitability on balance sheet profit
The result of the work of any motor transport enterprise, and of an individual entrepreneur too, is determined by the amount of overall profitability, which is the basic indicator when analyzing its financial activities.
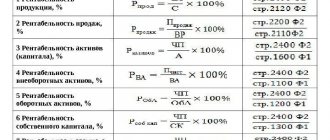
In general, profitability is determined based on book profit and is calculated using a universal formula.
Transportation profitability - formula
To calculate the overall profitability P of motor transport enterprises whose main activity is cargo transportation, use the formula:
P=Pb/F x 100% [1]
Here:
Pb – total balance sheet profit of the enterprise;
F – average annual cost of fixed production assets and working capital:
F=(Fop + Sob)
Fop - average annual cost of fixed production assets;
Sob - the average annual cost of standardized working capital.
If necessary, using the formula [1 ], determine the efficiency of use:
- assets. In this case, F is the total value of assets;
- capital. In this case, F is the annual amount of own funds used.
Calculation of profitability for certain types of transportation
Performance indicators for individual types of transportation are calculated using the same formula [1] . However, in this case it is necessary to redistribute fixed production assets and normalized working capital by type of transportation. In this case, the amount of profit P is determined as the difference between the amounts of income and expenses, taking into account 2% of deductions from total income (go to the construction and reconstruction of highways). Formula for calculating total balance sheet profit:
P = D - (R + 2% D), [2]
where D is income;
R - expenses.
The results of calculating profits for individual types of transportation are summarized in Table 1:
More on the topic: Motor transport + cross-docking = delivery speed
Transportation tariffs ↑
Setting tariffs for cargo transportation is a complex task with a hundred nuances. Each mistake in the future can cost significant financial losses. Tariffs depend on a number of factors (distance, weight, volume, characteristics of the property and even seasonality), in addition, they come in several types:
- Piece work. The price is indicated for each ton of transported property, taking into account the transportation distance.
- Time-based. An hourly rate is established for the use of a vehicle of a certain carrying capacity. The tariff is in demand when it is not possible to carry out a quantitative accounting of the cargo, with frequent trips over short distances.
- Per kilometer. The fee is determined based on the mileage of the car.
It’s easy to set tariffs when the cost is known: you need to add the desired percentage of profit to the calculated value - that’s all the mathematics!
Profit table
| Indicators | Total for the enterprise per year | Including (for example): | ||
| Transportation of garbage | Transportation of grain | Servicing retail outlets | ||
| Income, thousand rubles | ||||
| Expenses, thousand rubles | ||||
| Contributions for the construction and reconstruction of roads, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Profit/loss, thousand rubles | ||||
| Other profit/loss, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Total profit/loss, thousand rubles. | ||||
Fixed production assets generally include:
- buildings and constructions;
- equipment;
- rolling stock, etc.
The main role here is played by the cost of rolling stock, distributed among transportation categories. Information about this is recorded in Table 2.
Main production assets
| Data | Average annual cost of transport | Including cargo transportation such as | ||
| Rolling stock, total, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Including (for example): | ||||
| dump trucks... | ||||
| flatbed cars... | ||||
| Gazelle cars... | ||||
| … | ||||
| Total, thousand rubles | ||||
The cost of the remaining production assets is distributed among types of transportation in proportion to the cost of vehicles in them. Data on fixed assets are summarized in Table 3.
Data on fixed assets
| Indicators | Total | Including cargo transportation | ||
| Average annual cost of vehicles, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Distribution of vehicle costs, % | 100 | |||
| Average annual cost of fixed assets (not taking into account the cost of vehicles), thousand rubles. | ||||
| Average annual cost of fixed assets, thousand rubles. | ||||
The structure of standardized working capital includes:
- funds, the consumption of which depends on the mileage of the vehicle:
- fuel;
— fuels and lubricants;
- spare parts;
— operating materials (rags, etc.).
- low-value and high-wear items.
Moreover, their distribution between categories is carried out in percentage terms, based on:
- Vehicle mileage - for products whose consumption depends on mileage.
- Machine-hours of transport operation - for high-wear and low-value items.
Accounting for mileage, and especially actual machine-hours worked, is a rather labor-intensive, but necessary process that allows one to objectively determine the effectiveness of transportation. The results of this rather labor-intensive work are summarized in Table 5.
From words to deeds: principles of cost calculation ↑
The efficiency of the company is determined by two significant evaluation indicators: cost and profitability of cargo transportation. They will help you weigh the possibilities of your activities, plan future profits and the payback period of your investments. At the first stage, it is important to understand the concepts: what is the difference between cost and price?
- The cost includes all expenses incurred by the enterprise for 1 km of freight transport mileage.
- The price consists of the cost and a certain increase, which is made in order to make a profit from the activity.
Calculation of the initial cost of the service is calculated based on 5 main items:
- Material costs (fuels and lubricants, tires, components, “consumables” for maintenance).
- Staff costs.
- Tax deductions to state funds.
- Depreciation of vehicles.
- Overhead expenses: telephone bills, utility bills, travel allowances.
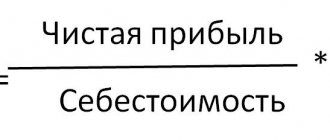
To find out how much 1 km of car mileage actually costs, use a simple formula: divide the total costs for a monthly period by the total mileage of the vehicle fleet. This value will help you set the correct price for services without a loss on your wallet. Special online calculators help simplify calculations.
Efficiency of transportation carried out
| Indicators | Total | Including cargo transportation such as | ||
| Machine operating hours, thousand hours. | ||||
| The share of actually worked machine hours. | 100% | |||
| Average annual cost of wearable and low-value items, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Total mileage, thousand km. | ||||
| Share of actual mileage. | 100% | |||
| Average annual cost of fuel, spare parts, etc., thousand rubles. | ||||
| Average annual cost of standardized working capital, thousand rubles. | ||||
Using the obtained values (Table 2...Table 5) according to formula (1), the overall profitability of cargo transportation is determined, including by type of work. The calculation results are reflected in the final table.
Final table for calculating the profitability of cargo transportation
Profitability of cargo transportation
| Data | Total | Including by type of cargo transportation | ||
| Balance sheet profit, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Average annual cost of fixed assets, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Average annual cost of vehicles, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Average annual cost of standardized working capital, thousand rubles. | ||||
| Total, thousand rubles | ||||
| Total profitability, % | ||||
How to register a private enterprise for transporting passengers
So, the issues with vehicles and their beneficial use have been resolved. Now, in order to avoid trouble with the law and penalties, you should choose the type of business activity. You can register yourself as a private entrepreneur, or you can open a law firm with more than 50 employees. In order to competently resolve all issues with the legalization of business activities, it is necessary to promptly contact the tax authority at the applicant’s place of registration.
The main differences between a private enterprise (individual enterprise) and an LLC (limited liability company, which is a legal entity) in the following circumstances:
- Registration of a private entrepreneur (IP) is a little simpler and faster than opening an LLC;
- The financial costs of registering a private enterprise are lower than when registering an LLC;
- Tax reporting and the amount of monthly tax payments are carried out according to a simplified scheme in a private enterprise - in an LLC there is a much more complex tax reporting scheme.
The conclusion is clear: if you do not have experience in individual entrepreneurship, then it is easier and more reliable to open a small private enterprise in the first stages of activity.