Employee Bonus Deprivation Act 2020?
Labor legislation (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) gives the concept of wages as remuneration for work performed depending on:
- conditions;
- quality of execution;
- employee qualifications;
- as well as other incentive and compensation payments.
Bonuses are precisely incentive payments. However, when establishing any additional payments in favor of employees, the employer must be guided by its local acts, which follows from the text of Art. 135 Labor Code of the Russian Federation .
The system of remuneration and bonuses in the organization is established:
- collective agreement;
- local regulatory documents;
- stated in the employment agreement with employees.
All of them must not contradict current labor legislation.
The bonus can be an incentive for conscientious work or a component of wages. In any case, it is established by order of the employer, indicating the employees subject to bonuses, the amount of the bonus and the calculation procedure.
Local documents of the organization also establish the possibility of depriving employees of bonus payments, and prescribe cases and grounds when such a procedure can be applied.
What is a bonus deduction clause?
Sections of the regulation on bonuses
In order for the deprivation of an employee’s bonus for errors in work activity to be legal, it is necessary to correctly prepare a provision on the deprivation of bonuses to employees. This is an administrative document approved by order of the manager.
It is recommended to specify the following nuances in the regulatory act.
Section "General provisions". Regulatory and legislative acts are indicated. Here you should include a link to labor legislation, as well as other regulatory documents. It is imperative to indicate the goal, for example, to stimulate high-quality performance of employees’ production tasks and prevent defects in work and other negative events.
In the general section, you can indicate the algorithm for depriving employees of bonuses, namely: when the fact of this case was recorded; what document needs to be drawn up; where to report what happened; which manager will make a decision on this matter, as well as the publication of an administrative document on the punishment of the employee. It is necessary to familiarize the employee and his immediate supervisor with the issued order, so that the former knows why he was punished.
In the “Rights and Responsibilities” section, it should be clearly stated that violations must comply with legal requirements, otherwise the employer may be held liable.
Reasons for deprivation of bonuses
Labor legislation does not establish the grounds and procedure for deprivation of bonuses, as well as the amount of reduction in incentive payments. They are determined by the employer independently within the framework of his organization and secured by relevant regulations. Typically, the reason for deprivation of bonuses is directly related to the performance of labor functions, for example:
- delay in performance of work or provision of services;
- failure to fulfill the work plan for a certain period for which the bonus is calculated;
- refusal to comply with management orders within the scope of official duties;
- the presence of a disciplinary action within the time period for which the bonus is awarded;
- failure to comply with safety regulations;
- deviation from the production process, as well as the production of defective products;
- establishing shortages, identifying cases of theft and criminal prosecution in this regard.
Let us note that deprivation of a bonus is the result of a violation of labor order or discipline; it must only be thorough. The grounds for deprivation of bonuses must be listed in the organization’s document regulating the bonus system. Otherwise, the court will consider the employer’s actions illegal.
Employer's liability for illegal deprivation of bonuses
What if the employer illegally deprived the employee of his bonus?
Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides that for violation of labor legislation, an administrative penalty in the form of a fine may be imposed:
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
- for an official and individual entrepreneur - from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for organization - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
If an offense under this article is committed repeatedly, the punishment is as follows:
- official - fine from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. or disqualification from 1 to 3 years;
- Individual entrepreneur - fine from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- organization - from 50,000 to 70,000 rubles.
If an employee's salary or other payments are delayed, the employer is obliged to pay them with interest, which is accrued in the amount of 1/300 of the current refinancing rate for each day of delay.
At the same time, the payment of compensation is not related to the presence/absence of the employer’s fault.
Who should not be deprived of a bonus?
The legislation does not establish a list of categories of workers to whom bonus reduction cannot be applied.
Just keep in mind that deprivation of a bonus is not a disciplinary sanction. Art. 192 of the Labor Code strictly defines the list of disciplinary sanctions, these include:
- comment;
- rebuke;
- dismissal.
But the regulatory document of the organization can provide for a reduction in bonuses based on the results of the imposition of a penalty, observing the sequence: imposing it for a misdemeanor, and then depriving the bonus for the presence of a penalty.
There is also a time period during which a person who has violated discipline can be deprived of bonus payments. This is a calendar month from the date of the commission of the offense and its documentation.
Why can a bonus be deprived?
First, you should determine that the bonus is part of the employee’s additional salary. And if it is accrued and paid, they no longer have the right to withhold it. Unless a counting error is discovered, or the court determines that its payment was illegal.
But there are also some features that should be remembered. The bonus is not calculated automatically. Usually, in order to obtain it, it is necessary to fulfill a number of indicators provided for by the enterprise. Only after this does the employee have the right to such a payment. Indicators are determined in the Regulations on Bonuses, which is an integral part of the collective agreement.
This approach does not mean that the employee is always required to pay a bonus. Its size may be reduced or not paid at all under the following circumstances:
- the presence of a disciplinary sanction (reprimand);
- failure to meet one or more bonus targets;
- the presence in the Regulations on bonuses of conditions for reducing the achieved bonus indicators (violation of labor protection conditions, injuries, theft);
- dismissal of an employee in the middle of the month. It doesn't matter on whose initiative this happened. The bonus will need to be calculated in proportion to the time worked;
- the presence of other conditions that negatively affect the final result of the work of a particular unit.
Here it is necessary to take into account that such conditions must necessarily be present in the Regulations on bonuses. If this is not the case, then the presence of a reprimand is not an obstacle to limiting payments in the form of bonuses.
Remember, the administration may reduce or, under certain conditions, not award a bonus to an employee. It is prohibited to deprive (withhold) bonus payments “retroactively” (except for cases expressly provided by law).
Step-by-step instructions for depriving an employee of a bonus under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The employer has the right to independently establish the procedure for depriving bonuses in its regulatory documents. If it is fixed, then it should be strictly followed, otherwise the employee will be able to challenge the legality of the bonus deduction in court.
Recommended course of action:
- The heads of structural units or the head of the organization can initiate a reduction or deprivation of bonuses. In the first case, an official or memorandum with the reason for the deprivation of bonuses is submitted to the director. The basis may also be an act of misconduct committed by the employee.
- Before making a decision to deprive a bonus, study all the documentation in accordance with which the organization has adopted a team incentive system:
- local documents regulating the bonus procedure. From their text it should be clear that the payment of bonuses is of an incentive nature and is not a guaranteed payment. It is also important to note that the employer decides to pay it depending on the results of the team’s work and the activities of the organization as a whole, establishing the appropriate amount;
- employment contract. If the employer fixes the payment of the bonus in a fixed amount and stipulates this in the employment agreement with the employee, then it cannot be deprived. It is more expedient to indicate in the contract that the bonus is a payment that is established by the decision of the employer and in a manner consistent with local regulations;
- collective agreement. The employer has the right to provide for a system of incentives for employees through a collective agreement.
- The employee may be asked to provide a written explanation as to why a situation occurred that resulted in non-compliance with the terms of the employment contract.
- If the grounds comply with the conditions for deprivation of bonuses prescribed in the local acts of the organization, an order for deprivation is issued.
Employer's order
The content of the manager's order should be as follows:
- Full name and position of the employee (or several employees) who, based on the results of the period, are deprived of the bonus in whole or in part;
- the period for which the premium will not be paid;
- the basis on which such a measure is applied with reference to the document where it is provided.
Documents that are the basis for depriving the employee(s) of a bonus are attached to the order. They are listed in the text of the order and stored with it. This is necessary to prove the legality of the employer’s action if the employee goes to court.
It is prohibited to impose a disciplinary sanction and deprivation of a bonus on an employee with one order. In this case, first a “disciplinary notice” is issued and only then a depreciation.
It is mandatory for the employee to familiarize himself with the order against signature.
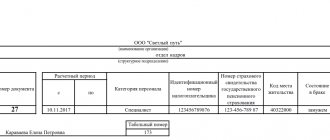
Sample order to deprive an employee of a bonus in 2020
Sample order for deprivation of a monthly bonus due to disciplinary action:
Sample order for deprivation of bonuses for violation of labor discipline (reprimand):
Supporters and opponents: desired and reality
The topic of monetary punishment leaves few people indifferent. Therefore, managers are divided into two camps: supporters and opponents of deprivation of bonuses. Perhaps both sides are right. “Opponents” say: “a manager must be able to create a “problem” for a subordinate even with a verbal warning - a reprimand, for example”
. I certainly agree with this. But, alas, this skill is not available to all managers.
Verbal persuasion is somewhat akin to hypnosis. To achieve results, you need to be an extra-class professional.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that authorization (punishment) is part of the list of actions performed by line managers, i.e. so-called “middle management”. Their managerial qualifications often leave, to put it mildly, much to be desired, because these positions are usually occupied by the “most capable specialists,” but rarely by professional managers . Yes, it is certainly necessary to cultivate real managers from middle management. And the grade system can help with this. It is described in detail in the article “The Grade System, or How to Raise Professional Managers and Employees.”
Deprivation of bonuses is not a panacea, and in no case does it negate the manager’s managerial competencies (motivation, presentation of decisions, operational motivation, etc.), as well as other types of punishments, as well as incentives. The list of manager competencies can be studied in the article “Key competencies of a manager for effective management of subordinates - a “scary” checklist for self-examination and assessment.”
Go to contents
In what cases will deprivation of bonuses be considered illegal?
Deprivation of bonuses to employees is considered illegal in the following situations:
- the basis on which the bonus was deprived is not in the corresponding list in the local regulatory act of the organization;
- an order has not been issued in accordance with which the bonus is deprived;
- the employee is not familiar with the order (order) imposing deprivation of bonus payments on him;
- the procedure for deprivation of bonuses due to the imposition of a disciplinary sanction was not followed (read above).
In such cases, the employee has the right to challenge the deprivation of the bonus in accordance with Art. 392 TK. It can be done:
- in court no later than 90 days from the date of establishment of a violation of the law by the employer;
- pre-trial, the employee has the right to resolve the situation through the Labor Inspectorate.
Deprivation of bonuses to employees: approaches and design
Enterprises can use a system of depreciation of employees in order to increase labor efficiency. But such a method of censure must be introduced taking into account all the requirements of the law and fair treatment of all subordinates. Otherwise, undesirable consequences are possible: from administrative fines to reduced business income.
Many organizations reward their staff for good achievements at work (exceeding standards, high quality work) with bonus money.
This encourages subordinates to constantly strive for the best results and improves the efficiency of the business as a whole. The accrual conditions, types and amounts of such bonuses are prescribed in internal regulatory documents. Of course, deprivation of bonuses to an employee is possible if a disciplinary offense is committed.
It implies deprivation of the full or partial amount of the bonus that comes with the salary.
Deductions can be made, for example, in the following cases: