Hello! In this article we will talk about the features of paying land tax by an individual entrepreneur.
Today you will learn:
- In what cases does an individual entrepreneur need to pay land tax;
- When land tax is not taken into account;
- How to calculate tax payable;
- Should an individual entrepreneur pay land tax using the simplified tax system?
Land tax
The generally accepted taxation system also includes a tax on land use. If you are the owner of a plot, you are required to pay contributions to the treasury for it. This applies to individuals and legal entities.
Land tax is regulated by three main legal acts:
- Law No. 141 of 2004;
- Law No. 382 of 2014 (everything related to changes in accrual);
- Tax Code, in particular Chapter 31.
There are two main tax rates that are adopted at the state level. They are the maximum possible for each region. Local authorities can reduce this rate, thereby reducing the tax burden in a particular region of the country.
Basic tax rates:
- 0.3% – for agricultural land in urban areas, construction of housing and communications, maintaining your own garden or vegetable garden, personal breeding of domestic animals; lands used for customs, security or defense purposes;
- 1.5% – for all other types of land plots not included in the above list.
Within one region, the land tax rate can be differentiated, that is, different between individual taxpayers. This rule is set at the discretion of the local administration.
You can find out the rate that applies in your region of residence via the Internet or by contacting the authorities directly. If you want to find information online, you need to visit the official website of the tax service of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
To find an accepted bet, follow these steps:
- Specify region;
- Go to the “Electronic Services” section;
- Select the “Betting Information” link;
- Indicate the tax of interest, namely land tax;
- Select a period;
- On the map that appears, mark the location of your site;
- Click on the “Search” button;
- You will see a table with a regulatory act that sets the rate in the selected region;
- On the right in the table you will see a link to the document, click on it to access the information;
- In the file that opens you will find all the necessary information.
Land tax under the simplified tax system: payment procedure, deadlines
Ignatiev, experts from the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
The organization applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income minus expenses”. The organization has several land plots on its balance sheet at purchase price; the acquired land plots are not intended for further resale. Land plots are not depreciated. How to write off the cost of land in accounting?
According to paragraph 3 of Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting”, organizations that have switched to the simplified tax system are exempt from the obligation to maintain accounting records, except for accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets.
This means that an organization using the simplified tax system must keep records of fixed assets in accordance with PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets” (hereinafter referred to as PBU 6/01).
Land plots for accounting purposes are accounted for as part of fixed assets (clauses 4, 5 of PBU 6/01).
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting at their original cost (clause 7 of PBU 6/01). The initial cost of fixed assets acquired for a fee is recognized as the amount of the organization's actual costs for acquisition, construction and production, with the exception of VAT and other refundable taxes (except for cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation) (clause 8 of PBU 6/01).
As a general rule, the cost of fixed assets is repaid through depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01).
At the same time, fixed assets whose consumer properties do not change over time, including land plots, are not subject to depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01).
Consequently, the value of land plots can be written off from accounting only in the event of their disposal, which occurs in cases of sale, transfer in the form of a contribution to the authorized (share) capital of another organization, a mutual fund, transfer under an agreement of exchange, gift, deposit contribution under a joint activity agreement and in other cases (clause 29 of PBU 6/01).
Income and expenses from writing off fixed assets from accounting are reflected in accounting in the reporting period to which they relate and are subject to credit to the profit and loss account as other income and expenses (clause 31 of PBU 6/01).
According to paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization,” other expenses include, among other things, expenses associated with the sale, disposal and other write-off of fixed assets and other assets other than cash (except foreign currency), goods, and products.
For your information
Organizations applying the simplified tax system and choosing income reduced by the amount of expenses as an object of taxation can take into account for the purposes of forming the tax base only those expenses that are listed in the closed list contained in paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, provided that they meet the criteria specified in paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the object of taxation, the taxpayer reduces the income received by expenses for the acquisition, construction and production of fixed assets (taking into account the provisions of paragraphs 3 and 4 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, fixed assets for the purpose of applying Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation include fixed assets that are recognized as depreciable property in accordance with Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 4 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, land is not subject to depreciation and the list of expenses taken into account when determining the tax base under the simplified tax system, established by paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, does not provide for expenses for the acquisition of land plots, the organization does not have the right to take into account expenses in the form the cost of land plots when forming the tax base for the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system (see, for example, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 30, 2011 No. 03-11-06/2/101, dated September 16, 2010 No. 03-11-06 /2/145).
Does the individual entrepreneur pay land tax?
In matters of payment of land tax, an individual entrepreneur is treated as an individual. If your activity, one way or another, involves the use of an allotment that brings in cash, then you must pay tax.
The mandatory contribution is paid in the following cases:
- If the land is privately owned;
- The allotment was transferred for indefinite use;
- With lifelong inheritance.
If you have title documents for the land you are using, then you are a taxpayer. Moreover, this type of collection is municipal, that is, all contributions are sent to the local budget, and not to the general treasury of the country.
Should an individual entrepreneur submit a land declaration using the simplified tax system?
To pay land tax as an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system, you do not need to submit a declaration. The tax office independently calculates the tax.
Formula for calculating land tax:
ZN = KS × CH × K
Where:
ZN - land tax;
KS - cadastral value (the assessment is carried out by Rosreestr and transmits the data to the tax office);
SN - tax rate;
K - ownership coefficient (calculated if the land is owned for less than 12 months).
Rates for calculating land tax:
- 0.3%: land for agriculture, livestock breeding;
- land for housing and communal services and residential buildings;
- land for personal farming, gardening;
- lands used for customs and defense facilities;
- land plots with other purposes
But local authorities have the right to set other rates.
Federal tax benefits:
- Categories of citizens exempt from land tax: Peoples of the Far East, Siberia, the North, recognized as indigenous and small in number.
- Disabled people with groups 1 and 2.
Local Administrations have the right to establish additional benefits. All explanations on local benefits and tax rates are available on the Federal Tax Service website in the “Reference Information” section.
But to receive the benefit, you need to submit an application (KND form 1150063) to the tax office - without your application, the Federal Tax Service will not take it into account.
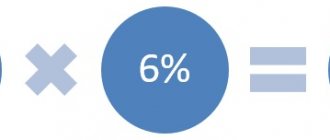
We recommend reading: Taxes and reporting of individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system 6% + what is considered income and how to work with primary documents.
Calculating taxes
Not all beginning entrepreneurs know whether they submit a land tax return. Currently, individual entrepreneurs are exempt from drawing up and filing a declaration.
Previously, it was necessary to submit reports to the tax service, but now individual notifications with the amount are sent to the entrepreneur’s address.
Such notifications are sent before October 31 of the year following the reporting year. That is, for taxes for 2020, the payment letter will arrive in October 2020. Payment deadlines end on December 1st after receiving a receipt from the tax office.
There are often cases when the tax authority does not send notifications. It is important to understand that this does not exempt you from paying the fee. For late repayment of debt, penalties will be charged from your account, regardless of whether the tax authority sent the notification on time or not.
Therefore, if a payment receipt has not appeared in your mailbox by October 15, we recommend visiting the tax authority to clarify the circumstances and receive a notification.
Depending on what dates in the month you purchased the plot, that month may or may not be included in the payment.
A full month will be taken into account if:
- The plot is registered from the 1st to the 15th of the month (for the buyer);
- The plot was sold from the 16th to the 31st (for the seller).
The month of purchase/sale will not be taken into account for tax purposes if:
- The plot was purchased from the 16th to the 31st (for the buyer);
- The plot was sold from the 1st to the 15th (for the seller).
The land tax payment process includes the following steps:
- The tax authority draws up a notice of payment with a receipt;
- The document is sent to the individual entrepreneur’s registration address;
- The entrepreneur pays the tax using the specified details at any bank that provides such a service.
Land tax is payable once a year. For individual entrepreneurs, advance payments are not provided - this means that the entire tax amount must be paid at once.
Land tax for individuals and legal entities
Any person who owns a land plot is obliged to pay contributions to the budget for this area. The rates applied to owners are the same, regardless of whether they are private users, entrepreneurs or organizations.
The only difference is the timing of payment and the procedure for completing documentation. Firms and companies independently fill out declarations and submit reports to the supervisory authority. Individuals only need to make contributions on time according to the statements that come from the supervisory service.
Payment benefits
The state has created benefits for paying taxes on land plots for certain categories of citizens. Exemption from contributions is carried out on a full or partial basis.
The tax base for the following persons is reduced in the amount of 10,000 rubles:
- Disabled people of groups 1 and 2;
- Disabled since childhood;
- Heroes of the USSR or the Russian Federation;
- WWII veterans;
- Participants in man-made disasters and persons taking part in their liquidation (persons exposed to radiation).
For these categories, 10,000 rubles are deducted from the tax base. Also, each region can establish additional benefits. For example, in some areas there is a regulation establishing the area of the plot that is not subject to tax.
If the plot is larger than this area, then only a contribution is paid for the difference between the actual size and that established by law. For those whose plot is less than or equal to the area specified in the legal document, the tax is equal to zero.
If you are the owner of several plots in different regions, then you are entitled to benefits for each individual plot. If you own lands within one subject of the Russian Federation, then you can use only one of them for preferential tax purposes.
What are the land tax rates in St. Petersburg
As mentioned, the amount of tax paid, the procedure and terms are regulated by local legislation. St. Petersburg Law No. 617-105 contains a list of persons for whom various privileges are provided. For example:
- pensioners who own a plot of land with an area of up to 2.5 thousand m2;
- Chernobyl victims;
- some types of economic entities.
The table below shows what tax rate for land tax is in effect in the region in question (excerpt from the law).
Who doesn't pay tax
In addition to the current benefits for the population, there is also the possibility of complete exemption from paying contributions.
This rule applies throughout the Russian Federation and applies to areas:
- Managed by the forest fund;
- Seized as a result of a decision of local authorities (for example, for the purposes of a nature reserve or the disposal of radioactive waste);
- Limited in use (occupied by cultural heritage or natural water bodies);
- Used for highways;
- Being the common property of an apartment building;
- Available for free use;
- Rented (in this case the owner of the plot pays the tax);
- Inhabited by small numbers of indigenous people (if the plot is used for living and conducting their own fishing).
The owner has the opportunity to reduce the value of the tax base. This is due to the cadastral value, which may not always be adequate.
If you think that the price of your plot is too high (and the higher it is, the higher the tax to be paid), you need to invite an independent appraiser who, based on experience and knowledge, will draw up a document on the real value of the property.
With the received certificate, you need to contact the commission for the consideration of such disputes. If the issue is not resolved in your favor pre-trial, then it is necessary to file a statement of claim.
Tax amount
There is a simple formula to calculate the contribution payable:
Land tax = tax rate adopted in the region * cadastral value of the plot.
The cadastral price is updated on the 1st day of the reporting year (the one for which the tax must be paid).
For example, the cadastral value is 578,000 rubles. The tax payable at a rate of 0.3% will be; 578000*0.3% = 1734 rubles. If a rate of 1.5% is applied, then the tax will be equal to: 578,000 * 1.5% = 8,670 rubles.
The cadastral value and the applicable tax rate will be indicated on the payment receipt. If you have payment benefits, they must be recorded with the tax office. To do this, you will need to collect a package of documentation confirming the availability of benefits and provide it to the operator for further accounting.
Interest rate of land tax in Moscow
The type of mandatory payment in question is regulated by Law No. 74, which also establishes benefits and payment terms.
Thus, organizations must transfer the final tax no later than February 1 of the following year. Otherwise, the procedure and requirements coincide with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Interest rates on payments for residents of the capital are presented in the table:
Certain cases of tax payment
Let's consider non-standard situations of paying land taxes. The first such case is taking into account the mandatory contribution for joint ownership of a plot. If there are several owners of one plot, then they pay land tax in proportion to their share.
Example. You own a plot of 75 square meters. Your plot is part of one large plot of 238 square meters. The total cadastral value of the land is equal to 300,000 rubles. Since the plot is used for breeding livestock for sale, the tax rate is 0.3%. First you need to calculate the cadastral value of 75 square meters. It is equal to: 300,000*75/238 = 94,538 rubles. The tax amount will be: 94538*0.3% = 283 rubles.
It is important to understand that if you are the owner of the participant jointly with the state authorities, you will pay tax on the entire plot. Even if you only use a small plot, the fee will be charged on all square meters.
This is due to the peculiarities of state ownership of land. Local authorities are limited in the ways they can dispose of land, and therefore are exempt from paying taxes.
Let's consider the second case, when the plot was in your ownership for an incomplete number of years.
Example. The plot was purchased on May 23, 2020. On January 1, 2020, the cadastral value was 652,000 rubles. The region has a rate of 0.3%. For tax purposes, only the months from June to December are accepted, since the property was purchased in the second half of May. We get the amount of tax to be paid: 652000*0.3%/12*7 = 1141 rubles.
There are also situations in which, when paying land tax, both benefits and an incomplete number of months of use of the site are taken into account.
Example. A disabled person of group 1 registered an individual entrepreneur in August 2020. For business purposes, a citizen acquired a plot of land on November 19, 2020. The cadastral value of the land is equal to 523,000 rubles. The local administration has established a tax rate for this plot of 0.9%. To calculate the tax required to be paid in 2020, it is necessary to calculate the tax base. It will be (taking into account the benefit of 10,000 rubles for a disabled person of the 1st group): 523,000 - 10,000 = 513,000 rubles. The plot was owned for 1 full month. The tax amount will be: 513000*0.9%/12*1 = 385 rubles.
Land tax
The Russian Tax Code (Article 388) obliges entrepreneurs to make payments on land plots. It arises if the relevant property belongs to a businessman on the basis of property rights, inheritance, and perpetual use.
In accordance with the general rule, an entrepreneur acts as a payer of land tax if two conditions are simultaneously met:
- ownership is documented for the businessman;
- the land plot is located on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in which the corresponding tax applies.
If for some reason individual entrepreneurs do not have documents confirming their ownership, two situations are possible:
- A businessman does not have an obligation to pay the corresponding royalties if the land was purchased after January 31, 1998, but the right to it was not registered. It is important to remember that deliberate evasion of state registration of land to reduce taxes threatens the entrepreneur with a fine. The amount will be considerable and amount to up to 40% of the tax penalty.
- If the land plot was acquired before January 31, 1998, the individual entrepreneur is obliged to pay land tax even in the absence of ownership papers. This is because in this situation it is possible to prove ownership of other documents, for example, a purchase and sale agreement.
It is important to know that there are conditions under which businessmen are exempt from paying.
Such situations can be divided into three main groups. All of them provide tax benefits.
The first group includes situations that arise taking into account the characteristics of the earth:
- the site belongs to the forest fund;
- according to the law, the land is withdrawn from circulation;
- there are restrictions on turnover;
- the site is occupied by cultural heritage sites or related to the water fund;
- the land is part of the property of a multi-apartment fund.
The second group includes situations related to the law, as a result of which individual entrepreneurs own land. You will not have to make payments on the land if the businessman uses the land on the basis
and rights of free use or under a lease agreement.
Indigenous minorities are exempt from paying taxes. This applies to areas where living, farming and fishing are carried out.