On the territory of the Russian Federation, every citizen or foreigner who has the right to temporary residence is obliged, when running his own business, to obtain the appropriate status of a business entity. If a person makes a profit without state registration, the tax office will charge a fine for working without an individual entrepreneur. Those who deliberately do not want to obtain the status of an individual entrepreneur in order not to pay taxes to the budget can be brought not only to tax and administrative (Administrative Code) liability, but also to criminal liability.
In what cases is it necessary to register an individual entrepreneur for work?
Entrepreneurship should be understood as an activity aimed at systematically generating income from the provision of services, from the rental of property, from the sale of goods. All business transactions of individual entrepreneurs must be reflected in the appropriate accounting register KUDIR and used to account for cash received at the cash register cash desk.
Individual entrepreneur registration
Business activities are classified as follows:
- purchase of inventory or property for further resale or involvement in the production process for the purpose of making a profit;
- formation of stable partnerships with contractors;
- When concluding a transaction, documentation is drawn up, for example, waybills, invoices, which is used to keep records of all business transactions.
Note! To identify the activities of an individual and define them as entrepreneurial, various methods are used. If a citizen carries out one-time commercial transactions with counterparties, in this case a civil agreement is concluded between the partners. Having such an agreement in hand, a citizen will not have to register with the Federal Tax Service as an individual entrepreneur.
IP: how to determine the normative field of status
The immediate grounds for talking about the need to register an individual entrepreneur as an entity deriving regular profit from a certain area of economic relations may be:
- regular trading;
- performing a certain range of services;
- performing certain technical work related to the operation of special equipment;
- provision of property for temporary use.
In addition, the legislation provides for some other forms of economic activity aimed at generating economic profit, which may be the basis for registering an entity as a full-fledged individual entrepreneur in 2020.
In case of failure to register, a system of fines and other economic and administrative penalties is provided. In particularly large-scale cases, in particular, trading on a particularly large scale without the appropriate documents, criminal liability is provided for, since fines are not always able to stop offenders.
What is the penalty for working without an individual entrepreneur?
What happens if you don’t submit your individual entrepreneur’s declaration on time - what is the fine?
Carrying out entrepreneurial activity without registering an individual entrepreneur will entail a fine of 500-2000 rubles for the citizen.* In accordance with the Tax Code regulations, the regulatory authorities will first conduct an inspection, the purpose of which is to confirm the entrepreneurial activity. If an individual carries out commercial activities without using a cash register, for such a violation he will have to pay a fine, the amount of which varies from 4,000 rubles. up to 6000 rub.*
Important! If the fiscal authorities cannot prove that the individual being inspected systematically made a profit, they will not be able to apply a fine to him for the lack of an individual entrepreneur. They will also not be able to hold a citizen accountable for working without registering as an individual entrepreneur if he made one-time transactions to generate income.
If business activities are carried out without a license (for example, selling alcohol), individuals are deducted from the treasury in the form of a fine of 2000 rubles. up to 2500 rub. In parallel, all identified products are subject to confiscation. Devices, instruments and equipment through which goods were manufactured for illegal sale will also be confiscated. If commercial activity is carried out in violation of the rules stipulated by the license, then a penalty will be imposed on the violators, namely a fine for carrying out business activities without state registration of 4000 rubles. up to 8000 rub.*
Sanctions for illegal business
When is individual entrepreneur registration required: general approach
You need to understand the difference between a one-time sale and an ongoing business. In the first case, registration of an individual entrepreneur is not required. An example would be the periodic sale of unnecessary items through advertisements.
Constant trade involves purchasing goods at wholesale prices and selling them at market value on a regular basis. To do this, citizens need to obtain the status of an individual entrepreneur. Otherwise, the law provides for liability ranging from administrative to criminal. When engaging in trade without registering as an individual entrepreneur, almost every businessman receives fines.
What falls under illegal business activities
Illegal business activity - what does it include?
To prove the fact of illegal business activities, Federal Tax Service employees must conduct an inspection. They need to prove that the citizen is in fact an individual entrepreneur who has not passed state registration. In this case, fiscal authorities are guided by the following related factors:
- a citizen systematically carries out activities (working as a manicurist, providing photo studio services, tachograph, etc.);
- if a person does not have time to sell his goods or perform services, he may be fined without an individual entrepreneur after he makes a commercial offer to the client;
- the citizen creates all the conditions for individuals or organizations to purchase the products he offers or use his services (presentation of goods is a prerequisite).
Note! Financial sanctions for illegal business activities will be applied regardless of the form of commerce. In this case, it will not matter whether the citizen sells his product on his own or involves agents in the process, posts it on the Internet, etc.
When conducting an inspection, Federal Tax Service employees will use a variety of methods of influencing and obtaining information:
- survey of clients who used the services of an individual or purchased goods from him;
- checking bank statements, acts of acceptance and transfer of goods or services, contracts confirming the fact of transfer of property for rent;
- study of the media, articles in newspapers, specialized websites on the Internet where citizen’s advertisements were placed
Checking an entrepreneur conducting business without an individual entrepreneur
If a commercial activity does not meet one of the following criteria, then it cannot be classified as entrepreneurial:
- constant contacts with suppliers and buyers;
- accounting of completed transactions is carried out;
- goods are purchased or manufactured for subsequent resale.
Legal regulation
It is worth remembering that the activities of individual entrepreneurs aimed at making a profit in any form: be it trade or the provision of services, must take place in a regulated legal field, otherwise you will inevitably face a fine or a more serious penalty.
The activities of individual entrepreneurs in the Russian Federation are regulated by the Tax Code, in particular Articles 83 and 84, as well as many by-laws and regulations.
Studying this legal framework is a rather labor-intensive and lengthy process, so in this article we will try to acquaint you with the basic tenets of the legal responsibility of individual entrepreneurs before the law and the public, which determines the penalty in case of violation of certain norms.
The activities of any individual aimed at making monetary profit can a priori be qualified as the activities of an individual entrepreneur carried out without registration. Therefore, if you are engaged in trading agricultural products and do not want to bother yourself with the lengthy registration procedure, be prepared to pay a fine first. And already in this case you come under increased attention of fiscal control authorities. And this can be quite burdensome for a young, developing business.
Therefore, before you enter into open conflict with the state financial supervision system and earn a fine, you should think twice. Do you, as a beginning individual entrepreneur, need problems with the law and the endless fines that will inevitably follow after the lack of registration is discovered?
How to avoid violations
Is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur with temporary registration? What is needed for registration?
To conduct business without an individual entrepreneur and at the same time prevent problems with the law and subsequent punishment, Russian citizens must take into account the following nuances:
How to avoid inspections and fines
- Supervisory authorities will not hold tax, administrative or criminal liability for unsystematic trade in the market of products grown on a private farm or made with one’s own hands. But, individuals must remember that they will have to reflect the income received in their tax return for the reporting period - a year.
- In order to prosecute a citizen for engaging in illegal business activities, the regulatory authority must prove the fact of work without registering as an individual entrepreneur. At the same time, tax authorities must confirm the systematic nature of the transactions.
- The punishment for an individual will be determined by the court, so employees of regulatory authorities will collect evidence: testimony of witnesses, advertising online and in the media about the sale of goods, provision of services, decryption from card accounts (payment is taken into account if the purpose included the corresponding wording), etc. .
Note! The ideal solution would be to obtain the status of a business entity. Today, individual entrepreneurs are provided with preferential tax regimes, thanks to which they will be able to optimize costs. If for some reason a citizen does not want to register an individual entrepreneur and receive a certificate, then he can legally carry out commercial activities as a self-employed person. In this case, he does not need to worry about what will happen if he starts working without an individual entrepreneur.
Why is registration not completed on time?
So, what prevents a specific individual from timely obtaining the status of an individual entrepreneur and avoiding problems with the law, including significant fines?
Firstly, this is basic ignorance. If people are not familiar with the legal framework for carrying out entrepreneurial activities, they consider themselves entitled to make profit in a way available to them, bypassing the bodies of state fiscal control.
Further, a person may also have malicious motives. If you are aware of the need for registration, but try to avoid it by any available means, this is already classified as an offense and entails appropriate sanctions.
Thirdly, sometimes an entrepreneur may simply not have enough time to go through the registration procedure and register an individual entrepreneur. After all, this status requires the collection of a certain block of documents and the passage of legal procedures, sometimes quite extended over time. In this regard, the fiscal control authorities of the Russian Federation have recently been doing everything to simplify the registration procedure and make it as convenient as possible for each individual legal entity.
Responsibility of the individual entrepreneur
If we talk about various types of administrative sanctions, the state treats entrepreneurs more loyally than legal entities. Fines for individual entrepreneurs under the Code of Administrative Offenses are several times lower than for organizations.
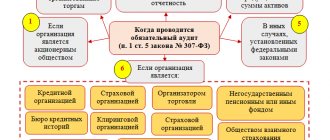
It is known that the state has been striving to reduce administrative pressure on small businesses for several years now. However, the ban on scheduled inspections applies only to non-tax authorities. Inspections by the Federal Tax Service and funds are not limited in any way.
| ✏ But when it comes to tax and personnel violations, as well as liability for reports not submitted on time, there is almost no difference between an individual and a legal entity. An individual entrepreneur may also come under criminal liability (the full list of sanctions is listed in Chapter 22 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), but this usually happens when causing large and especially large damage. |
Basically, judging by the completeness of the collection of taxes and contributions, individual entrepreneurs comply with the basic rules of doing business. To make this easier, we draw your attention to the main violations for which you may be fined.
Didn't apply for a license
Some of the activities of individual entrepreneurs are subject to mandatory licensing. This applies to cases if the entrepreneur is a private detective, or, for example, he has a bus on which he transports passengers.
If an entrepreneur works without a license, he may face a fine of 4 to 5 thousand rubles. (Article 14.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). And besides this, manufactured products, production tools and raw materials may be confiscated from him. Returning a couple of paragraphs back to the example about the driver, let’s clarify that the bus itself can be taken away.
Is IP a necessity or a desire?
The first thing to find out is whether citizens really have to register as individual entrepreneurs in order to make a profit on the territory of the Russian Federation? There are several options for the development of events.
If a person has made a one-time profit from his activities, he can simply pay personal income tax on his income. Single actions that entail the receipt of funds do not require any registration.
But any regular commercial activity requires opening an individual entrepreneur or LLC. Regularity should be understood as receiving profit from an activity more than 2 times.
Violation of tax rules
An entrepreneur must pay taxes on time and in full. Payment deadlines for different taxation systems are also indicated in our calendar. The fine for non-payment of taxes by individual entrepreneurs under Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is 20% of the amount of unpaid tax.
In addition, an entrepreneur, if he has employees, becomes a tax agent, and therefore must withhold personal income tax from their income and transfer it to the budget. For violation of the deadlines for transferring this tax, a fine is imposed on the individual entrepreneur according to the same rules, i.e. 20% of the amount not transferred.
Simplified registration
To avoid a fine and further economic penalties, you just need to go through a simple procedure for registering an individual entrepreneur. To do this, you submit a corresponding application and copies of identification documents to the fiscal control authority, and within a few days you receive a decision to include you in the unified registration database of individuals engaged in entrepreneurial activities.
It should be noted that the status of an individual entrepreneur in 2020 implies significant tax benefits and many additional social and legal guarantees. If you decide to open your own small business, it is much easier to do so within the framework of the statutory scheme, avoiding fines and other regulatory penalties. Not to mention, the lack of permitting documentation can result in a loss of customer confidence and a loss of customer base, which can be a significant economic blow to the profitability of your business.
The most common tax penalties for individual entrepreneurs in 2020
Tax return submitted late
For a certain period, the entrepreneur himself kept records of his business, after which he decided to hire a specialist. While accepting cases, the accountant discovered that the individual entrepreneur had sent a tax return through a convenient online service, but did not have confirmation that the required reporting had been submitted. If a reconciliation with the tax office reveals a failure to provide reporting data, you may face a fine.
Most often, the declaration is not submitted on time due to ignorance of the required periods or due to forgetfulness. However, violation of tax reporting deadlines entails sanctions. The fine for failure to file a tax return for individual entrepreneurs is imposed (according to Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- in the amount of 5% of the tax indicated in the declaration for each month of delay (both full and incomplete) - the total fine should not exceed 30% of the tax;
- in the amount of at least 1000 rubles.
Practical examples.
- The individual entrepreneur did not submit a zero declaration on time - the fine will be minimal, 1000 rubles.
- Tax fines for individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system, who were late in filing a return, but paid the tax (10,000 rubles) on time, again provide for a minimum penalty of 1,000 rubles.
- The individual entrepreneur was 3 months late in submitting his tax return under the simplified tax system, the tax itself was in the amount of 10,000 rubles. I paid after it was submitted. The fine will be 5% of the tax for each month of delay, that is, 10,000 rubles. / 100 * 5 = 500 rubles/month, multiply by 3, get 1500 rubles.
- The individual entrepreneur delayed reporting to the Federal Tax Service for 3 years, the tax amount was the same, 10,000 rubles. The fine for a late tax return will be assigned to the individual entrepreneur at the maximum permissible value, that is, 30% of the tax:
- 000 rub. / 100 * 30 = 3000 rub.
Top 3 articles that will be useful to every manager:
- Accounting services for companies: all the subtleties and nuances
- What to choose LLC or individual entrepreneur: pros and cons of different forms of ownership
- How to open a current account for an individual entrepreneur: choosing the best bank
Cash register receipt not issued
An individual entrepreneur worked in a large shopping center and sold goods. In such places, it is quite common for verification to take place, which takes the form of a secret shopper. The inspectors (at least two tax inspectors) make a test purchase and transfer the money. By law, they need to provide the KKM check, and immediately, simultaneously with the change. If the change was issued, but the check was not attached to it, the checking party will present work IDs and record that the cash register was not used. The product will be returned and a fine will be issued.
It is important to remember and observe: accepting money for any goods, services, or work must be accompanied by the issuance of a KKM receipt. There are some exceptions here: if an individual entrepreneur provides exclusively services to the public (individuals), he can do without cash register checks. But there must still be a document confirming payment - and in the presented case it will be replaced by strict reporting forms (SSR).
The amount of the tax fine for an entrepreneur if he did not issue a KKM check, in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses will be:
- from ¼ to ½ of the purchase amount;
- not less than 10,000 rubles.
Practical examples:
- The individual entrepreneur did not clear the check for the amount of 100,000 rubles. This will entail a tax penalty of 25,000–50,000 rubles.
- The individual entrepreneur did not clear the check for 100 rubles. You will have to pay a minimum fine of 10,000 rubles.