Grounds for awarding bonuses to employees
Labor legislation does not set itself the task of obliging the employer to pay bonuses to its employees. However, it does not prohibit this kind of stimulation.
Important ! It is quite legitimate for the management of an organization to refuse to pay bonuses to its employees, since the calculation of bonus payments is not an obligation, but a personal matter of the employer.
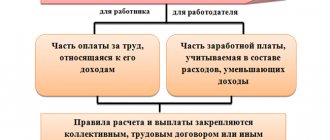
That is why each employer determines the possibility of payments independently. At the same time, the management of the organization has the right to independently set the amount of bonuses. For these purposes, internal local acts, collective agreements or employment contracts are provided. This documentation should also indicate when and under what circumstances the employee is entitled to a bonus payment. Often, the heads of the organization provide for the payment of bonuses on the day of payment of wages.
In order for the payment of bonuses to employees to be legal, after its calculation it is necessary to issue an order for its accrual. Two types of orders can be used for this:
- If it is decided to award bonuses to one employee - Form N T-11;
- If a group of persons is subject to bonuses, use Form N T-11a.
But no one prohibits the employer from using their own forms to issue this order.
Year-end bonus: taxation
The bonus, including the annual one, is part of the salary from which personal income tax is generally withheld. The “thirteenth salary” is subject to insurance contributions, incl. for “injuries” (clause 4 of article 226 and clause 1 of article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
According to the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance (letter dated September 29, 2017 No. 03-04-07/63400), when calculating personal income tax on bonuses at the end of the year, it should be taken into account that:
- the date of actual receipt of income will be the day it is paid in cash or transferred to the employee’s account (clause 1, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), despite the fact that it was accrued for the past tax period;
- tax is withheld upon actual payment of income to the employee (clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- Personal income tax is paid no later than the next day after the payment of the premium (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When paying bonuses at the end of the year, what will be the taxation of the enterprise's profits?
Bonuses for production results are labor costs (clause 2 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But if such a bonus is not provided for by a collective agreement or an employment contract, it should not be taken into account in expenses that reduce profits (clause 21 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, it is important to include a reference to the “Bonus Regulations” in the text of employment contracts.
When taxing profits, a one-time bonus based on the results of work for the year is taken into account in the period in which it was accrued.
Main types of employee bonuses
Along with the possibility of making incentive payments and their size, company managers can choose any of the possible types of bonuses, which is also indicated in the above-mentioned regulatory documentation.
So, there are several main types of bonuses: (click to expand)
- Monthly – bonus payment is made monthly;
- Quarterly – the bonus is paid once a quarter;
- Annual – payment is made once a year;
- Lump sum – a lump sum is paid for an event or circumstance.
Payment of bonuses to employees can be made both for work-related reasons and regardless of the amount of work done.
Payment of bonus funds in most cases occurs according to two scenarios: the bonus is calculated as a percentage of the salary monthly or once a year.
How are bonuses accounted for in accounting?
Since there are several types of these payments, they are reflected in accounting differently. The company management itself makes the appropriate decision, and usually remunerations are included in the income of employees, and therefore are represented as a full-fledged object of taxation.
Important! Bonuses are part of income, so they are strictly taken into account by the accountant.
Bonuses through postings
Rewards in the company can be issued at the expense of the free profit of the company. To do this, all remunerations must be reflected in the accounting records with the corresponding entries.
Important! If funds are issued in the form of dividends, then the management of the company issues a special order, and it is studied by all employees, who then put their signature on it. You can learn how to pay dividends to the founders of an LLC here.
Typically, account D20 K70 is used to reflect payments, indicating that payments were made from expenses in the main area of the company's work. If other expenses are used, then wiring D91.2 K70 is used.
The procedure for filling out form 6-NDFL.
Procedure for calculating monthly salary bonuses
Often the monthly bonus provides an amount calculated as a percentage of the salary. The percentage of wages in which bonuses are supposed to be awarded to employees is prescribed in labor regulations.
The procedure for calculating the monthly payment of wages to employees, taking into account the salary bonus, is as follows:
- If the employee worked all days, then the whole salary is taken for calculation. If an employee missed several days due to illness or vacation, then the salary for the period worked is calculated proportionally.
- Then the percentage specified in the contract is multiplied by the amount of salary received that month, resulting in the amount of the bonus.
- Next, the size of the salary and the bonus received in the previous calculation are added up.
- The amount obtained in the previous calculation is multiplied by the regional coefficient, if one is used at the enterprise, resulting in the amount of accrued wages and bonuses. If a regional coefficient is not provided, then the payment amount will be the amount from the previous calculation.
- Next, from the result obtained in paragraph 4, the amount of personal income tax is calculated. To do this, the resulting amount is multiplied by 13% or 30%, depending on whether the employee is resident or not.
- To determine the amount of payment of earnings and bonuses, it is necessary to subtract the amount of personal income tax and the amount of the previously paid advance from the amount received as a result of the actions indicated in paragraph 4.
For clarity, we will provide an example of calculating the monthly bonus from salary and the total payment for the month below.
The concept of the award and its purpose
Important!
A monthly bonus is in the form of a monetary reward or incentive for an employee of a company, and is usually paid if he has performed well in his work. This remuneration may be specified directly in the employment contract or in the regulations of the organization itself. It can have a fixed amount or be constantly calculated, for which the employee’s earnings and a certain percentage are taken into account.
Monthly rewards can be presented in two types:
- production, which are part of the salary itself, and therefore relate to the amount of work performed by the employee;
- non-productive, for example, a salary increase is given due to the employee having a minor child or other reasons for the payment of this bonus.
Both types are paid only at the initiative of the employer. How to carry out the operation of calculating and paying monthly bonuses in 1C - see this video:
How is the monthly premium calculated?
In Art. 114 of the Labor Code contains information that the company itself establishes and controls the calculation and transfer of bonuses. The firm determines when funds are paid and in what amount.
Important! To calculate the optimal amount of monthly remuneration, the employee’s salary and the specific period of work are taken into account.
Article 114. Annual paid holidays
Employees are provided with annual leave while maintaining their place of work (position) and average earnings.
Formula and calculation example
A simple formula is used for calculation:
Bonus amount = salary / number of days in the period * number of days worked for a certain period of time.
For example, an employee of an organization has a salary of 35 thousand rubles, and in a month he worked 22 days, but for 3 days he did not come to work, since for personal reasons he was forced to take leave without pay. In this case, the premium amount is: 35,000/22*19=30,227 rubles.
Also, a formula can be used for the calculation, which takes into account not only the salary, but also the incentive, presented as a percentage of this value. In this case the formula is used:
Bonus amount = salary * incentive percentage / 100 / total number of days per month * number of days worked.
Under the above conditions, it may additionally be established that the percentage is 40%. In this case, the premium amount is: 35,000*40%/100/22*19=12,090 rubles.
Contents and forms of bonuses for employees.
An example of calculating a monthly bonus from salary
To begin with, let us outline the conditions for calculating payments for June 2020. For M.M. Krotov, whose working week is 40 hours (8 hours a day), the salary under the employment contract is 20,000 rubles and he also provides a bonus of 10% of the salary. At the same time, Krotov M.M. is not a resident of the country, and there is no regional coefficient for the territory where the enterprise is located. Also, this employee was sick for 5 days, took a 4-hour day off and received an advance payment of 10 thousand rubles.
Let's start with the calculations:
- So, first of all, let’s calculate the amount of salary received by this employee in June (20 working days, 159 working hours):
The cost of one working hour in June for M.M. Krotov: 20,000 rubles: 159 hours = 125.79 rubles/hour
Number of hours worked by M.M. Krotov in the billing period: 159 hours – (5 days * 8 hours + 4 hours) = 115 hours
Salary in the billing period: 115 hours * 125.79 rubles/hour = 14,465.41 rubles
- Let's calculate the bonus for June for this employee:
14,465.41 rubles * 10% = 1,446.54 rubles
- Let's calculate the amount of the accrued payment:
1446.54 rubles + 14,465.41 rubles = 15,911.95 rubles
- Let's calculate the amount of personal income tax withheld by the tax agent:
15,911.95 rubles * 30% = 4773.59 rubles
- The payout amount will be:
15,911.95 rubles – 10,000 rubles – 4,773.59 rubles = 1,138.36 rubles.
Procedure for calculating annual and quarterly salary bonuses
The procedure for calculating the annual and quarterly bonus from salary is not much different from the procedure for calculating the monthly bonus from salary. So, the employee’s total earnings for this period of work are initially calculated, and a fixed percentage is taken from it, this will be the amount of the bonus.
Important ! The quarterly bonus is paid in the month following the quarter, while the annual bonus is paid, as a rule, at the end of the year.
Next, consider an example of calculating the annual salary bonus.
An example of calculating an annual salary bonus
Let’s leave the conditions of our example the same, however, let’s assume that employee M.M. Krotov worked regularly all year without going on vacation, and only in June he was sick for 5 days and took a 4-hour day off. Only one thing will change - a bonus of 10% is accrued once a year.
So, let's calculate the amount of the bonus based on the salary for the year:
- Let's calculate the annual salary:
20,000 rubles * 11 months + 14,465.41 rubles = 234,465.41 rubles
- Let's calculate the premium amount:
234,465.41 * 10% = 23,446.54 rubles
- Let's calculate the amount of personal income tax withheld from the premium:
23,446.54 rubles * 30% = 3,048.05 rubles
- Let's calculate the amount of the bonus payment in hand:
23,446.54 rubles – 3,048.05 rubles = 20,398.51 rubles.
The annual bonus is usually issued in December, so the amount of the total payment of bonus and salary in December will be:
20,000 rubles * 70% + 20,398.51 rubles = 34,398.51 rubles
Taking into account the annual bonus when calculating average earnings for vacation pay and business trips
Art. 139 and 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the provision “On the specifics of the procedure for calculating the average salary”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922.
However, remuneration for the year will be taken into account in its own special manner in this calculation. The annual remuneration will be included in the calculation of average earnings, regardless of the time of actual calculation. But there are a number of conditions: the premium must relate to the year preceding the year in which the calculation is made. Moreover, if at the time of calculation the bonus for the year has not yet been accrued, then after its calculation you will have to recalculate the average earnings and, accordingly, the amount of payment depending on this earnings (clause 15 of regulation No. 922, letter of Rostrud dated 05/03/2007 No. 1253-6 -1).
Inclusion in the calculation of the full or partial amount of remuneration for the year, as well as for other bonuses, will depend on:
- on the completeness of the employee’s work during the pay period;
- correspondence between the periods for calculating the bonus and the settlement period;
- accounting or non-accounting of the employee’s actual work time when calculating bonuses.
For more information on how year-end remuneration is taken into account when determining average earnings, read the article “Is a bonus taken into account when calculating vacation pay?”
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question N1: Good afternoon! I would like to know how to calculate the bonus when calculating wages from the production of a finished product. (click to expand)
Answer: Hello! Calculation of bonuses as a percentage of wages from output assumes the same calculation principle as presented in this article. That is, the amount of wages accrued from production is multiplied by the bonus percentage. It should be noted that often with this option for calculating wages, the employer sets a fixed amount of bonus payment for producing a product in a certain volume, and not a percentage rate of wages.