Who is entitled to deductions for children Amount of deduction for a child If you have a common child in a remarriage Deduction for a disabled child Until what age is a deduction for a child allowed? Maximum amount of income for a deduction for a child How to get a double deduction for children under personal income tax Procedure and documents for receiving a deduction for a child How to return deductions for children for previous years
The standard child tax credit is an amount that the government provides to reduce your tax base.
For a working parent, this base is wages, from which the employer monthly transfers 13% of personal income tax to the state budget. If you have a child, your employer deducts a tax deduction from your salary and transfers income tax from the remaining amount.
If a non-working parent has income and pays tax on it, then the tax base can be reduced by the amount of the deduction. Thus, each parent who cares for children saves certain funds.
Receive a tax deduction within a week with the Quick Deduction service!
Get a service
Personal income tax: main features
Personal income tax is a tax on the income of individuals, through which the state treasury is filled. This tax is levied on the profitable part of the tax subject, which are individuals, namely:
- tax residents of the Russian Federation (persons staying in Russia for at least 183 days a year);
- tax non-residents of the Russian Federation (persons receiving profit in Russia).
Currently, there is talk behind the scenes in governments about equalizing personal income tax rates for residents and non-residents. Where this alignment will lead and when it will be done remains unknown. In any case, the Russian Federation budget for 2020 has already been approved, so if such an event occurs, it will not be earlier than 2021. Therefore, let’s look at the current personal income tax situation for 2020.
Personal income tax or personal income tax is calculated based on interest rates. It should be noted that the calculation of interest on wages is carried out only after taking into account tax deductions provided by the state. Personal income tax is calculated from the amount remaining after deduction. Tax deductions for children for non-residents are not provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Up to what age is the child deduction allowed?
The standard tax deduction is paid until your 18th birthday. But this does not mean that the last payment will occur in the month when the child turns 18 years old - your right remains until the end of the calendar year.
If the child is a full-time student, the deduction is extended for the entire period of study or until he turns 24 years old, whichever comes first.
If the child is 24 years old and has not yet graduated, the standard tax deduction is provided until the end of the current year (or earlier if the diploma is issued in the same year). If a child has completed his studies and is not yet 24 years old, then receiving a tax deduction stops after receiving a diploma.
Example:
After school, your 17-year-old son entered a full-time university and graduated in four years. Despite the fact that the boy is not yet 24 years old, starting from the next month after receiving his diploma, you will no longer receive a tax deduction.
Example:
Your daughter finished school, then graduated from a full-time university and entered graduate school full-time. Even before graduation, she turned 24 years old. You will continue to receive the standard tax deduction until the end of the current year or until your daughter graduates, whichever comes first.
Receive a tax deduction within a week with the Quick Deduction service!
Get a service
Personal income tax rates in 2020
Personal income tax rates exist at 9%, 13%, 15%, 30% and 35%.
Tax rate 9%:
- receiving dividends (until 2020);
- receiving interest on mortgage-backed bonds (before January 1, 2007);
- receipt of income by the founders of the trust management of mortgage coverage (before January 1, 2007, based on the acquisition of mortgage participation certificates that were issued to managers of mortgage coverage).
Tax rate 13%:
for tax residents:
- wage;
- remuneration under civil contracts;
- income from the sale of property;
- other income.
From 2020, dividends are taxed at a rate of 13%, rather than 9%.
for tax non-residents:
- from carrying out labor activities;
- from carrying out labor activities as a highly qualified specialist (based on the law “On the legal status of foreign citizens in the Russian Federation”);
- from the implementation of labor activities of the State program to assist the voluntary resettlement to the Russian Federation of compatriots living abroad, as well as members of their families who jointly moved to permanent residence in the Russian Federation;
- from the performance of labor duties by crew members of ships that sail under the state flag of the Russian Federation.
Tax rate 15%:
- dividends received from Russian organizations by non-resident individuals of the Russian Federation.
Tax rate 30%:
- all other income of non-resident individuals of the Russian Federation.
Tax rate 35%:
- income from winnings (prizes) in excess of the established amounts;
- interest income on deposits in banks in terms of excess of the established amounts;
- income from savings on interest when taxpayers receive borrowed (credit) funds in excess of the established amounts;
- income in the form of fees for the use of funds of members of a credit consumer cooperative (shareholders), as well as interest for the use of funds by an agricultural credit consumer cooperative (which were raised in the form of loans from members of an agricultural credit consumer cooperative or associated members of an agricultural credit consumer cooperative) in part of the excess established sizes.
How to calculate deduction
The rules for calculating the amount by which the taxpayer’s base subject to mandatory tax contributions will be reduced are quite simple. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely Article 218, specifies the amounts that are deducted monthly from the salary of an applicant for a tax discount. Moreover, for the calculation it is necessary to take the monthly salary before personal income tax is withdrawn from it.
Amount of discounts for raising children
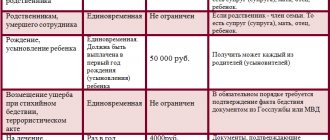
The amount of deductions depends on the number of children in the family, the category to which they belong, as well as who is raising them, and amounts to:
- 1,400 rubles – both for the first child in the family and for the second;
- 3,000 rubles – for large families with three or more children. A deduction of 3,000 rubles is provided only starting from the third child, and for previous children it is paid in the standard amount;
- 6,000 rubles – for individuals who have formalized guardianship or trusteeship of a child with a disability, as well as for adoptive parents;
- 12000 rubles – for natural parents raising a disabled person, as well as individuals who have become adoptive parents of a disabled person.
Please note that there is a certain limit - 350,000 rubles, which prohibits the use of the tax discount. If in any month counted from the beginning of the tax period, the income of the applicant for the deduction is more than 350,000 rubles, then from that moment on, monetary compensation for him is no longer accrued.
1400 rubles
In order to figure out how to calculate the amount of monthly salary after calculating the standard deduction, we suggest considering a specific case. A certain Andreeva Daria Sergeevna, whose salary excluding taxes is 29,000 rubles, gave birth to twins and wants to receive monetary compensation for them. The following mathematical operations must be performed:
- 1400 + 1400 = 2800 rubles - this is the total amount of the tax discount, 1400 rubles for one child and exactly the same for the second;
- 29,000 – 2,800 = 26,200 rubles – this is the total salary, which will be subject to personal income tax at the rate of 13%;
- (26200/100)*13 = 3,406 rubles - this is the amount of income tax that is withdrawn from Daria Sergeevna’s salary every month;
- 29,000 – 3,406 = 25,594 rubles – this is the final monthly salary, taking into account deductions and tax contributions, which the mother of two children will receive in her hands.
Now let’s calculate the salary without taking into account the tax rebate, but with the deduction of personal income tax. Since the personal income tax is set at 13%, we find them from the amount of 29,000 rubles and get the figure 3,770 rubles. Subtracting the result obtained from the total amount of wages, we get 25,230 rubles.
After comparing salaries calculated with the tax rebate (25,594) and without it (25,230), we come to the understanding that a mother of two children, when applying for a deduction, will be able to receive 364 rubles more monthly.
Calculation of deductions for large families
In situations where there are more than three children in a family, the amount that reduces the tax base is calculated in exactly the same way as for one child. However, there is still one difference - this is the amount of the total amount that is deducted from wages until income tax is removed from it.
Amounts of deductions for parents with many children:
- 5800 rubles – the tax base can be reduced by this amount if there are three children in the family;
- 8800 rubles – the amount of deduction provided to parents of four children;
- 11,800 rubles – tax discount for families raising five children.
Further, to get the amount of the deduction for six children, it is enough to add an amount equal to 3,000 rubles to the amount of 11,800 rubles. Thus, in the event of the birth of each subsequent child, 3,000 rubles will simply be added to the amount of the tax discount.
It must be remembered that the deduction is provided only for children who have not yet turned eighteen years old, or for students of children under 24 years of age. If there are three children in a family, and one child is an adult and does not study anywhere, then the tax authorities will issue compensation only for two.
General rules for calculating personal income tax
The general rules for calculating personal income tax are established by the provisions of Art. 225 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
1. To calculate personal income tax for the tax period, all income subject to income tax is determined (clause 3 of Article 225 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. For each type of income, the tax rate should be clarified in accordance with Art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
3. The tax base for personal income tax for the tax period is calculated. It must be remembered that in order to calculate personal income tax when applying several tax rates, the tax base is calculated separately for each type of income.
How to calculate it correctly
How to find out what taxation system an individual entrepreneur is on - is it possible to check?
The declaration for the tax period is the main document that displays factual information regarding the actual income received. This is an official statement to the state about the results of business activities of a particular entity. The declaration is signed by the entrepreneur to confirm the completeness of the information provided.
For contributions
With UTII
In this case, real income may differ from the estimated or imputed one. To confirm it under such circumstances, two main documents are used:
- patent;
- a book of accounting for expenses and income from business activities is a prerequisite.
In the case of a book, the following requirements are imposed on the document:
- lacing;
- numbering;
- certification with a seal;
- in some cases, a tax stamp is required, otherwise the information will not be considered correct regarding revenue or profit.
For your information! The tax office puts its stamp only if you give it at least one copy of the accounting book. If the UTII system is used, there is no alternative to the above solutions, even if there is a significant difference between real and imputed income.
On OSNO
Here, the income received by the individual entrepreneur is taken into account minus the VAT charged to customers. The picture is even simpler if the participant in the transaction is exempt from VAT. In this case, income and revenue are the same numbers, which are not difficult to calculate.
The amount of annual income is usually taken from the fourth section of the accounting book for any business transactions. In the 3NDFL declaration, line number 030 is used to record the relevant information. The information is also displayed as part of the annual reporting; they are used when it is necessary to determine alimony.
Note! The calculation of the additional insurance premium for the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation deserves special consideration. Then professional deductions or accepted expenses contribute to a decrease in overall income.
simplified tax system
If an entrepreneur works on the simplified tax system, then he receives income:
- non-operating;
- sales for the year.
Determining the final figures involves using the so-called cash method. Everything will be easy to calculate.
simplified tax system
Annual income is the figure from column 4 KUDiR. 113 or 213 are declaration lines where such information is required to be displayed. They need to be calculated in advance.
PSN
The patent system is considered a simplified option for paying taxes and interacting with regulatory authorities. The main subjects for this taxation option are representatives of small and ultra-small businesses. But there are some features that you need to know about in advance:
- the patent is calculated based on the approved amounts for potential income;
- there are restrictions on the amount of actual revenue and the amount of hired labor;
- contributions are paid separately. Supervisory authorities give recommendations on how to solve the problem.
Important! Potentially possible income in this case is called the estimated amount approved by the regional authorities for tax purposes. This is a hypothetical profit, in relation to which taxes established by the state apply.
There are two options by which this indicator is calculated in the case of patents.
- when an individual entrepreneur does not have hired workers, there is only one object of taxation. Then just look at the information in your Personal Account on the Federal Tax Service website;
- It’s another matter when there is hired labor or several objects for taxation. Then everything is more difficult to check.
For your information! Depending on the number of employees, local authorities may increase the amount of calculated income. In this case, the standard rate of 6% is multiplied by the estimated number of units covered by the scheme. It is better to find out the features of the formula in advance.
Regional laws or deflator coefficients are the most important indicators when it comes to changes in income; they must be checked. The main thing is to check the necessary information in time and carry out an inspection. Then everything is simple to calculate.
How to calculate personal income tax on wages in 2020
In order to calculate personal income tax on wages, you need to use a special formula, which looks like this:
N = PS x OS, where:
N - personal income tax, PS - interest rate, OS - taxable amount.
Please note that in order to determine the fixed assets, it may be necessary to make additional calculations due to the fact that tax deductions may be used on the income side.
OS = DC - V, where:
DC - income part of the person, B - deductions.
An example of calculating personal income tax from salary without deduction:
Citizen Ivanov A.S. receives a salary of 35,000 rubles. It is necessary to find out how much his monthly personal income tax will be.
In this case, the calculation of personal income tax in 2020 is made from wages, which means at a rate of 13%. Thus:
35,000×13% = 4,550 rubles.
In this amount from citizen Ivanov A.S. Personal income tax will be withheld every month. His net income will be:
35,000 - 4,550 = 30,450 rubles.
As you can see, calculating the personal income tax amount is quite simple.
Example with deductions
In the example below, we will consider how to calculate personal income tax on employees’ salaries if deductions are allowed for 3 children.
Example conditions:
Sidorova N.N. one is raising three children, the first of whom is 12 years old, the second is 14 years old, and the third is 21 years old and is studying at a university as a correspondence student.
In this case, personal income tax deductions rely only on the two youngest children, since the eldest has already reached the age of 18 and is not a full-time student.
Sidorova's salary is 40,000. How to calculate income tax on her salary under such conditions?
Calculation:
Per month, the amount of the monthly personal income tax benefit for two children will be 1400 + 3000 = 4400 rubles. (the eldest is also taken into account when calculating birth order, despite the fact that no benefit is provided for him).
Since we are talking about a single mother, the deduction doubles and amounts to 8,800 rubles.
Per month, personal income tax will be withheld from her salary in the amount of:
(40,000 (salary) – 8,800 (deduction)) × 13% (personal income tax) = 4,056.
The amount of salary received by Sidorova N.N. will be:
40,000 (salary) – 4,056 (personal income tax including deduction) = 35,944.
Provided that the salary has not changed since the beginning of the year, in September Sidorova’s total income will exceed 350,000 rubles, and she will lose the right to personal income tax benefits. Her net income from this month will be:
40,000 (salary) – 40,000 × 13% (personal income tax) = 34,800.
Certificate and calculation of 2-NDFL
Certificate 2-NDFL is a document in which a person reflects his income, wages and the amount of taxes paid.
The 2-NDFL certificate must contain the following information:
- employer information;
- employee information;
- income taxed at a rate of 13%;
- tax deductions;
- calculations of taxes, income and deductions.
An example of data entered into the 2-NDFL certificate:
Citizen Petrov S.N. has a monthly income of 55,000 rubles. Child deductions (5 years old) are applied to his salary. Let's consider what calculations in this case need to be made to fill out the 2-NDFL certificate.
Calculation of annual income
55,000×12 (months) = 660,000 rubles (per year).
Tax deduction calculation
The deduction per child is 1,400 rubles. In 2020, you can use the benefit with an income not exceeding 350,000 rubles (for 2020, they plan to raise the maximum income bar by 50,000 rubles to 400,000 rubles), which means you need to calculate how many months Petrov can use the child deduction:
350,000 / 55,000 = 6 months.
Calculation of the amount of deduction for the year
6 months x 1,400 rubles = 8,400 rubles.
Let us subtract the amount of deduction from the total annual income:
660,000 rubles - 8,400 = 651,600 rubles.
Calculation of tax paid
653,000 rubles x 13% = 84,704 rubles.
Thus, S.N. Petrov, having calculated the personal income tax, must enter the following information into the 2-personal income tax certificate:
- tax amount - 84,704 rubles;
- income - 660,000 rubles;
- the amount of deductions is 8,400 rubles.
Reducing personal income tax when calculating wages
How to reduce the tax burden on wages if there are children in the family?
If there are one or more children under 18 years of age or full-time students under 24 years of age in a family, persons receiving taxable income are entitled to a fixed tax deduction.
Due to this benefit, the tax burden on the employee is reduced. What to do if the required deduction is more than the salary?
Standard benefits apply only until the month in which the total salary amount does not exceed 350 thousand rubles in total since January. In subsequent months, the right to this type of benefit is lost until the end of the year.
Not only natural parents, but also adoptive parents, as well as guardians and trustees, that is, everyone who legally raises children in their family, are entitled to this type of standard deduction.
If a deduction for children has not been provided for the current year, then you can apply to the Federal Tax Service for a refund next year.
Example:
If the employee Ivanov A.A. One minor pupil has the right to a benefit in the amount of 1,400 rubles. per month.
Let's assume that his annual contract income is: 20,000 × 12 months = 240,000.
The full amount of income tax at a rate of 13% will be equal to 31,200 rubles, and his net income in hand:
240000 – 31200 = 208800.
If in this situation we apply a deduction for one in the amount of 1400 rubles. per month or 16,800 per year, then the amount of personal income tax for the entire year, taking into account the deduction, will be:
(240000 – 16800) × 13% = 29016.
And the employee will receive:
240000 – 29016 = 210984.
Amount of non-taxable amount in 2020
A deduction is an amount of income on which income taxes are not withheld.
Their sizes for children are indicated in paragraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What amount is not subject to income tax if there are minors (or students under 24 years of age):
- 1400 – applies to each of the first two children;
- 3000 – applies to the third and subsequent ones.
If a student is diagnosed with a disability, then in addition to the non-taxable amounts indicated above the following is added:
- 12,000 – for natural parents, adoptive parents;
- 6000 – for guardians, adoptive parents.
Important! Personal income tax is not taken from the indicated amounts, so income tax will be calculated from the difference between the accrual and deduction.
Receiving the child tax benefit
To receive the required state deductions if you have children in order to reduce the tax burden, you can go in two ways:
- Submit an application for deduction to your employer's accounting department. The form must be accompanied by a birth or adoption certificate, marriage certificate, and documents confirming that the children are full-time students at a university. If a parent applying for a benefit is registered with several companies at the same time, then he can submit an application only with one company.
- If time is lost, and the company did not apply deductions when paying salaries, withholding tax in excess, then you can contact your tax office at your place of registration within 3 years with an application for a refund of the excessively withheld income tax. The application will need to be accompanied by a 3-NDFL declaration, completed manually or using online services. The same documents are attached to the declaration as when applying to the accounting department, only a certificate from the place of work in form 2-NDFL is added for the year for which the deduction is claimed.
In the first case, the tax benefit will allow you to immediately receive a larger salary. In the second case, the tax that was withheld in excess of the required amount will be returned by the state 3-4 months after filing the tax return.
Calculation if there is one minor
The non-taxable deduction amount for one child is set at 1,400 rubles per month.
If an employee timely submits an application to his accounting department for a standard deduction, the company will begin to take it into account with each salary payment.
Example:
After receiving the application, when calculating the amount of personal income tax from the amount of the salary of V.V. Petrova, an accountant from a salary of 35,000 rubles. will deduct 1,400 rubles before calculating 13% and withholding tax.
As a result, the amount of income tax due will be as follows:
(35000 – 1400) × 13% = 4368.
And the employee will receive a salary as net income:
35000 – 4368 = 30632.
In this case, the total income of Petrov V.V. for 10 months from January to October will be 350,000 rubles. According to the norms of Russian legislation, from October the right to deduction will be lost, and the full amount of income tax without benefits will be calculated from wages for this month.
If there are two people in a family
How much is deducted from wages if there are two minor children in a family?
The amount of personal income tax deductions for the first and second child is 1,400 rubles each. per month for each or 2800 rubles. for two at once.
A timely declared right to this benefit in the presence of two minors will allow you to save an amount of 4,368 rubles on personal income tax. in year. It is calculated as follows:
2800 (benefits) × 13% × 12 months = 4368.
This statement is true that for the entire year the employee’s total income since January did not reach 350,000 rubles.
If there are three or more
For large families, an increase in the tax-free amount of income is provided in order to reduce the tax burden on them and increase the income received.
In large families, a personal income tax deduction in the amount of 3,000 is added to the third and each subsequent child.
The total deduction per month for three will be:
1400 + 1400 + 3000 = 5800 rub.
This means that for a full year of applying the tax-free amount for three children, you can save 5800 * 13% * 12 = 9048, if your income does not exceed 350,000 rubles.
If before the birth of a minor in the family, the spouses each had 1 child from previous marriages, then the child born is considered the third.
From a single mother
If children are raised by a single parent, usually a single mother, then she has the right to receive a double personal income tax deduction.
So, if a single mother is raising three children, then the total deduction for her will be 11,600 rubles. per month:
(1400 + 1400 + 3000) × 2 = 11600.
The annual personal income tax savings will be (if the total salary limit is not exceeded):
11600 × 12 months × 13% = 18096.
Calculation of 3-NDFL
Certificate 3-NDFL is a special document intended to be filled out by certain categories of persons (for carrying out activities that are related to a certain type of income). Such persons include:
- persons who independently calculate taxation (lawyers, individual entrepreneurs);
- residents of the Russian Federation (whose income was received outside of Russia);
- persons with additional income (profit).
The above categories of citizens are required to annually provide the tax service with information about the income received and the taxes that were paid on it.
It should be noted that this document makes it possible to apply for the use of a deduction. To receive it, you need to make the necessary calculations and indicate the amount to be returned.
An example of calculating personal income tax in 2020
Citizen Sidorov bought an apartment worth 1,700,000 rubles. This purchase was subject to tax. At the end of the year, Sidorov plans to submit an application for deduction. Let's calculate what the amount of the deduction will be. The operation was taxed at a rate of 13%.
1,700,000×13% = 221,000 rubles.
Thus, Sidorov will indicate in the 3-NDFL certificate the deduction amount of 221,000 rubles. In addition, to receive a deduction, you must have all supporting documents (purchase agreement, receipts, etc.).
What is included in total income?
Cumulative is the return for a specific period of time. This indicator combines all forms of profit, both in material (monetary) and intangible forms. If a person receives some property, then the official price is used when calculating the final amount.
Because this amount is taxable, it does not include tax-exempt payments. These are pensions, subsidies, payments to cover damage, social benefits.
This indicator can be used in various concepts:
- For individuals. In this case, the result consists of the sources of profit that an individual has - salary, pension, inheritance received, profit from business, borrowed funds, proceeds from the sale of property.
- For a legal entity. Includes the amount of revenue that was received during the reporting period.
- Family. It is the sum of incoming transactions that all family members receive. This calculation is used when determining whether a family is low-income. In this case, the average annual family income is calculated (salaries and other types of funds received are summed up, and then the result is divided by the number of relatives). If the amount is lower than the minimum established by the state, the family is considered poor.
- Monthly. It is calculated in cases where family solvency is determined (obtaining a loan, subsidies, compensation for utility bills).
When calculating, the following are summed up:
- Salary (received in person - with all allowances and minus fees).
- Benefits and forms of financial assistance.
- Maternity payments.
- Alimony.
- Pension.
- Scholarship.
- Insurance payments.
- Profit for doing business.
- Social payments.
- Interest on bank deposits.
- Profit received from the rental of property.
- Funds received from the sale of securities.
- Funds received from the sale of property.
- Received inheritance.
- Property received as a gift.
Calculation of funds
Only those funds that a person received for the sale of their own home are not taken into account if they were immediately spent on the purchase (reconstruction, construction) of a new home for living.
Calculation of penalties for personal income tax
For late payment of personal income tax, fines are provided in the form of a penalty, which is calculated according to the formula:
Penalty = Arrears X Refinancing rate (key rate) valid during the period of delay X 1/300 X Number of days of delay
The penalty is calculated for each subsequent day after the deadline for paying taxes.
Example
Citizen Elkin was 8 days late in paying taxes. The amount of mandatory payment was 2,800 rubles. Let's calculate how much penalty will need to be paid along with the main tax.
1. Calculation of the amount of fines for one day:
2,800 rubles X 7.75% X 1 / 300 X 1 = 0.72 rubles.
2. Now let’s calculate the total fine for all days:
0.72 rubles X 8 days = 5.79 rubles.
If the delay in payment of personal income tax was more than 30 days, say 36 days, then the calculation of the penalty will be as follows:
(2800 rub. x 7.75% x 1/300 x 30 days) + (2800 rub. x 7.75% x 1/150 x 16 days) = 44.85 rubles.