Liquidity ratio
The liquidity of any organization and company is calculated using several financial indicators, one of which – the liquidity ratio – is calculated using special formulas. Using this ratio, you can compare the value of current assets, which have different degrees of liquidity, with the amount of current liabilities. There are coefficients:
- overall liquidity or coverage, which shows how capable the enterprise is of meeting its short-term obligations;
- current or quick liquidity, which shows what part of the company’s obligations can be repaid using cash and financial investments;
- absolute liquidity, allowing to determine short-term liabilities, the debt on which the company can repay urgently.
Functions of money. Cash liquidity
Money is the universal equivalent of value. Money is a special commodity that serves as a universal equivalent in the exchange of goods. Money is an absolutely liquid medium of exchange. Liquidity is the ability of a financial asset to convert into cash. The degree of liquidity of assets is determined by how quickly and at what costs (compared to the value of their monetary value) these assets can be sold. State-issued cash has absolute liquidity Treasury bills, short-term government securities, are considered highly liquid This is because the market prices of these securities vary only slightly from day to day, and also because they can be easily traded on financial markets (as they are highly reliable), and the transaction costs will be very low. Stocks and long-term bonds issued by private corporations have intermediate or medium levels of liquidity Real estate (houses, industrial buildings) is illiquid, since the market price for it is very volatile and difficult to predict before making a transaction. The costs of such transactions can be very high.
The essence of money is manifested in its functions: measures of value, means of circulation, means of payment, means of storage, world money. Money as a measure of value means that it is used to measure the value and price of goods. Money commensurates the value of goods, that is, a product is equated to a certain amount of money, which gives a quantitative expression of the value of the product. Price is the cost of a thing expressed in money. The state uses a certain monetary unit (ruble, dollar) as a scale for measuring value. Weight is also measured using weight units (grams, kilograms, etc.), the cost of the product has a monetary value. Thanks to this, we can measure the value of economic goods.
Money as a medium of exchange is involved in the purchase and sale of goods and services. In this case, money acts as a fleeting intermediary. Using money as a medium of exchange reduces circulation costs by reducing the effort and time required to complete purchases and sales. This function of money explains the appearance in circulation of inferior coins (coins whose gold and silver content is less than the face value, i.e., the weight indicated on the coin), as well as paper money.
Money acts as a means of payment when paying wages, paying taxes, insurance payments, selling goods on credit and in many other cases when the movement of money is not mediated by the movement of goods. If a product is sold on credit, then the medium of circulation is not the money itself, but debt obligations expressed in money. As industrial society develops, the means of payment increasingly replaces the means of circulation, and sales and purchases on credit become the most common. The fulfillment of this function by money led to the emergence of credit money: bills of exchange and bank notes.
Money as a means of accumulation does not participate in turnover and acts as a financial asset. Money is a convenient form of storing wealth. Here, money acts as a special asset, retained after the sale of goods and providing its owner with purchasing power in the future. True, storing money, unlike owning stocks, bonds, or savings accounts, does not bring additional income. However, the advantage of money is that it can be immediately used as a medium of exchange or means of payment.
The function of world money is performed on the world market when servicing the movement of goods and services, capital and labor. World money is the same as national money, only at the international level. The world money is the currencies of leading countries (dollar, pound sterling), as well as money created as a result of collective agreements (euro).
Current liquidity
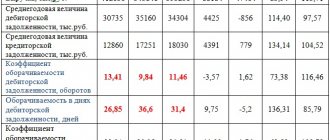
To know how much of a firm's or organization's current liabilities can be paid with existing cash or cash equivalents, investments, and accounts receivable, it is necessary to know what quick or current liquidity is. The quick liquidity ratio is calculated using a special formula. The indicator of this type of liquidity indicates how solvent an organization or firm is, how quickly it can pay off current obligations, paying debtors on time. Typically, a quick ratio of 0.6 is considered acceptable.
Liquidity, solvency and profitability
Many even experienced businessmen do not quite correctly imagine how these concepts relate to each other.
Solvency implies that the company has sufficient cash or cash equivalents to urgently repay accounts payable.
Liquidity is a broader concept, although inextricably linked with the previous one. The ability to cover debts for a specific time depends on its degree, and the future state of settlements is also determined. At the same time, there may be liquidity of total resources, such as the need to receive money in the event of liquidation or bankruptcy, and current assets, which ensure current solvency.
image from konspekta.net
Profitability, i.e. profitability is possible even with low liquidity.
Example
A small young company providing loader services took out a loan for its development. Has two used cars and a small staff. Its liquidity is not very high, since the existing assets, after their sale, will not be able to cover the debts. However, with good daily revenue, the profitability will be high, and accordingly, the business is profitable.
Conversely, a company with high liquidity and low profitability may go bankrupt soon.
Balance sheet liquidity
The financial indicator - balance sheet liquidity - shows the extent to which the company's liabilities are covered by assets that can be converted into money within a time frame corresponding to the maturity of the liabilities. The solvency of any company and enterprise depends on this indicator. To find out how favorable the financial position of an enterprise is, you need to know how much the value of current assets exceeds short-term liabilities. The higher this value, the better off the company is in terms of liquidity. Determining balance sheet liquidity is of particular importance during liquidation in case of bankruptcy of an enterprise or company.
Liquidity analysis
To analyze the liquidity of the balance sheet of a company or organization of any form of ownership, assets are grouped by degree of liquidity - from the fastest to assets with slow liquidity. A correct analysis of asset liquidity is carried out in the following order:
- the most liquid assets;
- quickly implemented;
- slow to implement;
- hard to sell assets.
As for liabilities, the most urgent liabilities are analyzed first, then short-term liabilities, long-term liabilities and finally permanent liabilities.
Investments in liquid assets
Investments in liquid assets are considered much safer, since the investor can quickly abandon his investment and withdraw money, whereas in the case of hard-to-sell assets, difficulties arise in the process of extracting his money. That is why the foreign exchange market (ForEx) looks so attractive to investors. By definition, it is reasonable to assume that money has the highest level of liquidity. For the same reason, the foreign exchange market offers such high leverage and a low difference between the purchase and sale prices - the spread.
Absolute liquidity
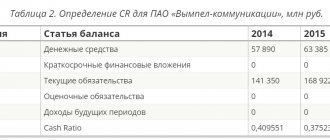
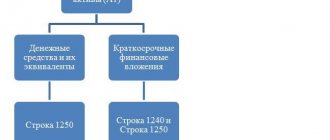
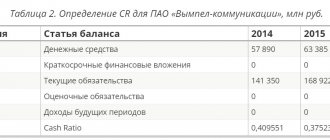
If you need to calculate the reliability of a company or quickly liquidate it, you need to know its financial indicators. One of them, absolute liquidity, is a ratio showing how much of short-term debt can be repaid immediately. The absolute liquidity ratio or Cashratio shows how capable a company or enterprise is of repaying a short-term loan immediately. This indicator is calculated as the ratio of current assets that can be immediately sold to the debtor's current liabilities.
The difference between absolute liquidity and current and urgent liquidity
If the absolute liquidity ratio shows immediate solvency, then critical and current liquidity data reflect the company’s ability to cover obligations in the medium and long term. Although all three coefficients are calculated in financial analysis, the resulting values are of interest to different groups of subjects. Thus, the quick liquidity ratio is important for creditors and banks to assess timely solvency.
The current liquidity indicator is used by investors to confirm the fulfillment of current obligations on time. And the absolute liquidity ratio is attractive for suppliers with short credit terms, because its value expresses the ability to immediately repay current short-term obligations.
The main difference between all three indicators is the composition of liquid funds involved in repaying the company’s debt.
Liquidity indicators
Liquidity is the most important indicator of the efficiency and reliability of an enterprise. It shows how creditworthy the company is. To know exactly how promising a particular company is, it is necessary to analyze their work. When analyzing the activities of any company, it is necessary to take into account balance sheet liquidity indicators. The main coefficients are:
- absolute liquidity;
- critical evaluation;
- maneuverability of functioning capital;
- current liquidity;
- security of own funds.
Asset liquidity
Company assets that can be quickly and profitably converted into money are called liquid. The most highly liquid asset is the funds that the company has in cash, accounts, and deposits. Good liquidity of assets in securities that can be sold profitably on the stock exchange at any time. The least liquid are considered to be inventories of raw materials, materials, and the value of work in progress. The accounting analysis of balance sheet liquidity is based on the principle of increasing liquidity; the most important when preparing the balance sheet are three coefficients:
- absolute liquidity;
- quick liquidity;
- current liquidity.
Bank liquidity
Any organization can be considered from a liquidity point of view, including financial ones. Such a concept as a bank's liquidity - its ability to quickly fulfill obligations to depositors, investors, creditors - is very important when choosing a bank. The obligations of a financial organization can be real, potential or contingent. Bank liquidity factors are external and internal. Internal factors are:
- bank management and its image;
- quality of funds raised;
- quality of bank assets;
- conjugation of assets and liabilities.
External liquidity factors are;
- the state of the economy in the country;
- development of the securities market;
- effectiveness of Bank of Russia supervision;
- refinancing system.
Liquidity of the enterprise
The liquidity of an enterprise is the ability to pay off its debts quickly and profitably. The degree of liquidity is determined by the ratio of balance sheet assets and liabilities and determines the stability of the enterprise. A company's liquid funds are all those assets that can be converted into money and used to pay off debts. This is money on hand, in accounts and deposits, securities that are quoted on the stock exchange, working capital that can be quickly sold.
There is general (current) and urgent liquidity of the enterprise. Total is the ratio of the sum of current assets and liabilities at the beginning and end of the year. The analysis of an enterprise's liquidity is determined by ratios. If the current liquidity ratio is below 1, this means that the company does not have stability. The normal indicator is over 1.5.
Quick liquidity ratio
Reflects the company's ability to pay short-term debts using medium- and highly liquid assets and shows how quickly inventories and receivables can be converted into cash.
We can calculate the quick liquidity ratio using the following formula:
KSLP = (TA – Z) / KO , where
KSLP is the enterprise's short-term liquidity ratio,
TA – current assets,
Z – reserves,
KO – short-term liabilities.
Market liquidity
Liquidity is an important indicator of any market. To make transactions on the stock market or the so popular Forex market, you need to know which exchange instruments can be quickly bought and sold just as quickly. Market liquidity is the opportunity to make a profitable deal with stocks, futures, and currency pairs without losing price or time. In other words, a market participant will receive any asset at the best market price as quickly as possible. Money has the highest liquidity - it can be instantly exchanged for goods. Real estate has low liquidity.
Liquidity of securities
The liquidity of securities is the ability to turn them into money quickly and profitably, and this opportunity is constant. It is this characteristic that is taken as the basis for understanding how effective certain securities are. High liquidity will allow the investor to instantly receive cash for securities.
The main characteristic of the liquidity of securities is the spread - the difference between sale and purchase prices. The smaller the spread, the higher the liquidity. Liquidity is influenced by the investment attractiveness of a particular issuer's securities. It can be calculated if the performance indicators of the enterprise and the assessment of its securities by the market are known.
Factors affecting the liquidity of an enterprise
[1]. Accounts receivable level . The smaller its size, the higher the liquidity indicators.
Reducing the volume of accounts receivable can be achieved through an assignment - assignment or transfer of ownership rights to property. In some cases, this will require tightening the terms of contracts.
[2]. Profit. The higher the profit, the more liquid the organization is.
There is no universal method for increasing profits. It all depends on the characteristics of individual markets, pricing policies, the number and activity of competitors, and the purchasing power of customers.
[3]. Organization's capital structure . It all depends on what exactly the organization’s capital was formed from: from its own or borrowed funds. If from borrowed ones, then whether they are short-term or long-term.
With an increase in equity in the capital of the enterprise and a decrease in the level of borrowed funds (especially short-term ones), the liquidity indicators of the organization also increase.
[4]. Money . Each organization needs to increase its working capital and reduce the indicators of tangible assets, especially inventories.
Liquidity indicators may be influenced differently by external environmental factors, for example, the decline of the entire manufacturing industry in the country, obsolescence of technologies (moral bankruptcy) of debtor organizations, etc.
In such situations, the negative effect on the decrease in liquidity can be compensated by issuing shares and additionally raising funds.
How to improve the listed factors and increase the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise?
Optimization is a difficult process, which hides the well-coordinated work of management personnel and the workforce.
Often for this it is necessary to hire qualified specialists from outside (analysts, economists and others). Such decisions have a positive impact on the work of the organization.
Liquidity of money
Money has the highest, one might say, perfect liquidity. The liquidity of money means that it can be used to obtain goods or services that are needed at any time. Money is a means of payment in any country in the world. They are most protected from fluctuations in their value. Universality as a means of payment, that is, liquidity, makes money the most sought-after asset. Cash has the greatest liquidity, followed by funds on the current deposit. In last place are securities that still need to be sold on the stock market.
Types of liquidity
I will consider in detail what types exist and what functions each of them has.
Assets
This parameter indicates whether the asset can be quickly sold at a price close to the market price or not. As I said above, the top is money (cash or short-term deposit in a bank). Highly liquid also includes all financial instruments (for example, securities) that are actively traded on the stock exchange.
Jar
This implies whether the bank will be able to timely and fully fulfill its obligations to clients.
Bank liquidity can be either insufficient or excessive. Insufficient - a signal of bank insolvency.
Excessive - prevents you from establishing high profitability. Simply put, if everyone can deposit and withdraw money at any time, it is difficult for the bank to invest it somewhere to earn interest. Therefore, time restrictions are often imposed on deposits.
Enterprises
This is an opportunity to pay off all debts in a short time. Simply put, if a company has enough available funds on its balance sheet (asset) to pay off all current debts (liabilities), it is liquid. This is one of the main indicators of his financial success and stability.
Market
If a market has a sufficient number of buyers and sellers to sell all commodities instantly without large price fluctuations, it is considered liquid.
Valuable papers
This refers to the speed of sale of securities at real market value. First of all, it depends on the issuer. Traditionally, the most liquid blue chips are the second and third tier companies, which depend on the financial performance and prospects of the issuer.
Money
This is the ability, at any time or a certain period, to turn cash into any product/service that the owner of the money needs.
Real estate
The liquidity of real estate is the opportunity to sell it profitably and quickly. A house or apartment (any type of real estate) that can be sold at market price in a short time will be considered liquid.