Why is a work permit required?
To carry out such processes, you need a special document - a work permit. It contains specific production tasks, determines performers, responsible persons, time, place and conditions for carrying out work.
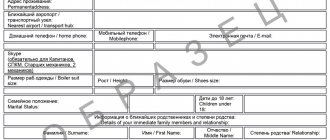
A work permit is issued to a team of workers. After familiarization with working conditions and labor safety instructions, the document is signed by each employee, then signed by the person responsible for the work (foreman). A sample work permit for high-risk work is as follows.
There are significant advantages in the transition from manually signing a work permit to an electronic one:
- for contractors - the ability to prepare sets of documents remotely, thereby eliminating time loss and transportation costs from existing work sites;
- for those responsible for drawing up the document - quick approval;
- for performers – reduction of time for registration.
The time for issuing a work permit in electronic form will be significantly reduced only if the processes are properly organized. Therefore, we decided to consider electronic identification keys as a new signing tool.
Why is a permit required and who issues it?
Before the start of installation or construction on the territory of a certain organization, the subcontractor and the administrative apparatus of the company constructing (operating) this facility are required to first obtain permission.
The lessor or main contractor, when performing actions on the production site that involve tenants or subcontractors, is obliged to:
- together with them, draw up a reliable schedule for the execution of combined actions, ensuring full control over safety during the period of work, mandatory for all enterprises and individuals in this territory ;
- ensure the implementation of labor protection measures common to all companies and the coordination of actions of tenants and main subcontractors in terms of carrying out measures for labor protection and complete labor safety, in accordance with the developed schedule and permission for combined work.
The work permit is issued to the work manager by an authorized person, according to the order of the head of the enterprise.
The work manager, in turn, conducts briefings with the organization’s performers with the corresponding mandatory entry in the work permit.
To carry out certain work in protected areas, a document is issued in accordance with the written permission of the company that owns the facility. The validity period of the document is the period necessary to fulfill obligations in full .
The salaries of employees of any organization are formed taking into account many factors. One of them is the cost of living. Information about what it is is in this article.
If unforeseen circumstances not covered by this document arise during the installation or construction process, production work should be stopped immediately and the permit canceled. Continuation of work is possible only after the appropriate registration of a new permit.
Definition of the concept of work permit.
Permission to work at high risk
When carrying out installation and construction work on the territory of an operating organization, two parties - the contractor and the customer - must necessarily draw up an approval certificate .
In this case, each party individually bears responsibility for the proper execution of the measures specified in the act .
The work order and act indicate the limits of the danger zone.
Knownly dangerous factors include:
- territory located near structures under construction;
- areas for movement of vehicles, movement of equipment and their parts;
- places where goods are moved by cranes.
Carrying out work involving increased danger is permitted only if there are special technological maps or a corresponding work plan containing a list of necessary measures to ensure the complete safety of installers.
When creating your own company, registration is required. Read the publication on the topic: “how to register an LLC yourself” by following the link.
Performing certain work at height with special permission
Before starting work at height, the employer must draw up and approve a list of work carried out at height in accordance with the work permit.
This list reflects all work at heights performed in unstable workplaces.
What should be classified as working at height?
Work of this type, which requires the issuance of an admission certificate, includes the following types of work, in which :
- there is a risk associated with the possibility of a sudden fall from a height of more than 1.8 meters;
- the employee rises to a height of more than 5 meters or descends from a height of more than 5 meters, on a vertical plane, with an inclination angle of more than 75 degrees;
- there is a risk associated with a specialist falling from a height of less than 1.8 meters , if work is carried out on complex mechanisms or machines, various protruding objects and water.
Registration of an individual entrepreneur requires increased attention; it is very important to collect all certificates and other papers on time. A complete list of documents for individual entrepreneur registration is available here.
Who is granted the permit?
This document is required for most construction specialties , such as:
- masons and installers;
- veneerers and molars;
- joiners and carpenters;
- antenna workers and roofers.
Work at height is also performed by most advertising company specialists. Rescuers of the Ministry of Emergency Situations and units of law enforcement agencies. Consequently, almost all production specialists are faced with the need to work at heights.
General requirements for admission.
Is it possible to transfer the work permit into an e-form?
Let us turn to the Order of the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision dated November 20, 2017 No. 485 “On approval of Federal norms and rules in the field of industrial safety “Rules for the safe conduct of hazardous gas, fire and repair work”:
4.2.16. Entries in the work permit for repair work must be clear and readable. It is allowed to fill out the work permit using a personal computer. It is not allowed to fill out the work permit with a pencil. Corrections in the text and signatures of responsible persons using facsimiles and photocopies are not allowed.
The possibility of using electronic signatures when coordinating work permits for repair work is established by the internal documents of the operating organization in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 6, 2011 “On Electronic Signatures”.
It is possible to issue and register a work permit for repairs in e-form. But in order for the electronic form of the work permit to carry out high-risk work to meet all the requirements, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of unauthorized changes to the information in the work permit to carry out repair work, and to ensure conditions for storing the work permit to carry out repairs for one year from the date of its closing.
Thus, filling out the work permit in electronic form is permitted.
Instructions for filling out a work permit for high-risk work
- At the top of the document in the middle of the line its name is written and the essence is indicated, and the number for internal document flow is also entered.
- Then indicate the full name of the organization whose employees carry out high-risk work, as well as the structural unit to which they belong.
- Next, enter the date the work order was written, as well as the date until which it is valid (usually this is the same day, otherwise the permit must be extended).
- We indicate the exact time of the work (here you need to enter the hours and minutes of its beginning and end).
- The next step is to enter information about all employees participating in the work process into the permit order. First, the surname and initials of the responsible work manager and the responsible executor are indicated. Then enter the name of the work. If there are several of them, then it is better to add a table here or indicate all the works as separate items.
- After this, the direct executors are entered into a special table, and they must sign next to their names that they have completed the training. Here you need to put the date of instruction.
The position, last name, first name, and patronymic of the employee who conducted the instruction is entered under the table.
- The next part of the document contains information about the object (here you must indicate its name and actual address)
- Next, you should enter the content of the work (clearly and sufficiently succinctly), the conditions of the work (i.e., those conditions that must be met to ensure safety in the workplace), as well as the methods of additional protection used (usually information about individual safety measures is included here).
- Then the permit entry contains information about factors that may interfere with the work process or affect it in any adverse way.
After entering all the above information, the permit must be signed by the employee responsible for preparing the workplace for work. His position, surname, first name and patronymic must be indicated here.
After all the work has been successfully completed, the fact of its completion must be recorded in the document, thus closing the work permit. Next, the responsible persons must sign the document.
Is it possible to record the completion of training using an electronic signature?
According to paragraph 8 of part 2 of Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide training in safe methods and techniques for performing work and providing first aid to victims at work, conducting labor safety briefings, on-the-job training and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements.
Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that all employees, including heads of organizations, and employers - individual entrepreneurs, are required to undergo training on labor protection and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements in the manner established by the federal executive body authorized by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the opinion of the Russian Federation. tripartite commission for regulation of social and labor relations. Conducting all types of briefings is registered in the relevant logs of briefings (in established cases - in the work permit for production) indicating the signature of the person being instructed and the signature of the instructing person and the date of the briefing.
According to Article 6 of the Federal Law of April 6, 2011 No. 63-FZ “On Electronic Signature”, information in electronic form signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature (ECES) is recognized as an electronic document equivalent to a paper document signed with a handwritten signature and is used in any legal relations in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, except for the case where federal laws or regulations adopted in accordance with them establish a requirement for the need to draw up a document exclusively on paper.”
Thus, we consider it possible to record the completion of training using an electronic signature.
Typical list of works with increased danger
Carrying out work with increased danger means that labor protection requirements must be observed especially carefully.
A typical list of high-risk jobs is established in the appendix to the Instructions on the procedure for training, internship, instruction and testing of workers’ knowledge on labor protection issues. They include the following works:
- Work within areas with constantly operating hazardous production factors.
- Dismantling of buildings and structures.
- Work from suspended cradles and work platforms, mobile lifting work platforms.
- Excavation work in areas with pathogenic soil contamination.
- Work in areas of high frequency currents, electrostatic and electromagnetic fields, using lasers.
- Hot work (electric welding, gas welding, gas cutting, soldering and other work associated with open fire), as well as maintenance, testing and repair of equipment used in carrying out these works.
- Heat treatment of metals.
- Work in existing electrical installations and on overhead communication lines that cross power lines and contact wires or are located on the same supports with them.
- Construction, construction and installation and repair and construction work.
- Work in security zones of overhead power lines, gas pipelines and other underground communications, as well as warehouses of flammable or combustible liquids, flammable or liquefied gases.
- Work in buildings or structures that are in disrepair.
- Work related to the laying and installation of cables in trenches and underground communications.
- Work using manual pneumatic and electric machines and tools (except for pneumatic tools used for mechanical assembly work on assembly conveyors).
- Production of glass and glass products.
- Production and use of chemical fibers, glass fibers and products made from them, asbestos, bitumen-based mastics, glass wool, slag wool, perchlorovinyl, bakelite and similar materials.
- Production of products from plastics and rubber.
- Work performed with the use of toxic, explosive and fire hazardous materials in the preparation of surfaces for painting, painting, drying and processing of painted surfaces.
- Anti-corrosion works.
- Operation, repair and maintenance of vehicles, self-propelled agricultural machines and crawler tractors.
- Forging and pressing works.
- Processing of metals by cutting using metalworking equipment.
- Work with abrasive and CBN tools.
- Work related to the production of rolled products, as well as castings from metals and their alloys.
- Work using pyrotechnic tools and equipment.
- Work on thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines.
- Coating work on parts and products.
- Forestry work.
- Woodworking production.
- Production, storage, transportation and use of pesticides, agrochemicals and herbicides.
- Roofing and other work on the roof of a building.
- Diving works.
- Lime slaking.
- Work with sandblasting and shot blasting machines and installations.
- Work on applying concrete, insulating and bricklaying materials using the spraying and sputtering method.
- Underground and open-pit mining (in mines, mines, during the construction of tunnels and subway stations, collectors and underground structures for special purposes, during the development of mineral resources).
- Work with hazardous substances (flammable, oxidizing, combustible, explosive, toxic, highly toxic).
- Operation, testing and repair of units and boilers operating on gas, solid and liquid fuels, other heat and power equipment, as well as steam and hot water pipelines.
- Operation, testing and repair of pressure vessels.
- Work on testing, adjustment, operation and repair of passenger and freight elevators and escalators.
- Operation, repair and maintenance of lifting cranes, mobile elevating work platforms and other lifting machines and mechanisms.
- Work performed using lifting equipment, and loading and unloading operations using mechanization.
- Operation, maintenance and repair of compressor and refrigeration units, as well as pump and compressor units pumping liquefied hydrocarbon gases.
- Installation, operation and repair of gas supply systems and main pipelines, gas pipelines, process pipelines of gas filling stations, gas distribution points, installation and welding of underground, external and internal gas pipelines, connection of newly installed gas pipelines to the existing gas pipeline, installation and operation of electrochemical protection means for underground gas pipelines, maintenance gas facilities and other gas hazardous work.
- Work on the extraction, transportation and processing of oil, gas and condensate.
- Work in security zones of existing gas pipelines.
- Production, storage, use, loading, transportation and unloading of explosive and fire hazardous and toxic chemicals.
- Work with radioactive substances and equipment containing radioactive substances.
- Measurement work in the radiation zone.
- Work with poisonous, carcinogenic, toxic and other harmful substances, as well as decontamination, disinfestation, deratization and disinfection of premises.
- Operation of cyclotrons, betatrons, ion doping installations, X-ray machines for medical and industrial applications, as well as instruments and devices emitting electromagnetic and other radiation.
- Work with inert gases, acids, alkalis, mercury, chlorine, lead, their compounds, rare earth metals.
- Production and use of biological products.
- Work on the construction of underground structures using special methods (cementation and chemical consolidation of soils and foundations, driving piles, artificial freezing of soils and dewatering, pushing tunnel structures under dams, structures, highways and reservoirs, and others).
- Geological and surveying works.
- Seismic and electrical prospecting.
- Erosion of rocks using hydraulic monitors and other means of mechanization.
- Work in confined spaces (wells, pits, pits, bunkers, chambers, tanks and underground utilities), as well as under water and in trenches at a depth of more than two meters.
- The work is top notch.
- Maintenance of swing gates and mechanically driven gates.
- Work on the manufacture and use of pyrotechnic products.
- Work of fire crews with anti-hail, powder charges and meteorological missile launchers.
- Servicing certain types of animals (bulls, dogs, wild boars, stallions and others), working with wild animals.
- Work in traffic services, tracks, rolling stock, tunnel structures, signaling and communications of subways.
- Operation, maintenance and repair of rolling stock and railway transport structures, urban electric transport.
- Operation, maintenance and repair of centrifuges, conveyors, aspiration and pneumatic transport systems.
- Work performed on and above water, on sea and river vessels, at crossings (ice, ferry, boat).
- Operation, maintenance and repair of aircraft.
- The work of circus performers and stuntmen.
- Work in infectious diseases, tuberculosis and psychoneurological healthcare organizations, as well as in contact with microorganisms, pathogens of infectious diseases and AIDS.
- Work on catching dogs and other animals.
- Emergency rescue operations, fire extinguishing, liquidation of the consequences of floods and other natural and man-made emergencies.
- Work on the operation, maintenance and repair of water supply and sewerage structures and networks.
- Work on the operation and repair of equipment and machines for washing and drying clothes of infectious patients, special clothing contaminated with radioactive substances, radioactive waste disposal sites.
- Protection of objects of any form of ownership.
- Excavation work carried out in the area where underground communications are located.
- Reception, storage and shipment of petroleum products.
- Agricultural, wood chemical, forestry, construction work carried out in areas contaminated with cesium-134, -137 over 5 Ci/sq.m. km.
- Work in the zone of dangerous (above the established maximum permissible levels) action of ultrasonic, infrasonic, electromagnetic and other fields.
- Drilling and geological exploration work.
- Operation, maintenance and repair of road, construction, earth-moving machines and mechanisms.
- Work carried out in the polar regions of the Earth.
- Carrying out work using industrial mountaineering methods.
An ergonomic solution to the problem of electronic signing
Imagine that the entire team gathers in one room, equipped with a separate personal computer with an electronic key reader connected to it.
After listening to the instructions, employees take turns approaching the reader and applying electronic identification keys - the system records information about the signing of the document by each of them. After this, the document is signed in the same way by the foreman and sent to the contractor.
Technically, “signing” is expressed in the formation in the system of many enhanced unqualified electronic signatures (UNEP) of workers and an enhanced qualified electronic signature (UEC) of the master.
A strong electronic signature (rather than a simple one) was chosen for two reasons:
- Permit orders are used to ensure labor safety, therefore their correct execution, compliance with requirements and briefing of the team of workers are important for the employer.
- The document will participate in electronic exchange between organizations (customer and contractor), so it is necessary to secure its legal significance.
Is it possible to send a document to the contractor only with the signature of the foreman?
In the case of employees using UNEP to sign a work permit, the employer must provide an internal procedure for its use and comply with the requirements of Article 6 of the Federal Law of April 6, 2011 No. 63-FZ “On Electronic Signatures”.
When exchanging work permits with the contractor, it is necessary to determine in a bilateral agreement that the presence of the foreman’s UKEP guarantees the presence of the workers’ UNEP that they have been instructed. Additionally, the agreement should provide for exceptional situations that the contractor has the right to request full information about the signing of the work permit; such information can be provided by downloading the document with all electronic signature files from the system.
In the described scheme, we consider it uncritical for the contractor to receive an authorization order without the workers’ instructions for instructions, it is enough to indicate the data of the workers.