When concluding a leasing agreement, the lessee first of all needs to check whether the agreement contains all its essential terms. If it turns out that the parties have not formulated at least one of them, the contract will be considered not concluded.
Unless the parties agree on other terms, there will be no risk of the contract being declared void. However, it still makes sense for the lessee to regulate relations with the counterparty in detail and formulate a number of conditions that are not essential (for example, conditions on the rights, obligations and responsibilities of the parties, the procedure for terminating the contract, etc.). Only in this case will the interests of the lessee be best protected.
What is the difference between renting and leasing?
Both individuals and legal entities do not always have sufficient funds to acquire ownership of one or another necessary movable or immovable property.
At the same time, this does not mean that it will take a long time to collect the necessary amount to be able to use this property, especially if it can already generate profit .
To do this, the market offers a number of tools to solve the problem, among which rental and leasing mechanisms can be classified as a separate category.
Description of the concept of rent
Rent is actually the rental of inventory , in which the owner transfers the goods belonging to him for use to another person. The latter, in turn, pays a certain amount of money for this.
These legal relations are formalized by an agreement between the parties, called a lease agreement, which specifies in detail all the essential conditions of the process. Such conditions necessarily include the term of the agreement, the amount of the fee, the amount and frequency of payments.
Note!
An essential feature of this form of financial relations is the possibility of transferring property for use or ownership to the lessor, which should also be reflected in the agreement.
At the end of the agreement, the parties decide to prolong the relationship or return the leased item to the owner . The subject of the agreement can be any objects of movable and immovable property, including land plots.
Leasing concept
A form of financial and property relations similar to rent is leasing. In this case, a legal entity acting as a lessor transfers certain inventory items (TMV) to an individual or legal entity.
This agreement is formalized by a leasing agreement, which necessarily stipulates the terms of the relationship related to terms, payment, rights and obligations of the parties.
An essential feature in this case is the recipient’s obligation to buy back the used inventory at the end of the agreement period at its residual value or on other terms agreed upon and fixed by the parties.
The duration of the leasing agreement is determined by the subjects individually, but in most cases it is drawn up for a fairly long period . The only limitation is that the term of the agreements cannot exceed the useful life period of the transferred inventory.
It should also be noted that, in accordance with the requirements of the current legislation, natural objects and land plots cannot be leased.
Similarities between renting and leasing
From a legal point of view, leasing is one of the special cases of the considered mechanism , which is why it is often called financial lease.
In both cases, an agreement is reached between the entities on the transfer of inventory items owned by right of ownership from one party to the other on a reimbursable basis.
The most important!
The purpose of the transactions is to obtain the right to use the property by the recipient and to make a profit for the party providing the goods and materials.
Both transactions are subject to appropriate legal registration and are urgent . The general legal basis for both types of transactions is the civil code, within the framework of which all disagreements arising between the parties in the process of interaction are resolved.
Differences between renting and leasing
Despite the presence of many common characteristics, there are a number of fundamental differences between the two forms of financial and property relations under consideration. The most significant of them are:
- is returned to the owner at the end of the agreement , while the leased subject is purchased by the recipient at its residual value .
- The fundamental difference in the terms of both financial instruments is that the lessee enters into a transaction for property that is already owned by the counterparty . At the same time, when registering a lease, the recipient independently selects the necessary property, which is purchased by the leasing organization and provided for use.
- Inventory and materials under a lease agreement can be provided by both an individual and a legal entity, while leasing is provided only by a legal entity that has the appropriate registration and charter.
- Leasing operations cannot be carried out in relation to natural objects and land plots.
- There are no mandatory restrictions on the urgency of leasing transactions, however, as a rule, their period is less than the duration of leasing transactions. At the same time, the terms of the latter are limited by the duration of useful use of the subject of legal relations.
- The risks of the lessor are significantly higher than those of a similar leased entity, since the company acquires ownership of inventory items needed by the recipient and if any problems arise, equipment or other item of the transaction that has narrow characteristics may turn out to be unclaimed. Therefore, almost always before concluding an agreement, the company conducts a thorough assessment of the counterparty’s solvency.
- Lease payments can be anything and, as a rule, exceed lease payments, all other things being equal . Moreover, the latter are usually calculated in strict accordance with the cost of the item, taking into account the required level of profit.
Source: https://vchemraznica.ru/v-chem-raznica-mezhdu-arendoj-i-lizingom/
Advantages of financial leasing
The financial leasing scheme has many advantages for participants compared to other methods of acquiring property:
- The intermediary’s risks of non-return of the provided finance are reduced, since he remains the owner during the validity of the contract.
- The recipient has the opportunity to receive credit for the full cost, while the first payments can be postponed in time.
- Payments for capital goods can only begin after the production process has fully started.
- Under a leasing scheme, funds can be obtained for a longer period.
- Flexible terms of the transaction enable participants to develop an optimal operating algorithm and payment mode.
- When the agreement expires, the recipient has the right to repurchase the property at par.
- The balance holder is the lessor, which makes it possible not to pay property tax.
- Leasing payments are accepted as expenses, which significantly reduces tax payments.
- This scheme is very often subsidized by the state.
- The selling party increases demand for its products.
Licensing of leasing activities is not necessary for its implementation
One type of rental is leasing. It has its own characteristics that distinguish it from regular rentals. Not so long ago, the issue of leasing activities being subject to licensing was discussed. Changes in legislation have meant that this procedure is no longer required for this type of lease.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call
+7
It's fast and free!
What is leasing
The word itself is derived from the English verb to lease - “to rent out”.
This is a financial transaction in which one party (the lessor) provides a product for temporary use to the other party (the lessee) on a reimbursable basis with the possibility of purchasing this property in the future. At the same time, a leasing agreement is concluded, which is intended to secure the deal in writing.
The repurchase itself is not obligatory for the lessee. He can take this or that object for a simple lease. This was enshrined at the legislative level after the Russian Federation joined the UNIDROIT Convention.
You can learn about leasing for trucks from this article.
The subject of this type of lease can be both movable (vehicles) and immovable property (houses, buildings, etc.). They cannot be land plots, any natural objects or property that cannot be used according to Federal laws.
Leasing is a type of rental.
Until 2011, leasing in Russia was used only for business purposes, but since this year it has also become possible for transactions with individuals.
As for the tax consequences, in Russia accelerated depreciation and redistribution of VAT payment deadlines are used.
In 2020, the issue of leasing reform was discussed. It involves the introduction by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation of a register where information about all leasing companies would be entered.
On topic: What numbers do scammers call from?
Who can provide leasing
Both an individual and a legal entity can act as a lessor They can purchase property and lease it with the possibility of further selling it to other organizations or citizens for the price specified in the concluded agreement.
To become a lessor, it is still recommended to become a legal entity or individual entrepreneur, since banks and other leasing companies are very careful about individuals who decide to engage in this type of activity.
Both an individual and a legal entity can act as a lessor.
Very often, lessors become commercial banks, non-banking organizations and other leasing companies that provide this type of lease for various objects - cars, trucks, buildings, etc.
What to do if a bank's license is revoked? You can find out more about this here.
There are several types of such organizations:
- subsidiaries of large banks;
- commercial banks;
- companies that appeared on an industry or production basis (engaged in leasing only in a certain narrow industry );
- semi-commercial organizations (they are created using funds allocated by the state or municipality, and therefore have preferential financing. They provide their services only to certain categories of clients );
- created by trading companies (the purpose of such organizations is to attract corporate clients who buy different types of goods in large quantities );
- foreign organizations acting as suppliers of equipment (they use leasing as one of the methods of marketing their products , for which they resort to the help of Russian banks acting as a guarantor);
- international companies (they finance sales of equipment from foreign suppliers or to companies operating in Russia ).
Is a license required to carry out leasing activities?
In 1996, the Government of the Russian Federation issued Decree No. 167 , which introduced a mandatory procedure for obtaining a license for leasing activities.
Later, this formality was abolished, and Article 6, containing information on it, was excluded from the Federal Law of January 29, 2002 No. 10. Officially, it was the Federal Law “On Licensing of Certain Types of Activities” that abolished this need.
A license is no longer required to carry out leasing activities.
This was done to stimulate the development of medium and small businesses, as well as limit risks for individuals and legal entities who resort to the help of such enterprises.
Federal Law No. 99 defines licensing as a measure necessary to suppress violations of the rights of Russian citizens, damage to nature, the political system of the Russian Federation, etc. That is why leasing is not a licensed activity.
Conclusion
Leasing is the provision of property (movable and immovable) for rent to citizens or organizations with the possibility of their subsequent purchase. Individuals, legal entities, and individual entrepreneurs can act as a lessor. This type of activity does not require licensing under Federal Law No. 99.
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
+7
It's fast and free!
Source: https://prava.expert/litsenzii/lizingovaya-deyatelnost.html
Operational leasing
Such a leasing scheme assumes that all risk factors lie with the leasing service provider. Thus, the leaseholder bears a minimum of responsibility, and the balance holder is the intermediary.
Operating leasing is a scheme that involves concluding a contract for a period not exceeding the depreciation period of fixed assets. After the expiration of the contract, the objects are transferred back to the owner. Responsibility for condition and maintenance falls on the party leasing the property. Very often, the lease recipient's payment is less than the owner's acquisition costs, so the agreement can be renewed.
The costs of an operational leasing scheme are higher than those of a financial leasing scheme. This is due to the fact that the leasing service provider bears many of the costs themselves, which is not the case with other options. Also, operating leasing is valid for a shorter period and the same object can be transferred in turn to different persons. At the same time, as depreciation proceeds, the cost of the fixed asset and the profitability from leasing it fall. An example would be car operating leasing.
Leasing is a mutually beneficial agreement with a complex relationship structure
The term “leasing” comes from the English word lease, which literally means “to rent, to rent.” The leasing agreement itself has become widespread since the late 50s of the 20th century. What is leasing? And why has it become popular in the practice of international and national entrepreneurship?
What is this?
Leasing is an agreement by virtue of which one party - the lessor - undertakes the obligation to acquire property and then provide it for temporary possession and use for business to the other party - the lessee for a certain fee. The lessee chooses which property the lessor must purchase and from which seller.
As you can see, the parties to this transaction are:
- lessor - the one who has funds and is ready to invest them;
- lessee – the one for whom the lessor will purchase the property and to whom he will transfer it for use;
- The seller is the one from whom the lessor will buy the property. It is not the lessor, but the lessee who will choose the seller. Although the contract may provide for the opposite situation.
From the above it follows that leasing is a type of contract that is quite complex. It has two groups of relations:
- relations between the lessor and the lessee;
- relationship between the lessor and the seller.
Let's study an example that reflects how this agreement works and determine what motivates the parties to enter into it. From theory to practice
Let's say there is an Alpha enterprise that wants to develop and expand. Of course, for this he needs new equipment, machines, and other technical means. But the problem is that there is not enough money and Alpha is not able to purchase the necessary machine. What to do?
The Alpha enterprise may submit a proposal to conclude a leasing agreement with Gamma Bank.
Bank "Gamma" (lessor) will acquire the machine indicated by "Alpha" (lessee) into its ownership and transfer it to the latter for use.
The benefit of the enterprise is obvious, but why does the bank enter into such a transaction? The bank certainly has its own interest, otherwise it simply would not have concluded this agreement.
Firstly, Alpha will pay a specific amount of money for the use of the machine; secondly, after the agreement between the bank and the enterprise expires, the bank, since the property is its property, can enter into a leasing agreement with another enterprise and get paid again. Thirdly, for a bank that always has certain amounts of cash, this is a good investment.
Why is leasing a separate type of contract?
This is determined by its features:
1. As we have already indicated, the subject of the contract, that is, the property that will be purchased, is selected by the lessee (in the example considered, this is an enterprise), BUT, however, the lessor (in the example, a bank) is responsible for choosing the subject and the seller.
We will show what this means by developing an example.
Gamma Bank entered into an agreement with the seller and bought the machine from him. The seller and the machine were chosen by the enterprise (lessee). The seller transferred the machine to the company (lessee). After some time, the Alpha company discovered defects in the machine.
In such a situation, the company can make claims against both the bank (lessor) and the seller. To whomever he wishes, that is his right. And the one against whom the enterprise makes a claim (the lessee) will be liable to it, since the bank and the seller are joint and several debtors.
Helpful advice!
This means that whoever the company turns to will have to compensate for losses in full, regardless of the guilty party. The seller is responsible for the bank, and the bank is responsible for the seller.
This is where the feature we indicated is expressed: the lessor is responsible for the choice of the seller and the subject of the contract to the lessee;
2. The lessee may acquire certain property for temporary possession and use only for business purposes. Therefore, if in our example the Alpha enterprise needed property, for example, to equip a gym or other place for leisure of employees, then there would be a need to conclude a rental agreement rather than a leasing agreement;
3. The price of the leasing agreement is established by the parties (lessor and lessee) when concluding the agreement. It consists of two parts.
Option 1.
The amount of investment expenses of the lessor, that is, the amount that he paid for the property indicated by the lessee, and the amount of remuneration, that is, the amount for the temporary possession and use of the property by the lessee.
The lessee pays monthly part of the amount that the lessor paid when purchasing the property, + pays monthly for the use and ownership of the property.
Option 2.
If the terms of the agreement stipulate that at the end of its validity, the subject of the agreement (the machine in our case) will not be returned to the bank (lessor), but must become the property of the enterprise (lessee), then the formula will look different.
On the subject: Where to Check KBM Using the RSA Base
The lessee pays monthly part of the amount that the lessor paid when purchasing the property + part of the redemption price, upon payment of which he will receive ownership of the property.
For every taste and for any purpose
Let's look at the types of leasing agreements.
Depending on the method of reimbursement of costs and whether the property becomes the property of the lessee, the following are distinguished:
- financial leasing , in which the price of the leasing agreement is calculated in such a way that the lessor (in the example, the bank that invested the money) receives 75% of the funds spent on the purchase. That is, if a bank bought a machine for 10 thousand dollars, then with financial leasing it will in any case receive 7 thousand 500 dollars;
- operational leasing, in which the lessor is reimbursed less than 75% of the amount he spent when purchasing the leased item, but under the terms of the contract, the item (in our case it’s a machine) does not become the property of the lessee at the end of the contract and can be leased by the lessor many times;
- subleasing, in which the lessee can also enter into a leasing agreement with a third party with the permission of the lessor. In this case, the lessee under the original agreement will become the lessor.
Here are some types of leasing:
- reverse leasing is a leasing in which the seller sells the leased asset to the lessor, and the lessor undertakes to enter into a leasing agreement with this seller. That is, with such a leased item, the seller and the lessee are one and the same person (such a lease is also called a return lease);
- compensatory – a type in which the lessor will receive as lease payments not money, but goods that are produced using the leased asset, that is, the property that was transferred to the lessee;
- Barter leasing is a leasing in which the lessor will receive from the lessee as payment not money, but any goods.
Depending on who pays for the maintenance of the leased item, there are:
- pure leasing, when the lessee bears all the costs of maintaining the leased asset (in the example of a machine), which means that lease payments do not include the amount of money that the lessee invests to maintain the leased asset in a normally functioning condition;
- wet leasing, in which, on the contrary, the lessor pays for the maintenance of the leased asset, that is, for its repairs, insurance and other expenses.
There is also a full lease, which provides for the repair or replacement of the leased property by the lessor.
The description of this complex treaty has come to an end. We hope that you were able to find answers to the questions that interest you, and when deciding on the advisability of concluding this civil law contract, you will be able to make the right decision.
Source: https://biznesluxe.ru/works/lizing-eto-vzaimovygodnyj-dogovor-so-slozhnoj-strukturoj-otnoshenij/
How are calculations made?
The most important thing for each participant in such a transaction is the procedure for settlements under the contract. Payments under a leasing agreement are set depending on the period for which the financial lease is issued, and the cost of the equipment itself transferred under the agreement is also taken into account.
In addition to the agreement, a payment schedule is drawn up, on the basis of which funds are deposited. It specifies exactly when funds should be transferred, as well as in what amount and in what way.
Often, even two schedules are drawn up for a property leasing agreement: a schedule for transferring money and a payment schedule for the leasing itself. The second document is required by companies to carry out optimal accounting, as it serves as the basis for reflecting payments in reporting.
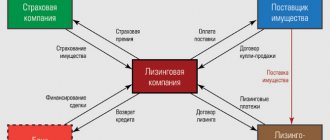
Lessor
The lessor is one of the subjects of the leasing transaction, which purchases the necessary equipment (equipment, real estate) from the supplier and transfers it for temporary use (rent) to the lessee. In this case, the transaction is executed on certain conditions that are stipulated in the leasing agreement.
The lessor is an individual or legal entity. In the first case, the participant in the leasing transaction can be an individual entrepreneur (individual entrepreneur) with the appropriate state registration in hand.
In the second case - credit institutions or banks whose charter makes it possible to carry out leasing activities.
In addition, this category of legal entities includes specialized leasing companies or organizations whose constituent documents allow them to deal with leasing issues.
Role and responsibility of the lessor
The lessor is one of the links between the selling company (supplier) and the leasing recipient (lessee). At the same time, the algorithm for registering leasing and the participation of the lessor in it is as follows:
— the leasing recipient finds a seller who has the necessary property;
— the lessor purchases the goods needed by the client as personal property. In this case, the equipment is not purchased for personal use, but for subsequent lease to its client (the recipient of the lease);
— the leasing company is engaged in the process of transferring the leased object based on the terms of the contract and for a certain fee;
— upon completion of the leasing transaction (depending on the terms of the agreement), the property is transferred to the leasing recipient (at the residual price) or returned to the leasing company.
For the entire period specified in the contract, the leased object is in the use of the lessee. In this case, the owner still remains the leasing company.
If the leasing recipient fails to fulfill obligations in a timely manner or in full, and also delays payments, then the leasing company, based on the terms of the contract, can take away the property from the leasing recipient.
In the event that the leasing recipient goes bankrupt, the leasing company must receive the first payments.
If the lessor in one way or another interferes with the client’s choice of the supplier company or the object of the leasing transaction, then he bears full responsibility for the untimely delivery of equipment.
Note!
In addition, the lessee is responsible for damage that may be caused to the life of the client or citizens during the period of use of the leased asset.
But recently, this clause is increasingly included in the leasing agreement, and all responsibility is shifted from the shoulders of the lessor directly to the user (lessee).
If we are talking about making a major transaction and purchasing a large batch of equipment, then the lessor has the right to attract investment funds, insurance companies, banking institutions, independent private investors, and so on as auxiliary investors.
Rights and obligations of the lessor
When drawing up an agreement, the lessor, as a party to the transaction, assumes certain rights and obligations. All of them are reflected in the contract and must be strictly observed by the party to the transaction.
Thus, the lessor undertakes the following obligations:
1. Buy from the product supplier (seller) a specific type of property, which for a certain fee and on fixed terms is transferred to the second party to the transaction - the tenant (lessee).
2. Notify the seller (supplier company) that the purchased property will be leased to a specific party to the transaction. This requirement is stated in Article 667 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, notification to the seller must be made exclusively in writing.
To implement such a requirement, the full details of the leasing recipient are specified in the goods purchase and sale agreement between the parties to the transaction.
In addition, when drawing up an agreement with the seller, the document may contain links directly to the leasing agreement. In addition, the seller (supplying company) can be notified of the relevant purpose of the purchase by writing a letter.
In this case, the seller may undertake the obligation to deliver the goods purchased by the lessor directly to the lessee.
3. Reimburse the second party to the transaction (the leasing recipient) for all costs of improvement, maintenance or repair of obvious defects of the leased asset (if such was provided for in the contract).
4. Accept back equipment transferred under a leasing agreement in the event of termination of the latter or expiration of its validity period.
5. Fulfill all other obligations that are specified in the agreement between the parties. These include:
— purchase of rights to intellectual property (license rights, brands, software, trademark rights, etc.);
— purchase from a third party of equipment necessary for commissioning;
— carrying out repair and commissioning work at the lessee’s facility (if there is an agreement on this);
- training;
— ensuring the repair of equipment transferred to the disposal and its timely post-warranty service.
The leasing company (lessor), as a rule, can undertake the most serious work, such as major repairs or routine operation;
— prepare the necessary territory for the installation of the necessary equipment;
— provide assistance in the installation of transferred equipment, its installation, adjustment, and communications;
— other types of activities without which it is not possible to properly use the leased asset.
Along with the obligations, the lessor also has some rights:
1. Invest funds to purchase an object to be leased. For these purposes, both personal and borrowed funds can be used.
2. Conduct inspections of the lessee to ensure that he is complying with the terms of use of the object of the leasing transaction, as well as the quality of the maintenance conditions.
3. Terminate the agreement and demand the return of the object of the leasing transaction if the conditions of the second party to the transaction are not fulfilled and on the basis of the conditions specified in the leasing agreement.
On the subject: Alfa Bank How to get your money back for insurance
4. Refuse from the agreement in those cases provided for by the law of the Russian Federation or a documentary agreement of the parties.
5. Reclaim debts from the leaseholder indefinitely, based on a notarial signature.
6. Demand from the second party to the transaction (lessee) compensation for all material losses in cases discussed in the leasing agreement.
7. Require the lessee to immediately return the object of the leasing transaction or fulfill financial obligations in the event of failure to comply with the terms of the subleasing agreement, for example, an obvious delay in the agreement.
Costs and remuneration of the lessor
The leasing agreement, as a service, relates to investment activities.
Consequently, the leasing recipient undertakes to compensate the leasing company for expenses in financial and material form, as well as to pay remuneration in full.
In this case, the total amount of the leasing transaction consists of two components - payment of remuneration and compensation of investment costs. Each of the “components” has its own characteristics:
1. Investment costs are the costs and expenses of the leasing company that are associated with the purchase and use of the object of the leasing transaction by the leasing recipient.
“IZ” includes:
- property tax; - payments for the provision of guarantees and sureties to the leasing company;
— directly the price of the leased object.
Source: https://utmagazine.ru/posts/10444-lizingodatel
financial leasing
The main characteristics are:
- The leasing service provider buys an object for a specific request, which distinguishes this scheme from others. The selling party is notified that it is a participant in the leasing transaction.
- All questions about the quality of the property are directed to the selling party.
- The financial leasing scheme can be supplemented with other types of contractual relations. Thus, the source of financing may be a fourth party.
- It is long lasting and can last up to ten years. Early termination of an agreement is associated with a number of difficulties.
- All responsibility for the condition of the property falls on the lessee as soon as he officially accepted these objects.
- This scheme gives less profit, but is more reliable.
What is leasing? Main types, process descriptions and examples
Most Ukrainians today do not have the opportunity to immediately buy expensive equipment, for example, a car.
Then many take out a loan and buy the necessary equipment, but there is another way out - to use leasing. This service is available for both individuals and legal entities.
What is leasing? What is better - installments, credit or leasing? Pros and cons of leasing and how to arrange it?
Leasing service - concept and features of the procedure
In Ukraine, the bank loan service is considered more popular, despite the fact that many people in Europe and around the world are already starting to use leasing. Legally, leasing operations are a certain type of investment that is provided by the lessor to the lessee with the right to subsequently purchase the goods.
In most cases, the product is a car or other expensive equipment. Car leasing – what is it? The essence of the procedure is as follows: a person who wants to buy a car signs an agreement with a financial leasing company.
The company pays the entire cost of the goods, if it is a car, then registers it with the MREO, pays for insurance and collects all the documents. The car itself is given to the user, who, according to the terms of the contract, will pay a certain amount monthly.
In fact, this cost, which is given to the company, is the payment for the cost of the car. As a result, after a few years the buyer will have the opportunity to purchase the goods with full ownership rights.
In summary, in simple terms we can say that leasing is one of the types of rent.
The most profitable option is installments, credit or leasing
Financial institutions today offer many services that benefit both them and the users themselves.
Most often, Ukrainians use a bank loan, looking for better offers with lower interest rates and the opportunity to get a higher value.
But now the leasing procedure is becoming increasingly popular for individuals, businessmen or companies. What are the features of different types of transactions - installments, credit or leasing?
- Installment payment is a financial procedure, the essence of which is that the user buys a product and becomes its full owner. But the cost of the equipment is paid gradually. The advantage is that you don't have to pay a higher price right away, but you do need to be prepared to pay a much higher price as a result.
- Credit is the most popular financial service in Ukraine, used by more than half of the country’s population. The difficulty is that to get a loan you need to prove to the bank your solvency - having a job or providing collateral.
- Leasing is a more profitable procedure when purchasing expensive equipment than a loan or installment plan. In some countries, much more equipment is purchased through leasing than through other means. The main advantage is that you can gradually pay the cost, and then receive the equipment at your location.
What is a leasing company?
This is a commercial organization that is created in the form of a joint stock company. The work of companies is regulated by the Civil Code of Ukraine. It spells out the specifics of the company’s work, details of the contract, methods of returning funds and other subtleties of cooperation between the leasing organization and the lessee.
Who can be a lessor?
As a rule, a specialized company plays this role. But leasing can also be provided by a commercial bank, credit organization, or other institution.
It must be remembered that even an individual can be considered a lessor. A person buys a car or other product at his own expense, and then signs a leasing agreement with another private or legal entity.
All terms and conditions apply to this relationship.
Types of leasing and their features
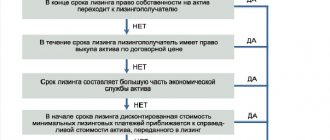
The leasing procedure is essentially of two types - financial and operational.
- Financial leasing is a service provided by the lessor on the basis of a contract. Upon expiration of its validity period or after full payment of the agreed amount with the one who provided the goods, the lessee becomes its full owner. The contract generally covers a period that is the useful life of the device, that is, until the end of its operation. Such relationships are considered as long-term lending.
- Operating leasing is also a form of a kind of rental of goods. It differs from financial leasing in that use is provided only for a certain period, and at the end of the period the lessee must return the goods. In accordance with the terms, a certain value is paid for the car or equipment. In fact, operating leasing is a form of rental of goods.