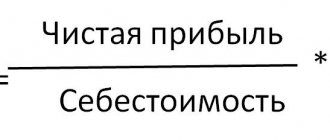
What is accounting profit
Accounting profit is the total income of an organization for the past period, implying a positive financial result, which is calculated for the past period, minus all expenses incurred for the production and sale of products. Accounting statements are usually prepared quarterly and for the year as a whole. In this case, all business transactions carried out at the enterprise are taken into account.
The concept of accounting profit contains two basic principles:
- Saving capital is a principle based on increasing the well-being of the enterprise as a whole. In other words, the accounting department keeps records of funds that are an emergency reserve for the enterprise and are not wasted unless absolutely necessary.
- Capital building is a principle that involves increasing the capital of an enterprise. Here is a comparison of cash inflows and outflows. Based on these indicators, the accountant makes a conclusion about the advisability of adjusting the activities of the enterprise.
To improve the results of enterprise development, in practice, as a rule, both principles are used.
Let's consider what the essence of accounting profit is. Any enterprise makes a profit over a certain period of time. If it does not exist, the company may go bankrupt. The manager must know what income and expenses are generated in his organization in order to compare them and identify the financial result. There are two types of profit: accounting and economic, which have significant differences between themselves. To obtain an overall picture at the end of the reporting period, it is necessary to calculate these indicators as a whole.
What is the difference between accounting and economic profit?
Accounting profit is calculated simply. They take all the income of the enterprise for the reporting period and subtract the expenses that go towards the purchase of raw materials, production and marketing of goods or services. But this has its drawbacks. With this calculation, it is not always possible to accurately compare results and profit indicators. Inflationary losses are not taken into account. Accounting profit cannot accurately predict how changes in capital will occur in an enterprise over time.
Accounting profit is calculated on certain approved forms. Subsequently, this data is provided to the tax authorities for verification.
Calculating economic profit gives a more accurate financial result. It is also calculated by the difference between income and expenses, but other financial transactions are also taken into account. This is the profitability of an enterprise, which reflects the degree of efficiency of all resources, the cost of investment, and income from investment activities. Based on economic indicators, you can most accurately assess the efficiency of the enterprise as a whole and determine how stable it is.
Formula for calculating accounting profit
The amount of accounting profit is calculated as the difference between revenue from sales of products, goods or services and the external costs of the enterprise. Let us introduce the following notation:
BP = B – VI, where
BP – accounting profit;
B – sales revenue;
VI – external costs.
External (explicit) costs are payments for resources that are not the property of the enterprise. This may include the costs of paying employees, purchasing raw materials and materials, paying for rented premises, depreciation of fixed assets and utilities.
Economic profit is different from accounting profit. It is calculated as the difference between revenue from sales of all products and economic costs, which consist of explicit and implicit (external and internal) costs.
EP = B – EI, where
EP – economic profit;
B – sales revenue;
EI – economic costs.
Internal (implicit) costs are the costs associated with the use of all resources owned by the enterprise. This indicator is associated with lost profits. For the manager of an enterprise, these are expenses incurred to pay for the labor of personnel servicing production. If the employer could do all the work himself, there would be no need to make such expenses.
Capital owners invest their funds in business development, thereby incurring certain losses. If, for example, free funds are invested at interest, they will begin to generate income. Financial losses here are calculated as the lost percentage of the investment. For entrepreneurs who own real estate, the cost is rent.
Economic, accounting and normal profit
Economic profit is the difference between the company's profit and the company's expenses - explicit and implicit.
EP = TR - TC,
de ER – economic profit;
TR—zagalny vitorg;
TS = EU ІС,
de EC - clearly vitrati;
ІС - implicit deductions.
Accounting profit is the difference between hidden profits and obvious expenses of the company. Such an income is also called a disbursement income, because at the time of its calculation, the penny payments are insured, which are recorded in the accounting records of the company.
AcP=TR-EC,
de AsR – accounting profit;
The EU is clearly a waste.
Normal income is the minimum income that an entrepreneur can earn in order to lose money from his business. This is a fee for the implementation of administrative functions. One can also say that what is the income, what kind of power of the company can be taken away by investing their resources in another business, the other power resources of their company.
For zero economic profit, the company covers all its expenses - explicit and implicit. A company with EP = 0 is such that it has withdrawn normal profits (NP), which covers part of the company’s implicit expenses. If a company cannot fully cover its economic expenses, its owners will seek the best alternative resource allocation between companies.
Normal profits will be high enough so that existing firms are forced out of the market, and low enough so that new firms cannot enter the market. Normal income reflects an implicit expense item.
Normal income is partly of the firm's illegal economic expenses, a payment to the manufacturer and manager for preventing the drain of resources from the given waste into another. There will be any excess over the illegal economic expenses and economic profits. Economic income is not included in the waste, but instead is income, deductions from the foreign waste of companies.
economical expenses and great profit
Profit is the main indicator of the efficiency of a business operation. The absolute size of the profit is not a sufficient basis for characterizing the value of a business. The amount of profit that entrepreneurship generates lies (behind other equal minds) in the work of recruitment, which attracts many officials. Therefore, the efficiency of the enterprise is determined by the main indicator, which reflects the stage of profitability of one hundred percent of the other production factors. This indicator is profitability.
The profitability of an enterprise is calculated as the return on income to the cost of the main production and working capital, expressed in hundreds.
The level of profitability is often called the normal profit. This indicator allows us to compare the efficiency of work of various enterprises.
In addition to the profitability of the enterprise, to determine the effectiveness of the production of other speeches, calculate the profitability of the product. The level of profitability of the product is calculated as the relative income from the sale of products before expenses This is what vibrancy is all about.
| Zagalny Vitorg | 50,000 UAH. |
| for virahuvannyam obvious vitrat | |
| Salary | 20,000 UAH. |
| Variety of raw materials and materials | 10,000 UAH. |
| Accounting profit | 20,000 UAH. |
| for virahuvannyam of implicit vitrat | |
| Lost wages | 10,000 UAH. |
Factors affecting profit
Thus, we can identify the main factors that influence increasing the profitability of an enterprise. They are divided into two types:
- Internal factors that influence the amount of profit by increasing the volume of products produced, selling them, improving them, increasing prices and reducing costs.
- External factors that do not depend on the operation of the enterprise and have virtually no effect on the amount of profit.
The first category, that is, internal factors, includes the following indicators:
- level of business activity;
- labor productivity at the enterprise;
- quality and competitiveness of products or services;
- professional qualities of managers and specialists;
- level of enterprise efficiency;
- planning and forecasting financial results.
The second category, external factors, includes:
- production factors showing the availability and use of labor and financial resources in production;
- non-production factors related to the sales and supply function, social conditions of work, and environmental measures.
Production factors are divided into two subtypes:
- extensive , which affect the extraction of profit in quantitative terms: financial resources, number of employees, equipment operating time, working time fund;
- intensive , affecting the profitability of the enterprise in qualitative terms:
– modernization of equipment and increase in its productivity;
– programs to increase capital turnover;
– increasing labor productivity by increasing the level of education of management and specialists;
– improvement of labor organization in production;
– reducing the labor intensity of products;
– effective application and use of financial resources.
External factors affecting increased profits:
- economic situation on the market;
- prices for purchased raw materials, materials for production;
- fuel and electricity prices;
- deductions for depreciation;
- state pricing policy, taxes, penalties and benefits provided under labor legislation;
- Natural resources.
In order to find out how the listed factors influence the gross profit of an enterprise, you need to understand what the cost of production is. The cost of a product, work or service is the valuation of all the costs that went into its production. This includes labor resources, raw materials and supplies, fixed assets and natural resources.
Note! When carrying out activities at an enterprise, external and internal factors are in close relationship with each other, and have a direct impact on the value of production costs, and therefore profits, revealing how rationally and economically material resources are used in the enterprise.
How to calculate net profit on a balance sheet
All types of profit are calculated on the basis of revenue, which is equal to the product of sales volume and unit price. Certain cost items are subtracted from primary income and thus each type of profit is found.
Revenue is found using the following formula: TR = P * Q, where
P (price) – price, rub.;
Q (quantity) – quantity of products, rub.
Marginal profit is equal to: MP = TR – VC, where
MP (marginal profit) – marginal profit, rub.;
VC – variable costs for production volume, rub.
Gross profit can be found using this formula: GP = TR – TCtechn, where
GP (gross profit) – gross profit, rub.;
TCtechn (total cost) – technological cost, rub.
Profit from sales is found as follows: RP = TR – TC, where
RP (realization profit) – profit from sales, rub.;
TC (totalcost) – total cost, rub.
Balance sheet profit is equal to: BP = RP – OE OR, where
BP (balanced profit) – balance sheet profit, rub.;
RP (realization profit) – profit from sales, rub.;
OE (other expenses) – other expenses, rub.
Operating profit is calculated using this formula: OP = BP PC, where
PC (percent) – interest payable, rub.
Net profit is found as follows: NP = BP – T, where
The calculation data is provided in the financial results statement. Available information from the financial statements allows you to calculate the two types of profit below using one formula.
Marginal and gross profit can be found using this formula: line 2100 = line 2110 – line 2120, where
line 2100 – gross profit, rub.;
line 2120 – technological cost, rub.
Profit from sales is found as follows: line 2200 = line 2110 – (line 2120 line 2210 line 2220), where
line 2200 – profit from sales, rub.;
(p. 2120 p. 2210 p. 2220) – total cost, rub.
Balance sheet profit is equal to: line 2300 = line 2200 – line 2350 line 2340, where
line 2200 – profit from sales, rub.;
line 2350 – other expenses, rub.
Net profit is found as follows: line 2400 = line 2300 – line 2410, where
line 2410 – amount of tax burden, rub.
Examples of calculations
| Indicator name | Line code | For 2014 | For 2013 |
| Revenue | 2110 | 130 000 | 70 000 |
| Technological cost | 2120 | 45 000 | 25 000 |
| Business expenses | 2210 | 6 000 | 4 000 |
| Management costs | 2220 | 18 000 | 13 000 |
| Other income | 2340 | 1 000 | 800 |
| Other expenses | 2350 | 2 000 | 3 000 |
| Percentage to be paid | 2330 | 6 000 | 4 000 |
| Income tax | 2410 | 12 000 | 5 960 |
Marginal profit: MP = TR – VC = 70,000 – 25,000 = 45,000 rubles
Gross profit: GP = TR – TCtechn = 70,000 – 25,000 = 45,000 rubles
Profit from sales: RP = TR – TC = 70,000 – (25,000 4,000 13,000) = 28,000 rubles
Balance sheet profit: BP = RP – OE OR = 28,000 – 3,000,800 = 25,800 rubles
Operating profit: OP = BP PC = 25,800 4,000 = 29,800 rubles
Net profit: NP = BP – T = 29,800 – 29,800 * 0.2 = 23,840 rubles
Marginal profit: MP = TR – VC = 130,000 – 45,000 = 85,000 rubles
Gross profit: GP = TR – TCtechn = 130,000 – 45,000 = 85,000 rubles
Profit from sales: RP = TR – TC = 130,000 – (45,000 6,000 18,000) = 61,000 rubles
Balance sheet profit: BP = RP – OE OR = 61,000 – 2,000 1,000 = 60,000 rubles
Operating profit: OP = BP PC = 60,000 6,000 = 66,000 rubles
Net profit: NP = BP – T = 60,000 60,00 * 0.2 = 48,000 rubles
In the liability side of the balance sheet there is line 1370 “Retained earnings (“Uncovered loss”). Net profit in the balance sheet accumulates precisely on this line. In order to determine the final financial result, you need to know its value at the beginning and end of the analyzed period. Net profit on the balance sheet formula in this case is as follows
PP = NPkts – NPnch, where
NPnch and NPkts – indicators of line 1370 for the first and last date of the period
However, this formula will allow you to correctly determine the value of net profit only if certain conditions are met. Namely, only in the case when the owners of the company decided not to distribute the profit received during the period. In this case, the change in the value of line 1370 of the balance sheet for the period is equal to the value of line 2400 of the income statement.
PP = NPkts – NPnch D PR,
Where D – dividends paid
PR – other areas for using profits (for example, replenishing the reserve fund)
Those. in this case, it is no longer possible to determine net profit based only on balance sheet data, because This reporting form does not contain information about the use of profits.
As a result of the calculations, it may turn out that the final result turns out to be negative, which indicates that a loss was incurred during the analyzed period.
Despite the fact that the balance sheet, unlike Form 2, is not directly intended to calculate net profit, many of its indicators directly or indirectly affect its value.
Most non-current assets are depreciable assets. The change in their value over the period (if we do not take into account the receipt of new objects and disposal) is depreciation, i.e. company expenses.
A decrease in balances under the item “material inventories” may also indirectly indicate an increase in costs. This indicates that more materials and goods were written off during the period than were purchased.
As for liabilities, only the item “Borrowed funds” directly affects costs. The larger the amount of loans and borrowings, the correspondingly more interest is accrued.
In addition to costs, the profit margin directly depends on revenue. It is almost impossible to determine this indicator from balance sheet data. Indirectly, revenue growth can be evidenced by an increase in accounts receivable and a decrease in accounts payable. But the reasons for such a change in indicators may be other, for example, repayment of previously incurred debt or payment of advances to suppliers of goods and materials.
Calculate the volume of net profit in stages:
- First, you should collect all the costs incurred in the production process - the cost of materials and raw materials, wages and contributions to funds, depreciation of production equipment and intangible assets, energy costs, utility bills, rent, commercial and administrative costs. This is how the cost of production is formed;
- Calculate revenue. She does:
- from the sale of products;
- from investments;
- from the company's financial transactions.
- Using the profit calculation formula “Profit = Revenue – Costs”, the company’s gross income is calculated;
- The intermediate link between gross and net profit is the indicator of profit from sales, which is found by reducing the amount of gross profit by the amount of commercial and administrative costs;
- The value of the profit before tax indicator forms profit from sales, increased by profit from other activities;
- Net profit is calculated by reducing the amount of gross income by the amount of tax and other necessary payments. Only extraordinary expenses incurred are deducted from the net profit figure.
Let us recall that the financial flows of companies are formed not only from trading revenue, i.e., operating activities. Many firms generate income from financing activities and investing. These items must be included in the net profit remaining in the company. The process of generating a company's profit is clearly demonstrated in the Financial Results Report. Based on the principle of its compilation, all companies, regardless of their form of ownership and industry affiliation, calculate profits.
The calculation formula “Profit = Revenue – Costs” is simple and unchanged for any type of profit, but the changing value of costs makes it possible to analyze this indicator from different angles.
The amount of profit is an indicator of how efficiently the organization operates. The amount is subject to the established tax, and the profit and loss statement is part of the mandatory financial reporting documents.
In this regard, it is extremely important to have the skills to calculate the profit of an enterprise.
The organization sells goods, services or works. At the same time, the established selling price is higher than the actual one, as a result of which the company receives a positive difference between prices - income.
During the implementation process, the following scenarios may develop:
- the amount of revenue is higher than the actual cost - a profit is formed;
- the amount of revenue is equal to the cost - no profit is generated, but no loss either: the revenue is enough to cover expenses;
- the amount of costs for the sale and production of goods exceeds the amount of revenue - a loss is formed.
The goal of each enterprise should be, if not to obtain maximum profit, then at least to strive to generate the net income necessary for a competitive position.
Profit is the main goal of entrepreneurship. On the one hand, it has a stimulating nature - both the management of the enterprise and the employees are interested in receiving it. After all, the higher the amount of profit, the higher wages employees can receive.
On the other hand, this expression is not always true. Increasingly, there are cases where profits are exploitative in nature: an enterprise increases profits by reducing wages.
This method may bring some benefit, but the effect will be short-lived.
Profit becomes the only correct method of financing an enterprise: the authorized capital cannot last long without receiving funds. Borrowed money is also not the best option for permanently securing a company.
Having understood that profit is the difference between the total income and expenses of an enterprise in monetary terms, let us consider the structure of profit from the point of view of economics. Main types of profit:
- from implementation;
- gross;
- clean;
- balance sheet;
- marginal.