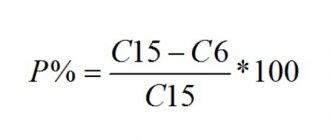In what case is the minimum tax paid under the simplified tax system?
In certain situations, a business entity may apply a preferential simplified tax system.
The provisions of regulatory acts establish the obligation of the single tax payer to calculate the actual and minimum tax if he chooses its type - income reduced by the amount of expenses.
This is due to the fact that the taxpayer must pay the largest of these amounts to the budget. That is, if a loss is received by the company and it has at least some income, it will have to calculate and transfer the minimum tax.
It is also necessary to pay the minimum tax in a situation where the enterprise has made a profit, but it is so insignificant that the organization ends up paying the minimum tax at the end of the year. This is the condition for using the preferential simplified taxation system.
Attention! The calculation of the minimum tax in accordance with the law does not apply if a business entity chooses the taxation system of the simplified tax system Income.
The minimum tax must be calculated based on the results of the past year. That is, in 2020, when calculating the single tax, it will be necessary to calculate the minimum tax according to the simplified tax system for 2020. The value of the minimum tax necessarily includes a declaration under the simplified tax system.
Attention! Regions are given the right to establish for entrepreneurs who have just completed the registration procedure for individual entrepreneurs and meet the conditions established by law to apply a tax rate of 0% under the simplified tax system Income minus expenses for two years. If an individual entrepreneur uses this benefit, then during these two years he does not have to calculate and pay the minimum tax to the budget.
Real and minimum taxes
When the object of taxation is “income minus expenses,” the “simplifier” reduces his income by a limited list of expenses (Article 346.14, Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that a minimal profit or even a loss may occur in tax accounting. But the requirements of the Tax Code are such that if any income was received by a “simplified” person during a calendar year, then the tax in any case must be paid no less than a certain amount. How to calculate the simplified tax system on the difference between income and expenses
Read more…
If the tax on the “income-expenditure” simplified tax system at the end of the year turns out to be less than 1% of the income of the “simplified” person, then he will have to pay not the actually calculated tax, but the minimum tax.
If the single tax turns out to be less than the minimum, then the minimum tax must be paid to the budget.
If the single tax turns out to be more than the minimum, then the real tax must be paid to the budget.
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system with the object “income” do not pay the minimum tax.
When do you need to pay?
For the minimum tax, the same tax payment deadlines apply as for the transfer of the simplified tax system based on the results of the year. That is, there is no need to calculate it and transfer it to the budget during the tax period.
Thus, a business entity must pay a minimum tax:
- If it is a legal entity - until March 31 of the year following the reporting year. If this deadline falls on a weekend, it is transferred to the next working day. Thus, for 2018 it is necessary to transfer the minimum tax by April 1, 2019.
- If he is an individual entrepreneur, then the deadline for payment of the minimum tax is set until April 30 of the following reporting year. Thus, for 2020 this tax amount must be transferred by April 30, 2020.
How to take into account the difference between real and minimum tax
If the minimum tax turns out to be more than the real one, then next year you will be able to include the difference between them in expenses (clause 6 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
But it is impossible to take this difference into account when paying quarterly advance payments for the single tax. This can only be done when calculating the single tax for the year. Therefore, last year's difference is shown in the annual return for the next tax period.
simplified tax system at the end of the year
Read more…
The minimum tax will have to be paid even if the company suffered losses (that is, its expenses exceeded its income). In this case, the amount of real tax will be zero. Therefore, the difference between the minimum and real tax will be equal to the amount of the minimum tax. This amount will need to be taken into account in expenses when determining the tax base for the next tax period, that is, in the declaration under the simplified tax system at the end of the year.
Calculation formula
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the minimum tax should be calculated in the amount of 1% of the amount of income received for the year.
Expenses are not taken into account when calculating this type of tax. Therefore, the formula for calculating the minimum tax can be presented as:
Minimum tax = Income for the year x 1%
When calculating tax according to the simplified tax system, it is necessary to calculate the actual tax based on the results of the entity’s work for the year, taking into account the single tax rate in force in the region under the simplified tax system Income reduced by expenses. The rate of this tax can be from 5% to 15%. For such entities as the Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol, the rate until 2021 is 3%.
The formula for calculating the actual tax is:
Single tax according to the simplified tax system fact = (Income for the year – Expenses for the year) x Tax rate
Once the two amounts have been calculated, they need to be compared. If we get the following inequality:
(Income for the year – Expenses for the year) x Tax rate < Income for the year x 1%,
The minimum tax will need to be transferred to the budget.
When a taxpayer made advance tax payments (STS) during the year based on the performance of a business entity, then, due to the fact that both taxes have the same BCC, these amounts can be taken into account when transferring the minimum tax.
Therefore, the formula for the minimum tax that needs to be transferred to the budget is:
Minimum tax payable = Minimum tax - Advance payments according to the simplified tax system
The situation may develop in such a way that the amount of advance payments exceeds the amount of the calculated minimum tax. Then there is no need to transfer it to the budget.
Important! If a situation arises with an overpayment (the minimum tax is less than the listed advance payments), then the business entity can offset it against the advance payments of the next period, or make a refund.
How to calculate the minimum tax
The minimum tax is calculated as 1% of the income of the “simplified” person at the end of the year.
The minimum tax is calculated not from the difference between income and expenses, but from the amount of all receipts.
The accrual of the minimum tax payable (instead of a single tax) is reflected by the following entries:
DEBIT 99 CREDIT 68 subaccount “Minimum tax calculations”
— the minimum tax has been calculated at the end of the year.
DEBIT 99 CREDIT 68 subaccount “Calculations for single tax”
— previously accrued additional amounts of advance payments for the single tax were reversed.
The difference between the paid minimum tax and the single tax does not need to be reflected in any accounting entries.
Example. We determine what tax needs to be paid to the budget - single or minimum. LLC "Passive" pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses. Situation 1 The total amount of income for the year was 1,000,000 rubles, and the amount of expenses was 550,000 rubles. All expenses can be taken into account when calculating the single tax. The single tax is equal to: (1,000,000 rubles - 550,000 rubles) × 15% = 67,500 rubles. The minimum tax will be: 1,000,000 rubles. × 1% = 10,000 rub. 10,000 rub. Since the single tax is greater than the minimum tax, the tax to the budget is 67,500 rubles. Situation 2 The total amount of income for the year was 1,000,000 rubles, and the amount of expenses was 980,000 rubles. All expenses can be taken into account when calculating the single tax. The single tax is equal to: (1,000,000 rubles - 980,000 rubles) × 15% = 3,000 rubles. The minimum tax will be: 1,000,000 rubles. × 1% = 10,000 rub. 10,000 rub. > 3,000 rubles. Since the single tax is less than the minimum, the company will pay the minimum tax to the budget - 10,000 rubles.
The minimum tax is calculated only at the end of the year. There is no need to do this at the end of a quarter, half a year, or 9 months.
KBK for payment in 2020
In 2020, it is necessary to use unified KBK codes to pay both the single tax and the minimum tax.
| Payment | Code |
| Minimum tax | 182 105 0102101 1000 110 |
| Fine | 182 105 0102101 2100 110 |
| Penalty | 182 105 0102101 3000 110 |
Attention! It should be noted that until 2020 inclusive, business entities paid regular and minimum taxes on various BCCs. Because of this, it was necessary to additionally submit an application to the tax authority to offset one tax as another.
Question and answer: Calculation of taxes at a loss
QUESTION:
Under the simplified tax system there is a loss for the year. Do I need to charge and pay a minimum tax?
ANSWER:
A taxpayer who uses income reduced by the amount of expenses as an object of taxation pays the minimum tax in the manner prescribed by this paragraph.
The amount of the minimum tax is calculated for the tax period in the amount of 1 percent of the tax base, which is income determined in accordance with Article 346.15 of this Code.
(as amended by Federal Law dated July 21, 2005 N 101-FZ)
The minimum tax is paid if for the tax period the amount of tax calculated in the general manner is less than the amount of the calculated minimum tax.
(as amended by Federal Law dated July 21, 2005 N 101-FZ)
The taxpayer has the right in the following tax periods to include the amount of the difference between the amount of the minimum tax paid and the amount of tax calculated in the general manner as expenses when calculating the tax base, including increasing the amount of losses that can be carried forward in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 7 of this article. Source: Art. 346.18, “Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part Two)” dated 08/05/2000 N 117-FZ (as amended on 12/28/2017) {ConsultantPlus}
Source: {Typical situation: How to pay and take into account the minimum tax under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” (Glavnaya Kniga Publishing House, 2018) {ConsultantPlus}}
The minimum tax is 1% of all income for the year. It must be paid only at the end of the year and only if it is more than the tax calculated in the general manner (clause 6 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, calculate the tax payable as follows.
If the result is zero or negative, you do not have to pay anything.
Example. Calculation of the minimum tax under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
| Period | Cumulative total since the beginning of the year (RUB) | |
| Income | Expenses | |
| 1st quarter | 220 000 | 100 000 |
| Half year | 510 000 | 230 000 |
| 9 months | 830 000 | 505 000 |
| Year | 1 000 000 | 970 000 |
Advance payments:
- for the 1st quarter - 18,000 rubles. ((RUB 220,000 - RUB 100,000) x 15%);
- for half a year - 24,000 rubles. ((RUB 510,000 - RUB 230,000) x 15% - RUB 18,000);
- for 9 months - 6,750 rubles. ((RUB 830,000 - RUB 505,000) x 15% - RUB 18,000 - RUB 24,000).
The total amount of advance payments is RUB 48,750. ((RUB 830,000 - RUB 505,000) x 15%).
The calculated tax for the year is 4,500 rubles. ((RUB 1,000,000 - RUB 970,000) x 15%).
Minimum tax - 10,000 rubles. (RUB 1,000,000 x 1%).
The minimum tax payable is RUB 38,750. (RUB 1,000,000 x 1% - RUB 48,750).
There is no need to pay anything to the budget.
The deadline for paying the minimum tax is the same as for regular tax for the year - no later than March 31 of the following year (clause 7 of Article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the minimum tax is higher than the regular tax, then the difference between them next year can be taken into account in expenses (Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 14, 2010 N ShS-37-3 / [email protected] ).
Even if a loss is incurred at the end of the year, you must pay a minimum tax - 1% of income (clause 6 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The review was prepared by specialists from the Consulting Institute of the Group of Companies "Zemlya-SERVICE"
Income minus expenses
This is the name of the “simplified” type, which obliges individual entrepreneurs and companies to pay a minimum tax. The simplified tax system “income - expenses” (hereinafter referred to as the abbreviation DSM) is more difficult to understand for novice businessmen. Therefore, many, not particularly understanding the topic, opt for a regime called the simplified tax system 6%. In this case, everything is extremely simple: the entrepreneur pays 6% of the profit of his enterprise as tax.
What about the other case? If a person chooses VHI, then his tax can vary from 5 to 15 percent. In general, first of all, an entrepreneur must find out the rate set for his type of activity in the region of its implementation. And the exact value is determined by performing some calculations. And it’s worth talking about this in more detail. But first, a few words about advance payments. This is an important nuance that cannot be ignored.
Income tax rate to the federal budget
As already mentioned, 3% of the total amount goes to the federal budget. It doesn’t matter whether the regional rate is 17% or it has been reduced by a decision of the authorities - 3% is a plus.
Example: Tax base = 1,000,000 rubles.
N/A = 1,000,000 * 20% = 200,000 rubles.
Of these, the main one:
To the federal budget = 1,000,000 * 3% = 30,000 rubles
To the regional budget = 1,000,000 * 17% = 170,000 rubles.
By reduced:
To the federal budget = 1,000,000 * 3% = 30,000 rubles
To the regional budget = 1,000,000 * 13.5% = 135,000 rubles.
Only three percent of the amount does not always go to the federal budget. This only happens when using the main bet. And the percentage to the budget that companies pay at non-basic rates goes to the federal budget in full.
What will we pay to the state?
If the “simplified” tax turns out to be less than the minimum tax, then the amount of the minimum tax will have to be paid to the budget.
In this case, the difference between the paid minimum tax and the actual simplified tax system does not need to be reflected in any accounting entries. If the “simplified” tax turns out to be more than the minimum tax, then the amount of the “real” tax must be paid to the budget.
note
The minimum tax is calculated only based on the results of the tax period—the year. There is no need to do this at the end of a quarter, half a year, or 9 months.
Dividends
This is any income that remains after paying interest to the budget; it is distributed among shareholders (participants) in proportion to their shares in the capital. They are usually paid in cash, but can also be issued in the form of shares or other property. If a company pays dividends to individual participants, then it, as a tax agent, is obliged to withhold and transfer a percentage from them to the budget. But this applies to personal income tax payment. The tax rate for personal income tax and income tax on dividends is generally the same - 13%. This simplifies the calculation, but does not in any way affect the payment of N/P.
If a company pays dividends to participants - legal entities, then it calculates and withholds N/P and reflects it in the declaration.
If the company itself received dividends, then it deducts the amount received N/A
The calculation formula is given in Art. 275 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If an organization received dividends from other companies and simultaneously paid them to its participants, then the amount of state duty is calculated using the formula:
Where NPD - Income tax on dividends; DNU - dividends paid to the participant; DNVU - paid to all participants; DPO - received by the organization.
Let's look at the formula using an example.
CJSC Serpentine received dividends from another organization - 80,000 rubles. And also distributes them among its participants. Distribution according to shares in capital: I. V. Kovalev - 700,000 rubles (individual, citizen of the Russian Federation); Imperia LLC - 400,000 rubles. Let's calculate how much you need to withhold: personal income tax on dividends I.V. Kovalev - 700,000 * 13% = 91,000 rubles. On the profit from dividends paid to the participant - Imperia LLC:
DNU = 400,000 rubles. DNVU = 400,000 + 700,000 = 1,100,000 rubles. DPO = 80,000 rubles.
CJSC "Serpantin" is obliged to withhold and transfer to the budget income tax on dividends of the participant - LLC "Imperia" in the amount of 48,218 rubles.
Foreign organizations pay tax on dividends at an increased rate - 15%. There are also cases of preferential taxation - 0%.
Let us remind you that the rate has been changed from 9% to 13% since January 1, 2020.
| Bid | Dividend income |
| 13% | for shares certified by depositary receipts; received by Russian organizations from Russian and foreign companies not specified in paragraph 1, paragraph 3, Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. |
| 15% | received by foreign companies: — on shares of Russian organizations; — from participation in the capital of companies in another form. |
| 0% | received by Russian companies from foreign and Russian organizations, provided that the receiving company at the time of the decision to pay: - owns no less than 50% of the authorized capital of the paying company for 365 consecutive days; — owns depository receipts with the right to receive at least 50% of the total amount of dividends paid. |