Citizens of Russia have the right to organize their business in the country within the framework of a large number of forms of business activity, each of which has its own specifics and is better suited for specific cases.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation clearly states all the provisions that are taken into account when choosing any form of doing business.
What features, for example, does the organizational and legal form of an individual entrepreneur have? What form of business activity is best to choose?
In what form can a business be registered?
The wording “entrepreneurial activity” implies those activities that are carried out at one’s own risk and are aimed at obtaining constant profit from the material goods used, the performance of work, the provision of services or the sale of products.
It is important to emphasize that entrepreneurship is a regular activity. Consequently, a one-time receipt of profit from any action cannot be called a business, and therefore it is not necessary to register it. Although the law does not specify the concept of “regular” and this must be constantly taken into account.
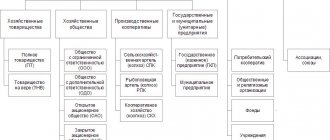
In the Russian Federation, common forms of business registration are:
- IP;
- OOO;
- JSC.
There are other forms.
Sometimes there are cases when a citizen runs his own business without any registration (even as an individual entrepreneur). In this case, it is important to note that not every business can be carried out in this way (most require registration).
For example, without creating an individual entrepreneur or registering a legal entity, it is legal to rent out your home.
Individual entrepreneurship
An individual entrepreneur is an organizational and legal form that is one of the most (if not the most) popular among businessmen. What is this connected with? For the most part, with ease of registration and further bureaucratic interaction with the state.
In order for a citizen to register himself as an individual entrepreneur, he collects a small package of documents and pays a relatively inexpensive state fee compared to other forms of doing business.
Individual entrepreneurs do not even have to open a bank account. In any case, the legislation does not oblige it, although it is more convenient to interact with business partners through it.
It was said above about the minimum bureaucratic burden. Indeed, individual entrepreneurs very rarely interact with tax authorities and other regulatory government agencies. In some cases, individual entrepreneurs can draw up and send a declaration and a small package of documents related to the staff once a year.
There are also some drawbacks, if they can be called such: the entrepreneur is obliged to pay insurance premiums to various funds for himself:
- regardless of financial situation;
- if the individual entrepreneur has no revenue at all;
- if he did not conduct business at all for some period;
- if he is employed and similar contributions are paid by the employer.
It is convenient for individual entrepreneurs to manage their revenue: they can easily withdraw it for personal use or invest it back into the business by paying taxes in advance.
What is the legal form of the individual entrepreneur? To find out, the peculiarities of the civil legal status of individual entrepreneurs are considered.
They are as follows:
- A person who has reached the age of 18 has the right to register an individual business. With parental permission - from 14 years old.
- Citizens in public service cannot be registered as individual entrepreneurs.
- An individual entrepreneur is not a legal entity, but an individual (previously, an individual entrepreneur was called PBOYUL - an entrepreneur without the formation of a legal entity). Consequently, they are responsible for their obligations independently.
- An individual entrepreneur owns his own business. It cannot be divided into shares and sold or gifted to anyone.
Individual entrepreneur is a form of ownership that is not without its small disadvantages (for some citizens, insignificant), which at the same time are offset by a large number of advantages.
What is the capital of the individual entrepreneur?
Opening an individual entrepreneur, compared to other forms of enterprise ownership, is significantly simplified: there is no need for lengthy legal red tape or significant capital investments. But a number of actions will still have to be done.
The procedure for registering business activities in 2017-18 includes several steps:
- A visit to the tax office, where the future entrepreneur receives an application form.
- Selecting in the OKVED directory the code of the activity you plan to engage in. It will need to be indicated in the application. It is possible to specify several codes, but only one appears as the main one.
- Choosing which tax system to work with.
- Payment of state duty.
- Filling out the application itself and a package of other necessary documents to the tax office.
- Receiving documents on registration of individual entrepreneurs.
The OKVED directory is available in the Consultant system and on other resources. For an entrepreneur planning to make, for example, kitchen furniture, the main code will be 31.02.
If the product list includes mattresses, then the second code will be 31.03 - and so on.
Code designations do not have to be indicated from related areas; in addition, their number for individual entrepreneurs is not officially limited.
[/su_box]
There is a recommendation to include up to 30 items from OKVED in the application. If necessary, they can be changed in the future.
Limited Liability Company
Another popular form of business registration in the country is LLC. It can be created either by one person or by a group of people not exceeding fifty people.
LLC is a legal entity, therefore the founders of the LLC are deprived of individual liability for their obligations (with the exception of contributions to the authorized capital).
The founders of a legal entity have the right not to pay for themselves contributions to state funds such as:
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
Advantages and disadvantages of the civil legal status of an individual entrepreneur
- Pension Fund;
- FSS;
- FFOMS.
When registering an LLC, an authorized capital must be created, the minimum amount of which is 10,000, as well as open a current account and register a seal. At the same time, the reporting provided for an LLC is much more complex than that required to be submitted by individual entrepreneurs.
The difference between an LLC and the legal form of an individual entrepreneur is the need for mandatory reporting to the tax authorities when disposing of its revenue. It was said above that individual entrepreneurs can easily manage their revenue. The founders of an LLC do not have such benefits: they need to formalize, for example, the withdrawal of funds as payment of dividends or wages, and also pay tax on them to the above-listed funds.
The specificity of LLC is that:
- The number of LLC founders cannot be more than fifty people. To expand the composition, the organizational and legal form of the business is changing.
- The authorized capital cannot be less than 10,000 rubles. When increasing it, it is taken into account that if the amount of the company’s net assets is significantly higher than this capital, then they will have to be reduced. When the price of the company's net assets is below RUR 10,000, the company will be liquidated.
- An LLC can change its legal status.
It is worth taking a closer look at the founders of the LLC.
- if the company’s charter allows, then one of the founders can leave the company by transferring his share to another person;
- It is allowed to sell one's own share in the company's business.
An LLC is a form of business activity that has greater opportunities for managing a company compared to an individual entrepreneur. At the same time, bureaucratically it is much more complicated.
Advantages and disadvantages
The organizational and legal form of an individual entrepreneur (for example, private stores, etc.) has both its advantages and disadvantages.
An entrepreneur who does not form a legal entity has the following advantages:
- a simple procedure for registering a business, as well as terminating activities;
- a small list of documents required for the procedure;
- a simple reporting form, a small list of taxes;
- lack of accounting: individual entrepreneurs only keep a ledger of costs and income, and also provide a quarterly report on expenses and income.
It is very important to make the right choice of organizational and legal form. The status of an individual entrepreneur obliges you to understand what shortcomings a business may have in its chosen form.
Among the disadvantages of IP are:
- responsibility for all issues with your property in its entirety;
- the impossibility of distributing responsibility for obligations that arose as a result of activities among the founders;
- difficulties in attracting investors due to lack of shares or shares;
- difficulties with selling a business, since it can only sell personal property in the form of assets;
- transferring a business by inheritance involves a lot of paperwork.
The organizational and legal form of ownership “individual entrepreneur” is convenient for the founder of a business, but often legal entities do not want to work with individual entrepreneurs, preferring the more powerful CJSC or LLC.
Joint-Stock Company
Organizing business activities as a joint stock company (JSC) can be beneficial to those citizens who plan to create a big business in the future.
Joint-stock companies, just like LLCs, have their own authorized capital. True, it has a slightly different form - the form of shares. These shares are needed to confirm the mandatory nature of the rights of the founders.
It is somewhat more difficult to prepare reports for a joint-stock company than for an LLC (we are not talking about individual entrepreneurs at all).
Since 2014, joint stock companies have been divided into:
- public;
- ordinary.
After the reforms that were carried out in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in 2014, the difference between LLC and JSC was noticeably reduced: both types of business received the same type of constituent documents - the charter, the development of which should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the relevant government bodies.
PJSC is the name of such legal entity:
- The securities of which are distributed in the format of the so-called open subscription, and are also quoted on the market in accordance with the provisions of the documents governing their circulation.
- The founders of which have the right to clarify the status of a PJSC in the company’s charter and in its corporate name.
The remaining joint stock companies do not have the right to have public status, but this may change if the company's management issues shares distributed by open subscription. Then it will be possible to obtain PJSC status.
What is a legal form
Organizational and legal form (OLF) is a form of activity that is approved by the norms of federal legislation and fully determines:
- rights;
- responsibilities;
- procedure for disposing of the assets of an enterprise or individual entrepreneur.
The organizational and legal form is approved by the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation
The main parameters by which employment can be classified include:
- business goals;
- approved form of ownership;
- secured rights of participants;
- composition of owners - head of the board, director, etc.
The norms of the Civil Code of Russia provide for several basic forms of entrepreneurial activity:
- commercial enterprises - the main task they face is to obtain the maximum amount of profit, which is subject to further distribution among all owners;
- non-profit companies - are not formed for the purpose of generating income; it is not subject to distribution among the founders, but is used to increase the amount of the authorized capital.
OPF is one of the forms of entrepreneurial activity
The organizational and legal form of commercial companies is also divided by federal legislation into several subtypes:
- business partnerships - can be either full or those that are based on faith in accordance with the provisions of Art. 69 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The main distinguishing feature between them is considered to be the degree of responsibility of the participants (partnerships);
- business entities - regulated by the norms of Art. 87 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. They mean LLC (Limited Liability Companies), JSC (Joint Stock Companies). At the same time, the capital of an LLC includes exclusively investments of participants, and is subject to distribution into shares, and in a joint-stock company they are divided into the approved number of shares;
- production cooperatives - regulated by Art. 106.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The civilian population unites in such organizations on a voluntary basis of membership and share contributions in particular. As a rule, they are based on the personal labor of their direct members;
- economic partnership - in practice it is quite rare and is little mentioned in the norms of civil legislation. When using, you need to rely on Federal Law No. 380-FZ;
- peasant farming - regulated by the norms of Art. 86.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. This refers to the association of citizens for the purpose of farming. As a rule, their activities are based on personal participation in business and property investments.
Important! According to the provisions of Art.
113 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is customary to classify commercial structures as unitary companies, which can be of only several types: state and municipal.
Partnership, cooperative and farm
The code of laws of the Russian Federation also provides for other forms of business organization.
In addition to LLCs, individual entrepreneurs and joint-stock companies, there are partnerships and cooperatives, as well as peasant farms. The former have much in common with such forms of business registration as LLC and JSC. Partnerships also act as legal entities with a certain authorized capital.
Partnerships are divided into:
- Full. The organizers of such a company are collectively responsible for these obligations.
- Limited rights. In this case, the organizers of the company are liable for these obligations within the limits of their contributions.
Cooperatives, in turn, are divided into:
- Consumer. They are associations of individuals or legal entities within which the property share contributions of the founders are combined.
- Production. These are associations of individuals (possibly including legal entities) for the purpose of organizing production activities, performing work or, for example, marketing any products.
In both cases, the participants of the companies bear subsidiary liability with the only difference that in the consumer type of organization the liability does not go beyond the unpaid part of the additional contribution, and in the production type it is within the limits of the amounts determined by law and the charter of the cooperative.
If people’s entrepreneurial activities are directly related to agriculture, then the law provides for them such a form of business registration as peasant farms.
Then a legal entity is registered on the basis of collective work and property contributions of the participants, who are at the same time the founders.
The main feature of such a farm is that all its property is in the common use of the founders of this farm. At the same time, the participants of the company bear collective responsibility for these obligations.
What is authorized capital?
Authorized (or authorized - both spellings are found) capital (MC) is one of the key differences between an individual entrepreneur and a legal entity.
This is a certain amount of money that the founder of the company invests in order to start operations. That is, the management company is a resource necessary to launch an enterprise.
The invested funds can be spent at the discretion of the legal entity - transfer salaries, pay for the services of suppliers or rent.
Different types of legal entities are required to have a capital in the amount of:
- opening an LLC will require 10 thousand rubles;
- The charter capital for an OJSC is calculated using the formula 10*minimum wage;
- The capital of a closed joint stock company must be 100 times the minimum wage.
The type and size of investments (not lower than the minimum allowable by law) is determined by the founders of the company. It is not necessary to contribute it in cash - it can be securities, material assets, trademarks, patents.
The procedure for entering the Criminal Code is approved upon the creation of the company and is reflected in the Charter; for example, you can pay it one-time or monthly in equal installments. Once established, the Criminal Code is changed only by a notary.
Speaking about individual entrepreneurs, we can note the advantage of this organizational form: authorized capital is not needed.
The law allows this based on the premise of full responsibility of an individual entrepreneur for his obligations and actions - except for the property that is prohibited from being recovered by law. But if several individual entrepreneurs decide to start acting together, they will have to create a new legal entity, with constituent documents and a management company.
Which OPF should I choose?
Special organizational and legal forms (OFF) are suitable for various businesses:
- if the business is run independently, without registering a large staff, then you can safely register an individual entrepreneur. In this case, you will have to submit minimal reports to regulatory authorities, not be distracted by a large number of bureaucratic operations, not have an expensive accountant on staff for this, and devote your free time to business development;
- If a business is created collectively, then first you can register an LLC. As soon as revenue begins to grow noticeably, you can increase it by issuing shares and switch to OPF of a joint-stock company of any of the two types;
- to unite labor efforts, you can join into cooperatives; if we are talking about agricultural activities, then to peasant farms.
In addition to these types of business - the most popular - there are also other types of business organization: NPOs (associations or unions) - however, they are much less common.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
What is the difference between individual entrepreneur and LLC and what to choose
All available OPFs can be found in the All-Russian Classifier of Organizational and Legal Forms or OKOPF, which is freely available on the Internet.
Code Definition
The organizational and legal form of an individual entrepreneur, CJSC or LLC is included in the classifier code.
To determine the code, you need to understand what each digit means.
- The first is section.
- The second from third digits are responsible for a certain type of organizational and legal form; and the fourth - for the type of specific organizational and legal form.
In order to look at the code, you need to use the classifier in the classifier system or turn to the services of consultants.
NPO
All non-profit organizations can be divided into two types provided for by law:
- Associations.
- Unions.
It is important that the laws of the Russian Federation do not officially distinguish these types of NPOs from each other. Moreover, in practice, associations are most often created by companies with the same organizational and legal form of relationship or belonging to the same branch of the economy; and unions are registered according to the remaining principles.
Associations can be:
- commercial enterprises;
- NPO;
- natural person;
- and commercial enterprises, and an individual with the legal form of individual entrepreneur.
Officially employed employees wishing to protect their rights do not have the right to join the association. This is prohibited by law. But they can unite into a trade union, according to Federal Law No. 10-FZ of January 12, 1996.
The association includes at least two members.
In this form of NPO, there is no mutual responsibility of participants to each other for obligations. Debts are paid with the organization's property. This is an important characteristic of associations. True, transferable responsibility is still secured by the charter or other document of the organization.
Issues significant for the association are decided by a meeting of participants, and the chairman of this NPO directly manages the organization. Also, collegial bodies such as a council or board have the right to manage a legal entity.
Example of conjunctions:
- Union of Enterprises of Yekaterinburg;
- Union of Writers of Russia.
Unions are usually created by individuals who have similar or identical interests and goals (professional or non-financial, for example).