What are operating expenses?
Operating expenses of an enterprise are expenses of an organization that are not directly related to its main activities. For example, purchasing a printer for an office is a capital expense, while purchasing paper, refilling cartridges, and maintaining it will be an operating expense.
Controlling company costs
Until 2006, enterprise costs were divided into two groups:
- Direct - cost items associated with the main activities of the enterprise and included in the cost of production.
- Indirect – related to maintaining the life of the company and not included in the cost of the final product or service.
Indirect, in turn, were also divided into three types:
- Non-operating – related to the acquisition of fixed assets.
- Operational – aimed at the functioning of the enterprise.
- Emergencies – caused by unforeseen emergency situations.
Production
Organizations that manufacture products calculate the profitability of their core activities:
Return on production costs = (Revenue – Full cost) / Full cost x 100%.
This formula takes into account all the costs of the enterprise: the purchase of materials, semi-finished products, payment of wages to workers, rent, utilities, advertising costs, etc. In production, raw materials and materials influence the amount of costs most of all. Production profitability of costs, the calculation formula for which is presented above, shows how much profit one ruble invested in cost will bring.
What is included in operating expenses
In 2006, Order No. 116n of the Ministry of Finance was adopted, which canceled the effect of PBU 10/99 in the previous edition and the term “operating expenses” ceased to exist at the official level. Since that time, all the company’s costs began to be divided into two groups:
Work of a company cost accountant
- Expenses associated with the main activity.
- Other expenses.
Despite the new order, the concept of “operating expenses” is widely used in everyday activities and applies to all simple other costs. According to the new document, operating costs are:
- expenses associated with the provision of temporary use of enterprise assets, including property;
- patent rights to intellectual property granted for paid use;
- investing in the authorized capital of third-party companies;
- payment of commissions for banking services;
- interest on debt obligations of the enterprise;
- costs associated with the disposal of assets, sale of property, goods or finished products of the company, with the exception of Russian funds;
- creation of valuation reserves provided for in accounting (AC) for doubtful debts, depreciation of material assets and financial investments.
- penalties in case of violation of contractual terms by the organization;
- compensation for losses incurred due to the fault of the enterprise;
- expired accounts receivable and other obligations that can no longer be collected;
- losses incurred when writing off the depreciation of assets;
- amounts of exchange rate differences;
- charitable contributions made by the organization;
- losses from previous years recognized in the current period.
Definition, formulas and application
The cost-benefit ratio provides the most benefit when compared to historical values.
Article navigation
- What is ROCS cost return and why is it determined?
- Calculation formula
- Information sources
- Standards
- What influences cost profitability
- Example of ROCS calculation
- conclusions
The effectiveness of any enterprise is determined by the ratio of the result to the resources spent to achieve it. Every company in the course of its business activities is forced to spend money. If profits exceed costs, then we can talk about positive profitability. The article will discuss one of the methods for assessing the success of a commercial structure - the ROCS indicator. It is called the cost-benefit ratio or cost-benefit ratio.
How operating expenses are taken into account in the activities of the enterprise
They are accounted for by the organization's accountant. During the reporting period, he makes entries into subaccounts, and at the end of the month he displays the difference, which is recorded.
Accounting for operating expenses
All other income and expenses of the company are reflected in account 91. Income is recorded in the credit of the account, and expenses in the debit. To highlight expenses, the accountant creates separate subaccounts:
- 91.1 for income accounting;
- 91.2 for accounting expenses.
For your information! Separate sub-accounts are created so that a specific result can be tracked for each financial transaction.
Management and accounting of enterprise operating expenses
The difference between income and expenses at the end of the month is transferred to subaccount 91.9. The final balance is closed to account 99, which shows the organization's profits and losses. Thus, the balance of account 91 is not reflected and has no balance at the reporting time.
Kinds
Depending on the direction, ODA is divided into two types:
- Variables.
- Permanent.
The variables include needs that proportionally depend on the growth or decline of production turnover. Before calculating and including variable overhead costs in the cost price, it is necessary to determine the relationship between cost growth and the size of output. Three dependencies are defined:
- Direct dependence of rising costs on increasing production volumes.
- Inverse relationship.
- Cost growth is outpacing production volume.
The relationship between the two indicators (needs and output volume) lies in the rate of wear (depreciation) of the main equipment, the need to increase its power, and the growth of energy and fuel needs.
Constant consumption includes constant consumption, or less susceptible to changes with an increase in output. These are mainly related to the management and accounting needs of the company.
Analysis of the effectiveness of operating expenses
Operating costs make up a significant portion of any organization's financial expenditure. Management accounting can solve the problems of recording monetary transactions and increasing the efficiency of the company through cost analysis.
It allows you to calculate the operating expense ratio (OCR) and understand how much it costs the company to produce products and whether the company’s activities are effective. Studying CDF over time helps track the potential for increasing production, sales or services without unnecessary costs.
Performance Analysis
The goal is to reduce the ratio while maintaining constant or even increasing production volume. This will be an indicator of revenue growth, and therefore an increase in the company’s net profit. The coefficient can be calculated using the formula:
OCR = Operating expenses (OR) – Total income.
Operating expenses - calculation formula
The ratio of expenses to income is used to calculate profits from other business operations of the enterprise. Separate accounting with the transfer of data from the main account to sub-accounts allows you to determine net income:
Net operating income (NOI) = Amount of gross income (GI) – Amount of operating expenses (minus depreciation, since it is not included in controllable costs).
The PSC does not take into account sales tax costs and financing costs. The resulting indicator will show the net profit from the use of company property, investments in securities and other types of income in the current period. This does not mean that the result will not change in the future.
Important! An enterprise can independently establish formulas for calculating operating income and expenses based on the legislation of PBU 9/99 and 10/99.
Formulas for calculating average total costs
We can write the following equation to express the relationship between total costs (TC), variable costs (VC) and fixed costs (FC):
TC = VC + FC .
If we divide both sides of the above equation by the output Q, we get the relationship between average total cost (ATC), average variable cost (AVC) and average fixed cost (AFC):
TC/ Q = VC/ Q + FC/ Q , that is
ATC = AVC + AFC .
This formula shows that average total cost is the sum of average variable costs and average fixed costs.
Factors for increasing the efficiency of operating expenses
An important task in enterprise management is to reduce operating costs in order to increase commercial profits. Factors influencing costs are divided into external and internal. Internal ones include:
- Increase in production volume and sales of finished products or services. With their growth comes an increase in costs, but the cost of production decreases, since the constant part of operating expenses does not change.
- Reducing the production cycle time. This entails a reduction in storage costs for products, losses due to natural loss, and costs for accounts receivable.
- Increase in labor productivity per employee. The higher the number, the lower the operating costs.
Reducing enterprise costs - Technical condition of the equipment. The more worn it is, the more often it will need servicing.
- The amount of own current assets also affects operating expenses. The more there are, the less you will have to turn to third parties for borrowed capital.
External factors include:
- Inflation in the country where the company is located.
- Increase in tax rates and other mandatory payments.
Operating expenses are an important indicator for calculating the net profit of an enterprise. Their control and analysis will help reduce current production costs, wisely use enterprise resources and quickly monitor the efficiency of the company.
Cost return indicators
Profit from activities can be calculated using the formula:
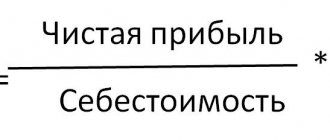
Return on sales = PE / Cost x 100%.
This same indicator can be calculated differently:
P prod = Gross profit / Cost x 100%.
The numerator can include income from sales. Then the formula will display the level of profit of the enterprise per ruble spent on the manufacture of products. This indicator can be calculated both for the organization as a whole and for individual divisions and types of goods. In the second case, the following formula is used:
P pr = (Price – Cost) / cost x 100%.
The dynamics of the indicator depends on:
- Structures of products sold. An increase in the share of profitable goods contributes to increased profitability.
- Increasing costs inversely affects production efficiency.
- Rising prices also contribute to increasing profitability levels.
Another important indicator is operating cost return. Formula:
R op = Income from operating activities / Expenses from operating activities x 100%.
It shows how much profit is generated per 1 ruble of expenses.
The profitability of core activities reflects the efficiency of not only the manufacturing processes, but also the sales of products.
Return on costs = Profit from sales / Total costs x 100%.
The numerator takes into account the cost of goods sold, selling and administrative expenses.
The following indicator gives an overall picture of the effectiveness of the use of funds:
Profitability = Total costs / Volume of products sold x 100%.
Cost: how to calculate the cost structure
The amounts of fixed and variable costs that were spent on the production and sale of one unit of goods in the economy are called cost . The cost structure directly depends on these costs.
Any entrepreneur should know the concept and composition of cost, the procedure for its formation, what factors influence growth or decline. Because it is of utmost importance in the activities of all enterprises.
Let's consider the economic meaning of the concept of cost. Its essence is that it is necessary to reflect the monetary amount of all resources that were used in production. Let's list the functions that cost performs:
- Necessary to control all costs: production, advertising, and general activities of the company;
- Pricing tool. Depending on the size of the cost, the company sets the selling price for its goods. To make a profit, the cost price (production costs) must be lower than the price. But other factors are also taken into account to set the price: the level of demand, the presence of competitors and their price, the capabilities of the company and its goals;
- Used to calculate profits and profitability;
- The cost of production is the basis for calculating income tax;
- It is an important indicator that is used to make decisions about increasing production.
The concept of production cost sounds like this: these are all the costs of producing one unit of goods, which are expressed in monetary form. The selling price of the product directly depends on it. Let's consider what is included in the composition or structure of the cost.
As you can see, it coincides with the elements of costs, so we can say that the concept of cost costs is the same as that of costs.
For different types of activities of the company, the structure of product costs will vary. For example, if an enterprise is engaged in the production of cars, then in its structure there will be large material costs (raw materials for production) and depreciation of fixed assets (for repair and restoration of equipment). If the company is engaged in the provision of consulting services, which do not require a lot of materials and machines, then the amount of these costs in the cost structure of the cost price will be small.
Each company must clearly define its cost structure, because it depends on various factors:
- Season, in the warm season there is no need to heat production premises or workshops, which means the amount of money that needs to be spent on heating in the summer will be lower;
- If a company decides to produce a new product, then this will require additional expenses (purchase of machines, rental of a building or retraining of personnel), which means that the enterprise will calculate the cost of production of a new product based on the amounts that need to be spent on the production of this product (equipment, personnel , additional room);
- Change of supplier of raw materials (for various reasons, for example, the supplier company closed). The new supplier from whom the raw materials are purchased can sell them at higher prices.
It is these factors that make it necessary to analyze the cost structure of an enterprise, which includes determining the composition of costs per unit of product and calculating this indicator. To carry it out, the following data is used:
- The size of the total cost of the product;
- Cost amount by economic elements (materials, depreciation, wages);
- The cost price of a single product;
- Cost of similar goods.
Let's look at how to calculate the cost of a product. Logos LLC is engaged in sewing dresses, but decided to also sew blouses. We present the calculation of the cost of one blouse in the table:
To simplify the example, to calculate the unit cost, other costs (salary deductions, depreciation, and others) are not taken into account. The example shows the calculation of one unit of goods (blouse). But the second option can also be used, when the total cost for a certain number of products is first calculated, which is then divided by the number of products produced. Then the formula will be used:
In order to calculate the cost of an enterprise, you need to know how it is formed. This order is shown in the figure:
Due to the fact that the cost includes different types of costs, there are several types of costs:
Enterprises that carry out production activities (production of tableware or furniture) calculate the cost of production. For companies that have a large range of products, the calculation process is complex; it is handled by an accounting employee.
If the company provides services, then the cost of the service is calculated. The concept of a service implies that it is also a product, only it does not have a material form, but costs are also required to provide it. Therefore, the cost of a hairdresser’s services will include: rent of a workplace, salary, cost of cosmetics (shampoos, paints), cost of electricity and water, as well as equipment - chairs, hair dryers and mirrors.