By Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 19, 2014 No. ММВ-7-2/483, the criteria for classifying taxpayers as the largest were adjusted. Let's analyze the positive and negative aspects of the changes made.
The Fiscal Department (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 23, 2012 No. AS-4-2/13912) noted that the established “largest” criteria are subject to regular clarification depending on the economic situation. And by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 19, 2014 No. ММВ-7-2/483 (hereinafter referred to as the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation), such changes were made to two documents at once:
1) in the order of the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2004 No. SAE-3-30 / [email protected] “On organizing work on tax administration of the largest taxpayers and approving criteria for classifying Russian organizations - legal entities as the largest taxpayers subject to tax administration at the federal and regional levels";
2) in the criteria for classifying organizations - legal entities as the largest taxpayers subject to tax administration at the federal and regional levels, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2007 No. ММВ-3-06/ [email protected] “On amendments to the order of the Ministry of Taxes RF dated April 16, 2004 No. SAE-3-30/ [email protected] "(hereinafter referred to as the Criteria).
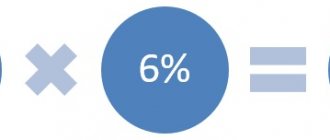
CHOOSING A “SIMPLIED” OBJECT: 6 OR 15%?
Payer classification
In accordance with Art. 19 of the Tax Code, taxpayers are individuals and legal entities who are responsible for making mandatory payments to the budget. Legal entities, in turn, are divided into foreign and Russian, and individuals - into those with and without the status of individual entrepreneurs.
Enterprises operating in specific areas are classified into a relatively separate category of entities. For example, we are talking about the gambling business, mining, etc. In these areas, separate types of taxes are established: on the gambling business, mineral extraction tax, etc.
Some experts identify persons who have the right to use tax benefits as a separate category of payers.
There is another category of subjects. It includes the largest taxpayers. The list of these individuals is quite impressive.
Further in the article we will look at the criteria by which taxpayers are classified as the largest, and what are the reporting features of such persons.
Subjects' rights
They are reflected in Art. 21 NK. According to the norm, taxpayers have the right to:
- Receive information from the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate at your place of registration about current fees and taxes, reporting forms, and advice on their preparation. These services are provided to subjects free of charge.
- Receive explanations from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, tax structures of municipalities and constituent entities of the Russian Federation on issues of application of tax legislation.
- Apply tax benefits enshrined in legislation if there are appropriate grounds. This right is exercised in the manner established by the Tax Code and federal regulations.
- Receive installments, deferments, and tax credits.
- Participate in tax legal relations personally or through your representative.
- Be present when regulatory authorities perform on-site inspections.
- Provide the Federal Tax Service with clarifications and explanations on the facts of calculation/payment of taxes, reports of inspections carried out.
- Require that employees of regulatory structures comply with the provisions of tax legislation.
- Receive copies of audit reports, decisions of tax authorities, tax notices, requirements for tax calculations.
- Do not comply with illegal demands of controlling structures.
- Challenge acts of tax authorities, decisions, actions/inactions of employees of the Federal Tax Service.
- Demand compensation for losses resulting from illegal actions of controlling structures.
- Participate in the consideration of inspection materials, as well as other acts issued by the Federal Tax Service.
These rights apply to all taxpayers, including the largest ones. At the same time, the activities of the latter are under particularly close attention of regulatory structures.
Responsibilities of legal entities
Taxpayers provide information about any changes in their organizational structure to the representative offices of the tax authorities in the region where they are located.
A period of one month is provided for notifying the tax authorities if the taxpayer begins to participate in Russian or foreign organizations (except for business entities and LLCs).
The same period is given in cases where a legal entity registered in the Russian Federation creates separate divisions within the country (not branches or representative offices). This also applies to newly emerged changes in the information about the created units that were provided earlier.
A period of three days is given to legal entities to notify about the closure of those separate structures through which the organization operated within the Russian Federation. This norm applies to branches, representative offices, and other forms of separate divisions.
Documents for download (free)
- Form No. S-09-2
- Form No. S-09-3-1
- Form No. S-09-3-2
- Form No. S-09-6
Largest taxpayers: determination criteria
The criteria by which a subject is classified into the category under consideration are established by the Federal Tax Service. These criteria are periodically adjusted depending on the developing economic situation in the country. The current legislation establishes a list of persons, a list of the largest taxpayers, which provides for the delimitation of their control in accordance with the subject of taxation at the appropriate levels (regional, federal).
To classify a payer as the largest, the following are taken into account:
- Indicators of financial and economic activity (FED). The value is determined on the basis of information from the accounting and tax reporting of the enterprise.
- Signs of interdependence with other participants in tax legal relations, indicators indicating the level of influence of the company on the activities of the interdependent structure and the results of its work.
- The economic entity has a special permit (license) to conduct a certain type of activity.
- Results of continuous monitoring of the analyzed enterprise.
"Regional" changes
The order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation clarified financial and economic indicators at the regional level:
| Indicator name | Regional level | |
| It was (as amended by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated June 27, 2012 No. ММВ-7-2/ [email protected] ) | Became (as amended by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 19, 2014 No. ММВ-7-2/483) | |
| The total amount of federal taxes and fees accrued according to tax reporting data. | Over 75 million rubles to 1 billion rubles | |
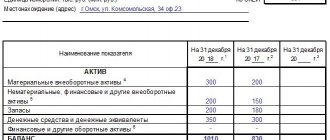
| The total amount of income received (form “Profit and Loss Statement”, line codes 2110 “Revenue”, 2310 “Income from participation in other organizations”, 2320 “Interest receivable”, 2340 “Other income”). | From 1 billion rubles to 20 billion rubles | From 2 billion rubles to 20 billion rubles |
| The total amount of non-current and current assets (form “Balance Sheet”). | Over 100 million rubles to 20 billion rubles | |
| Average number of employees. | There was no criterion | Exceeds 50 people |
Thus, for the largest regional taxpayers, the lower threshold of the total amount of income received has been increased and an additional criterion has been introduced - the average number of employees.
To become the largest taxpayer, the above conditions must be met at the same time. The changes introduced by the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation will lead to a reduction in the number of largest taxpayers at the regional level.
Thus, when summing up the results of the administration of the largest taxpayers in one of the regions (Chelyabinsk region), it was noted that as of July 1, 2014, the number of largest taxpayers was 264 organizations, which is 12 less than in 2013.
That is, the number of largest taxpayers in the region is already decreasing, and taking into account the new criteria in an unstable economic situation, their number will be even smaller. And given that payments from the largest taxpayers make up a large share of the region’s budget (up to 80-90%), the “loss” of budget revenues will also affect the region’s social programs.
In addition, clause 5 of the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation directly stipulates that the largest regional taxpayers in terms of financial and economic activity do not include organizations under special regimes.
But already now, restrictive barriers have been established in the relevant chapters of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation devoted to the application of special tax regimes. So, for example, organizations classified as the largest taxpayers do not have the right to apply UTII (clause 2.1 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 05.08.2009 No. 03-11-06/3/204).
Organizations using the simplified tax system do not meet the criteria established for major taxpayers based on financial and economic indicators. The introduction of a special tax regime in the form of the simplified tax system already implies restrictions on the amount of revenue, the number of employees, and the cost of fixed assets (Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
AUDIT OF ENTERPRISE REPORTING
And only when the fact of interdependence and the ability to influence the economic results of another largest organization is established (section II of the Criteria, first introduced by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated April 24, 2012 No. ММВ-7-2 / [email protected] ), such taxpayers can be classified as categories of largest taxpayers. Interdependence between organizations is determined in accordance with the rules of Article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let us recall that since January 1, 2012, Article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation established 11 grounds for recognizing organizations as interdependent.
The most difficult thing seems to be the calculation of the direct and (or) indirect participation of an organization in another organization (clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let us illustrate the calculation with a specific example.
Assignment of status
An enterprise can be classified as a major taxpayer (CT) based on the results of its work, considered for any 3 years before the start of the reporting period. Information for the current year is not taken into account.
It should be noted that the status of the largest taxpayer assigned to an enterprise is retained for 2 years after its activities ceased to meet the established criteria. In addition, the status can be maintained for 3 years. This is possible in the event of a reorganization of the largest taxpayer. The corresponding status is retained by companies formed as a result of this procedure. The three-year period includes the year of reorganization.
EXAMPLE No. 1
Organization A entered into an agreement with organization C. In this case, organization A owns 50% of the authorized capital of organization B, which owns 50% of the shares of organization C. Organization A owns 10% of the authorized capital of organization D, which owns 5% of the shares of organization C.
The share of indirect participation of organization A in organization C through organization D will be equal to 0.5% (0.1 x 0.05 x 100%). Thus, the total product of shares will be equal to 25.5%, therefore, organizations A and C are interdependent. Organization A is part of the same holding as organization C. Moreover, organization A influences the financial results of organization C (through the price mechanism). Organization C is the largest taxpayer at the federal level in terms of financial and economic indicators. Based on this, organization A can be classified as the largest taxpayer at the federal level, and its financial and economic indicators do not matter.
DEVELOPMENT AND DRAFTING OF CONTRACTS
Thus, the list of federal largest taxpayers will expand significantly while the number of largest regional taxpayers will decrease.
In addition to the negative aspects (increased attention from fiscal authorities), having the status of the largest taxpayer has a number of advantages in terms of using regional tax benefits. For example, the Law of the Chelyabinsk Region “On reducing the corporate income tax rate for certain categories of taxpayers” (No. 154-ZO dated June 23, 2011) establishes a reduced corporate income tax rate (but not lower than 13.5%) for organizations selling priority investment projects with a total investment volume for the project of at least 300 million rubles. In this case, the reduced rate will be calculated according to the formula, and the tax benefit will apply only to that part of the profit that is received from the implementation of the investment project, and not from the activities of the entire enterprise.
The Moscow government has submitted to the Moscow City Duma a draft law establishing a reduced income tax rate of 13.5% for oil companies, as well as consolidated groups of taxpayers. The adoption of the law will consolidate the presence and further attract the largest taxpayers of the oil industry to the city. According to the forecasts of the capital authorities, starting from 2015, the implementation of the bill will ensure an increase in budget revenues of the city of Moscow in the amount of at least 2 billion rubles per year (on the website of the Moscow government - mos.ru). Another positive aspect of the changes introduced by the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation is the reduction in the period for maintaining the status of the largest taxpayer. If the taxpayer no longer meets the established criteria in the reporting year, then, according to the new rules, the status of the largest taxpayer is retained for two years, and not three years (as was previously the case).
Loss of status
An enterprise ceases to be considered a major taxpayer if it has been declared bankrupt in court and bankruptcy proceedings have been initiated against it. The corresponding provision is enshrined in the order of the Federal Tax Service dated June 27, 2012. This rule, however, does not apply to credit organizations whose administration is carried out at the level of the Federal Tax Inspectorate for the largest taxpayers. They retain their status until forced liquidation.
FED indicators
An enterprise may be one of the largest taxpayers based on the results of its activities accepted for consideration for any 3 years preceding the reporting period. When determining the status of an organization, data for the reporting year is not taken into account.
For your information! The status assigned to a company remains unchanged for up to 2 years after its activities cease to meet the necessary criteria. The assigned status is retained by the enterprise that arose after the reorganization procedure of the largest taxpayer for a 3-year period (taking into account the year of the reorganization).
The status is recognized as a lost entity that has been declared bankrupt in court and against which bankruptcy proceedings have been initiated (Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ-7-2/428, 06/27/2012). This provision does not apply to credit companies administered at the federal NS level. They retain their status until forced liquidation.
A non-profit company is assigned CN status if it has income that meets the established criteria.
For enterprises falling under the federal level of administration, it is mandatory to comply with at least 1 of the following parameters:
- The level of tax charges exceeds the figure of 1 billion rubles. or for companies engaged in providing services in the communications or transport industries - 300 million rubles.
- The amount of income received is from 20 billion rubles. (according to codes 2340, 2320, 2310, 2110 data of reporting form No. 2).
- The total size of the enterprise's assets begins with a position of over 20 billion rubles.
For your information! The federal tax administration criteria also apply to legal entities engaged in activities in certain specific economic areas.
For example, similar indicators apply to some strategic structures, including the military-industrial complex:
- part of the state contribution covers more than half (50%);
- the average number of employees in the organization exceeds 100 people;
- the total amount of export contracts for strategic products exceeds 27 million rubles;
- the total amount of funds received from export agreements related to strategic goods is 20% of total revenue.
For enterprises classified at regional levels of administration, compliance with certain parameters is provided, but the scope of employment of the legal entity is not taken into account.
Among the controlled criteria that require simultaneous compliance with all of them:
- income received, reflected in reporting form No. 2, within the range of 2–20 billion rubles;
- the calculated amount of tax payments is within the range of 75 million rubles – 1 billion rubles;
- The company's assets correspond to indicators ranging from 100 million rubles. up to 20 billion rubles;
- The full-time number of employees is represented by more than 50 units.
For your information! The FED indicators that determine the inclusion of a taxpayer in the category of taxpayers when administered at the regional level are allowed to be established by tax administration departments of individual subjects of the country, subject to the mandatory approval of the criteria with the Federal Tax Service (Federal Tax Orders No. ММВ-7-2/483, ММВ-7-2/295 dated 09/19/2014, 07/20/2015 respectively). Enterprises operating under special taxation regimes do not legally have the right to move into the category of national property.
Indicators of financial and economic activity
For companies whose activities are monitored at the level of the Interregional Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service for the largest taxpayers, the corresponding status is assigned if one of the following conditions is met:
- The amount of taxes exceeds 1 billion rubles, and for companies operating in the service, transport or communications sectors - 300 million rubles.
- The amount of income received is at least 20 billion rubles.
- The total value of assets is not less than 20 billion rubles.
Additional criteria have been established for individual enterprises. In particular, military-industrial complex organizations under the control of the MI of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the largest taxpayers receive the appropriate status if:
- Investments of public funds account for more than 50% of all assets.
- The average number of employees is more than 100 people.
- The total value of contracts for the export of strategic products exceeds 27 million rubles.
- The total amount of income from the export of goods is 20% of the total revenue.
Enterprises administered at the interdistrict tax level for the largest taxpayers receive the appropriate status if:
- The amount of income reflected in f. No. 2, ranges from 2 to 20 billion rubles.
- The total amount of contributions to the budget is 75 million rubles. – 1 billion rubles
- The value of the enterprise's assets is 100 million rubles. – 20 billion rubles.
- The average number of employees of the company is more than 50 people.
These taxpayers are considered the largest, regardless of the type of activity performed.
Contents of the first criterion
The company will be administered directly by the Federal Tax Service if one of the indicators for the reporting year has the following meaning:
- the total amount of federal tax accruals according to reporting is from 1 billion rubles;
- for communications or transport organizations – from 300 million rubles;
- the total amount of income according to annual form No. 2 “Profit and Loss Statement” (indicator codes 2110, 2310, 2320, 2340) – from 20 billion rubles;
- assets – from 20 billion rubles.
Almost the same applies to defense enterprises (at least one of the criteria):
- the amount under export contracts for the supply of strategic products – from 27 million rubles per year;
- revenue from export deliveries of strategic products – from 20% of total revenue;
- average number of personnel – over 100 people;
- state share – from 50%.
The Federal Tax Service will also oversee organizations from the list of strategic enterprises for which one indicator is important:
- the amount under export contracts for the supply of strategic products – from 27,000,000 million rubles per year;
- revenue from similar transactions – from 20% of total revenue;
- average number of personnel – from 100 people;
- state share – from 50%.
Credit institution, insurance/reinsurance organization, mutual insurance company, insurance broker, professional participant in the securities market, non-state pension fund, if available:
- banking licenses;
- licenses for insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance, intermediary activities as an insurance broker;
- license of a professional participant in the securities market and/or license to maintain a register;
- license for pension provision and insurance.
If the company has submitted a request for tax monitoring, subject to the following conditions:
- submission of all information in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 105.27 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- compliance with the criteria of paragraph 3 of Art. 105.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- compliance of the information interaction regulations with its form and requirements;
- compliance of the company's internal control system with Article 105.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the level of the Federal Tax Service, administration will be subject to simultaneous compliance with the following conditions:
- The total amount of income according to the annual profit and loss report (codes 2110, 2310, 2320, 2340) is from 2 to 20 billion rubles inclusive.
- The average number of staff is from 50 people.
- Assets – from 100 million to 20 billion rubles inclusive, or the total amount of accruals of federal taxes and fees according to reporting – from 75 million to 1 billion rubles.
According to the law, special regimes cannot be classified as the largest taxpayers.
Nuances
Indicators of financial and economic activity for enterprises controlled at the regional level can be established by the Inspectorate Directorates of the Federal Tax Service for the largest taxpayers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with their coordination with the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
It must also be said that organizations using special taxation regimes cannot obtain IP status.
Registration and consequences
Organizations that have received this status are obliged to register based on the level and scale of activity . Tax structures, in turn, monitor the implementation of tax legislation without direct participation. During the registration process, these government agencies perform the following actions :
- assigning a new code for the reason for which registration occurred (the first 4 digits are the code designation of the tax service, the 5th and 6th digits are a sign of assignment of status);
- entering data into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- issuance of a notification in accordance with Form 9-NKU (taxpayer identification number, reason code, OKATO).
The status is assigned from the moment the registration took place with the relevant inspection. It can be inter-district and inter-regional.
Availability of permission (license)
Business entities that have received special documents from government bodies to conduct certain types of activities are controlled by the Federal Tax Service for the largest taxpayers. In this case, inconsistency (compliance) with other criteria for classifying an enterprise as a national economy (amount of income, amount of taxes, interdependence or staffing levels) is not taken into account.
Among the types of activities for which the presence of a license provides an economic entity with obtaining the status of a business owner, the following should be included:
- Banking services.
- Pension provision (in this case we are talking about non-state pension funds).
- Pension and other types of insurance, reinsurance.
- Services of brokerage companies.
- Professional participation in the activities of the stock market.
Contents of the first and second signs
The criteria for classification as the largest taxpayers (at least the first two) need to be deciphered. The content is also indicated in the order.
At the federal level, the total income of an enterprise should be more than 35 billion rubles. Also, the status can be obtained by a credit, insurance and reinsurance organization, insurance brokers, professional participant in the securities market upon receipt of a license for one of the following types of activities:
- conducting banking operations;
- insurance, reinsurance, insurance broker activities;
- carrying out work in the field of securities and maintaining their register;
- pension provision.
The Federal Tax Service may decide to assign such status without meeting the listed conditions. At the regional level, it can also be purchased according to this principle, the criteria are as follows:
- income from 2 to 35 billion;
- staff number - more than 50 people;
- assets - more than 100 million rubles or the amount of tax charges more than 75 million.
All signs must be present at the same time. Enterprises that use special regimes cannot be included in the list of major taxpayers.
The second feature is disclosed in accordance with Art. 105 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If a company can influence the economic performance of the organizations described above, they can also be recognized as the largest taxpayers.
Features of the relationship with the Federal Tax Service
In accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code, if the largest taxpayer has separate divisions, registration is carried out with all Federal Tax Service Inspectors at their location.
In case of a change in the organizational structure, the enterprise is obliged to notify the regulatory authorities. The corresponding notice should be sent to all Federal Tax Service Inspectors where registration was carried out. The largest taxpayer registered on the territory of the Russian Federation, creating separate divisions not in the form of representative offices or branches, or changing information about previously formed divisions, must send a corresponding notification to the regulatory authority within a month.
If an organization liquidates its structures operating on the territory of the Russian Federation, information about this is sent to the inspectorate within three days. This rule applies to all types of divisions, including branches and representative offices.
Information on the largest taxpayers in the Moscow region and other regions enters the unified database of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
What consequences will the transfer of this group of taxpayers to the status of the largest?
The main disadvantage of having the status of the largest taxpayer is the close attention of the tax authorities. The frequency of on-site tax audits is usually once every 2 years.
In addition to on-site tax audits (usually lasting six months, and in the case of several separate divisions - more than six months), tax inspectorates require additional information about the upcoming amount of tax revenues to the budget, planned revenue indicators and other indicators (for forecasting budget revenues).
In relation to the largest taxpayers, so-called “in-depth” desk tax audits are carried out, requiring additional information and documents.
That is, such organizations will be given special attention in terms of tax control measures.
According to clause 6 of the Order of the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation No. SAE-3-30 / [email protected], tax administration of organizations in the financial and credit sector will be carried out by the Interregional Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation for the largest taxpayers No. 9.
Thus, if an organization carries out financial activities, for example, in the Ural region and receives the status of the largest taxpayer, then it will be registered with MI Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. 9 in Moscow and, accordingly, will submit reports to the inspection for registration of major taxpayers ( regional and local taxes are paid at the location of the organization). In practice, this leads to an increase in the organization’s costs for sending documentation from the region to Moscow, for telephone conversations and travel expenses. It is impossible not to take into account possible problems associated with the transfer of personal accounts from one inspection (with which the taxpayer was registered) to another for the registration of major taxpayers (with which the taxpayer will be registered).
RESTORATION OF TAX ACCOUNTING
List of the largest tax payers in Russia
Despite significant fluctuations in oil prices and changes in raw material production volumes, Gazprom remains the main taxpayer in the Russian Federation. The latter will allocate about 2 trillion rubles to the budget by the end of 2020. This amount includes taxes from all 56 subsidiaries and will amount to approximately the same amount.
According to the Interregional Tax Inspectorate for the largest taxpayers, the main “donors” of the federal budget include Lukoil, TAIF-NK, Tatneft, Sibur, Novatek.
Significant funds into the budget come not only from oil and gas sector enterprises. Retail chains Magnit, Megapolis, and X5 Retail Group are also considered the largest taxpayers. The top twenty leaders also include metallurgical enterprises Norilsk Nickel, Severstal, UC Rusal, etc. One cannot fail to mention telecommunications enterprises, VimpelCom.
The total assets of each specified enterprise exceed 500 billion rubles. This data is provided by Forbes magazine for the current year 2020. The head offices of half of these companies are located in Moscow. Some enterprises are registered abroad (for example, VimpelCom).
The leading positions in terms of the average number of personnel are occupied by Gazprom and Rosneft. The first company employs about half a million people, the second has more than 250 thousand people. Among trading enterprises, the leader is Magnit. As of 2020, its staff numbers more than 300 thousand people.
Large enterprises and SMEs. How to distinguish?
Large enterprises can be distinguished from SMEs based on the following criteria:
| Company | Average annual number | Maximum income, million rubles. | |
| from | before | ||
| Micro | 1 | 15 | 120 |
| Small | 15 | 100 | 800 |
| Average | 100 | 250 | 2000 |
| Large | 251 and above | More than 2000 | |
It would seem that it is easy to distinguish enterprises based on such criteria. To become large, it is necessary to fill the staff with at least 251 employees and bring income to a level that is more than two billion rubles. But there are industries in which the number of employees may be less than 250, but they belong to large ones:
| Kind of activity | Number of employees, people | ||
| Medium enterprise | Large company | ||
| from | before | ||
| 1. Advertising agencies | 15 | 50 | < 50 |
| 2. Tour operators | 25 | 75 | < 75 |
| 3. Print media | 35 | 100 | < 100 |
Example No. 1. The travel agency employs 109 people and has an annual income of 2,500 million rubles. In this case, it is a large enterprise. Although the number of employees is less than 250, it is acceptable for this industry. The second indicator (income) corresponds to the generally accepted criterion.
The category of a business entity can be changed only when the threshold values of the criteria are lower or higher for three consecutive years.
Largest enterprises abroad
As a comparative analysis of companies in the USA and Russia shows, in both countries the leading positions in the list of large taxpayers are occupied by resource giants. In America, the list includes ConocoPhillips, Chevron and ExxonMobil.
Next on the list are enterprises that produce intellectual products. These include Intel, Apple, IBM, Microsoft. A large amount of funds comes to the US budget from banks, insurance companies, manufacturers of medicines, and cosmetic products. It cannot do without a network of fast food outlets. Thus, the world-famous company McDonald's contributes about $2 billion annually to the US budget.
Specifics of the tax burden
For regulatory authorities, the amount of tax deductions is largely a statistical tool and not a guideline for activity. As analysts note, this indicator has not become a key mechanism for ensuring the effective implementation of state fiscal policy. Meanwhile, some experts are confident that the authorities cannot help but see significantly different tax burdens. That is why regulatory authorities use indicators when planning desk audits.
It must be said that enterprises themselves are very sensitive to the disclosure of the size of their tax burden. Most of them refuse official comments. Unofficially, representatives of some economic giants talk about the tax burden being too high, but they do not risk speaking openly about this, since this could significantly damage relations with the Federal Tax Service.
If we talk about the leaders - enterprises of the oil and gas sector, then the general opinion about the load on enterprises was expressed, perhaps, by Igor Sechin, the head of Rosneft. In his interview on the Vesti 24 program, he spoke about the need to reduce taxes. Sechin pointed out that the state doubled the amount of deductions for the oil and gas sector, but prices for raw materials decreased significantly.
However, today there is no one to replace enterprises in the oil and gas sector: the “fashion for entrepreneurship” has long passed, the number of medium and small businesses is steadily decreasing, and the tax base is not increasing. At the same time, it is impossible to reduce social spending today. So the tax burden is placed on the largest payers, primarily on companies in the oil and gas sector.
Meanwhile, according to a number of experts, this consumer attitude of the state towards the largest economic entities brings exclusively short-term benefits. Experts note that the authorities always have the opportunity to receive more tax amounts. Whether the consequences will be negative or positive depends on the level of economic development of the country as a whole and the financial condition of a particular enterprise.
Small and medium enterprises – criteria 2020
| Name of the normative criterion for a medium-sized enterprise | Limit value of the indicator | Legislative norm |
| Number of employees (average) for 2020 | · 101-250 people | Subp. 2 clause 1 stat. 4 of Law No. 209-FZ |
| The amount of profitability for 2020 - the indicator is calculated according to NU information by summing up data for the enterprise as a whole, that is, for all types of OKVED and taxation regimes | · 2000000000 rub. | Subp. 3 clause 1.1 of Law No. 209-FZ, Decree of the Government of Russia No. 265 of 04.04.16 |
| The total share of participation of the founders in the authorized/share capital or mutual fund of the company | This indicator is determined according to the rules given in the previous table, that is, for small companies | Subp. “a”, “e” subp. 1 clause 1.1 stat. 4 of Law No. 209-FZ |
The tables above contain the 2020 criteria for small and medium-sized businesses. In 2020, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted a number of changes regarding SMEs (Resolution No. 1412 of November 22, 2017), but this applies only to organizations operating in the field of light industry (codes of sections 13-15 of the OKVED Classifier). All other enterprises do not have to apply the norms of this document.