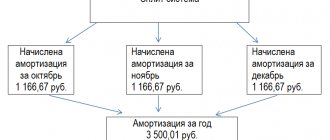
Any production process requires the availability of fixed assets.
Funds, based on the appearance of the production product, are subject to wear and tear (depreciation). This leaves its mark on determining the price of this product. Its cost also includes the cost of depreciation. These amounts are accrued in equal parts every month and then combined under the concept of “depreciation.” The state has established its own standards for this, which are called “depreciation standards.” In addition, tax actions also contribute their share.
The depreciation rate is measured as a percentage. Its value is not fixed.
- 1 General information
- 2 Details 2.1 Each company has its own methodology for calculating depreciation rates
- 2.2 The formula for calculating the depreciation rate is presented in two versions
- 2.3 There are certain deadlines
- 2.4 Only equipment that is the property of the organization can be depreciated
What is subject to depreciation
According to Russian legislation, property, results of intellectual activity and other objects of intellectual property of an economic entity are subject to depreciation.
Such facilities must be owned by the company, used to generate income and operated for at least 12 months. There are two types of such property:
- fixed assets;
- intangible assets.
Let us dwell on how depreciation rates for fixed assets are determined. There are different rules for accounting and tax accounting in the Russian Federation.
What it is?
Depreciation in the economic sense is usually understood as a process that reflects the gradual transfer of the value of fixed assets to the cost of the product that was produced and sold as they wear out (in this case, both material and obsolescence are important).
Thus, in the process of aging of buildings and various structures, cars and production equipment, as well as other operating systems, monetary deductions are activated from the cost of the final product, the main purpose of which is further renewal. Such cash flows are called depreciation charges. For this purpose, depreciation funds are formed, where absolutely all transferred funds are accumulated after the sale of the finished product.
The percentage required to reimburse the cost of a share of a capital good subject to wear and tear during the year is calculated as the ratio of the amount of deductions for depreciation made annually to the cost of the fixed asset. It is called the depreciation rate.
Determining the useful life of fixed assets
In both accounting and tax accounting, the cost of depreciable property is taken into account by straight-line write-off over its useful life. Who sets depreciation rates? Their value depends on the useful life (USI) of the fixed asset. In accounting and tax accounting, the procedure for determining the period is different.
According to clause 20 of PBU 6/01, the useful life of an object is determined based on:
- expected service life taking into account performance or power;
- expected physical wear and tear, which depends on operating conditions and environmental influences;
- regulatory legal acts, contractual obligations, etc. related to the operation of the facility.
Different objects have different terms of use. What is the depreciation rate for fixed assets? This is a percentage. It shows what share of the cost of an object in a certain period is allowed to be taken into account in the organization’s expenses.
Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation requires the distribution of property into depreciation groups and, based on this, determine the SPI. The classification of fixed assets by depreciation period was approved by the Government of the Russian Federation in Resolution No. 1 of 01/01/2002.
About the depreciation rate in simple words
Depreciation charges are based on the depreciation of the enterprise's fixed assets reflected in the corresponding accounting report. This mechanism works throughout the entire life of a given state of the company.
The amount of depreciation is transferred from depreciation accounts to an account intended for the costs of the production process. Subsequently, along with income, deductions are transferred to the company’s current account, where they accumulate for some time . It is from here that this amount of money is spent on paying for subsequent capital investments directed directly into fixed assets.
Shock absorption groups
The classifier provides for the division of all OPF into ten depreciation groups. For asset groups, the depreciation rate is determined taking into account the duration of operation of equipment, buildings, structures, and other objects. The organization has the right to establish the duration of useful use based on the time interval.
If the classifier does not mention the OS that the organization puts into operation, the period of its use is established based on the recommendations of the manufacturers and technical specifications.
The taxpayer may change the annual amount and depreciation rate. This is permitted if the service life is increased as a result of reconstruction, modernization or technical re-equipment.
Depreciation deductions
In order to correctly make this calculation, you need to clarify the following circumstances.
The starting amount for calculation is the original cost. Of course, its main part is the purchase price. However, it may also include:
- transportation cost,
- installation costs,
- other costs related to getting started with the asset.
The initial cost is the sum of the specified types of expenses.
When carrying out depreciation, the residual value is determined, which is the difference between the original cost and depreciation.
However, the reduction does not occur to zero, but only until the residual value is reached. After this, the latter can be immediately written off as expenses.
Not only accounting, but also tax accounting provides for the calculation of depreciation. In this case, two calculation methods are used:
- linear,
- depreciation accounting using the division of assets into groups of fixed assets.
How to calculate using the linear method
Using the straight-line method, an organization must calculate the amount of depreciation charges for each fixed asset item. For each object, the depreciation rate depends on its useful life and is determined individually.
With the linear method, the calculation is established by paragraph 2 of Article 259.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and has the form:
In practice, annual and monthly depreciation percentages are used. How to calculate the annual depreciation rate? In the denominator of the calculation formula, put the SPI in years. If it is necessary to determine the monthly standard, the SPI should be indicated in months.
Definition of the concept
Depreciation is a systematic transfer of the price of profit objects as they wear out to the final products of a particular enterprise manufactured through them. Thus, this economic mechanism is the financial equivalent of the loss of useful qualities of the company’s fixed assets.
The final amount of depreciation deductions must always correspond to the original cost of the enterprise. Only those company objects that have the following distinctive features :
- are on the balance sheet of the enterprise with the right of ownership;
- used for economic management;
- are used due to operational management.
Depreciation policy is one of the components of the economy of any country. At the same time, such features of this mechanism as the rate of deductions, duration of useful use, features of transfers, etc. differ in different countries.
Nonlinear method
When applying the nonlinear method, the depreciation rate is directly dependent on which depreciation group the object belongs to. They are established in paragraph 5 of Article 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
| Group | Useful life of fixed assets, years | Depreciation rates by group, % |
| 1 | From 1 to 2 inclusive | 14,3 |
| 2 | From 2 to 3 | 8,8 |
| 3 | From 3 to 5 | 5,6 |
| 4 | From 5 to 7 | 3,8 |
| 5 | From 7 to 10 | 2,7 |
| 6 | From 10 to 15 | 1,8 |
| 7 | From 15 to 20 | 1,3 |
| 8 | From 20 to 25 | 1,0 |
| 9 | From 25 to 30 | 0,8 |
| 10 | Over 30 | 0,7 |
The amount of accruals for the month is determined for each group using the formula:
Details
Each company has its own methodology for calculating depreciation rates.
The following methods are distinguished:
- 1.The most popular method is linear.
Based on the initial costs of fixed assets, the amount of depreciation charges for the year is established, i.e. depreciation rate. Every month, a twelfth part of the annual amount is subject to deduction during the reporting period. This linear depreciation rate is determined using a certain formula.
- When the amount of depreciation charges and fixed assets for the year are at the balance level at the beginning of the year for the reporting period, accrual is applied using the reducing balance method or acceleration depreciation. This takes into account how long the fixed assets have been in operation. The coefficient is calculated using the formula.
- The technique used without calculating the depreciation rate is called writing off the cost proportional to the quantity of finished products. Here, the depreciation rate decreases, since the total cost of wear and tear also decreases.
- When transferring the full balance amount of fixed assets to production costs, accelerated accrual is applied.
The formula for calculating the depreciation rate is presented in two versions
Option #1.
- Initial cost of the OS – Pst (rubles)
- Liquidation cost of fixed assets – Lst (rubles)
- Depreciation period – AP (years)
Us = (PST - Lst): (Ap*Pst)*100%
This formula is used to calculate the depreciation rate for the year.
Option #2.
Here is an indicator that needs to be calculated, how long (term in years: T) the object, which is represented by a specific fixed asset, has served.
Us = (1 : T) *100%
This formula is used for accounting and taxation.
When calculating the depreciation rate, a third formula is also used, which will help calculate how long the object served (Tm - service life in months) as a specific fixed asset:
Us = (2 : Tm) * 100%
There are certain deadlines
by which the benefits of the equipment that it can bring during operation are established. This takes into account:
- Operating mode.
- Natural conditions.
- Aggressiveness of the environment.
- Systematicity of repair work.
- Restrictions for use.
- Expected results in power and performance.
When calculating the depreciation rate, depreciation groups are taken into account that correspond to the service life of the objects:
Group 1 – 1-2 years Group 6 – more than 10 years, but up to 15
Group 2 – more than 2 years, but up to 3 Group 7 – more than 15 years, but up to 20
Group 3 – more than 3 years, but up to 5 Group 8 – more than 20 years, but up to 25
Group 4 – more than 5 years, but up to 7 Group 9 – more than 25 years, but up to 30
Group 5 – more than 7 years, but up to 10 Group 10 – more than 30 years
These calculations help determine how many resources are not subject to taxation and create a financial program for the production of fixed assets.
Enterprises often purchase equipment that has already been in use as fixed assets. The linear method will help you calculate depreciation. But it is identical to the new equipment. The only distinctive feature will be the calculation of how long the equipment used will be useful.
Only equipment that is the property of the organization can be depreciated.
, and its initial price starts from 10,000 rubles.
But if the equipment was transferred for use free of charge or has been mothballed for more than three months, and also if it has exceeded one year in the process of modernization or reconstruction, the depreciation procedure is impossible.
Equipment that is used in an aggressive environment is subject to depreciation according to special coefficients developed at the enterprise.
Depreciation of fixed assets is expressed in monetary terms and is called depreciation charges. They are accrued every month until the objects are disposed of. Such accruals accumulate, but their expenses are not accounted for in accounting. They are used for major or partial repairs of equipment, for investments, for financing capital investments.
Monetary expression of PF depreciation
These are depreciation charges, which are included in the cost of manufactured products for subsequent investment. As mentioned earlier, their standards are set as a percentage of the existing book value of the PF. Depreciation is calculated every month. It stops accruing in relation to disposed objects from the 1st day of the following month.
The accumulation of depreciation charges and their expenditure are not reflected separately in accounting. They go to finance capital investments, long-term investments. Depreciation charges are spent on full (partial) restoration.
In the case of a complete overhaul, they must cover both physical and moral wear and tear due to the fact that technically outdated operating systems are not economically viable for operation even if they are physically suitable.