Russian legislation provides for various commercial relationships that can arise between two or more business entities. One type of such relationship is commission trading. It offers the buyer non-food products. To regulate this type of activity, there are various legislative acts that allow a business entity to properly organize this process.
Commission refers to this type of trade in which the sale of goods that have been used or that have passed into the hands of the consumer at least once is carried out. The demand for such things is not very high. But, nevertheless, they are also of interest to a certain circle of buyers.
General provisions
Commission trade in non-food products must be conducted in accordance with the main regulatory act that regulates this type of relationship. This is Government Resolution No. 569, which was adopted on June 6, 1998. This document has a direct connection with the law on the protection of consumer rights.
Commission trading operates on certain concepts, such as commission agent, principal and buyer. They are nothing more than the names of subjects taking part in relations, which the state regulates. What do these concepts mean?
1. A commission agent is an individual entrepreneur or organization that accepts things and items for commission. Next, their retail sales will be organized.
2. The principal is a person who gives away the goods in order to sell them with the help of a commission agent. For such an operation the latter receives a certain amount of remuneration.
3. Buyers include citizens who express their intention to purchase the goods offered by the commission agent or who are already purchasing them. This status is given to those who have no connection with business and acquire the thing they need for personal use.
Commission trade in goods in the Russian Federation is not limited only to citizens of the country. Participation in it can be taken by persons registered in the territory of another state, as well as those who do not have citizenship at all. In this type of trade, the principals retain ownership of the products transferred by them. And this situation occurs until the item is purchased by the buyer.
In the civil legislation of Russia there are separate rules that provide for a slightly different procedure for the sale of goods. They say that the commission agent must be responsible for maintaining the consumer qualities of the product. In addition, his responsibilities include the use of special signs informing the buyer about the address and operating hours, as well as the name of the organization. Such requirements are also put forward for individual entrepreneurs.
Basic provisions
The first step is to understand the terms used in the document:
- A commission agent or intermediary is a legal entity or store or organization that accepts goods for sale.
- The principal or seller is a citizen who has transferred the goods for sale or wishes to receive them. This can be either a citizen of the Russian Federation, a foreign national or someone without citizenship at all.
- Buyer is the person who purchases this item.
It is worth noting: usually such a scheme is necessary if the principal is unwilling or does not have enough skills to sell. For example, if he inherited a work of art that he does not understand.
An agreement can be concluded for the sale or purchase of goods: in the latter case, we are talking about the acquisition of a certain thing on behalf of the principal.
Please note: the goods themselves belong to the consignor until they are purchased. Responsibility for the safety of things lies with the commission agent, and he is also obliged to inform other parties about changes occurring.
Reception of goods
According to current legislation, the process of transferring products from the principal to the commission agent requires the execution of the appropriate document. It can be an agreement or an invoice, a receipt, etc. The executed document must be signed by two parties (the commission agent and the principal) and include the following information in its text:
— the number of the relevant agreement and the date it was written; - name, as well as full details of the parties (for the commission agent this is the address, telephone number and current account, and for the principal - the details of his passport or other document that proves his identity); — name of the goods transferred to the commission; - percentage of wear and tear, as well as shortcomings of a used item; — cost of the item sold; - the amount and sequence of payment of remuneration due to the commission agent; — the conditions under which the goods are accepted; — the procedure for carrying out markdowns and its size; — terms of sale of an item before and after markdown; — conditions, as well as the sequence of returning unsold goods; — the procedure and terms of settlements between the parties; - subject to reimbursement of the commission agent's expenses for storing the transferred goods after accepting it for commission - the amount of their payment.
In addition to the points listed above, the legislation allows the use of additional descriptions of conditions, which in no way should violate the rights of the principal. The commission agent determines what kind of document these commercial relations will be formalized, reflecting such a decision in a local regulatory act.
In the event that several goods are submitted for commission at once, their price and name can be indicated in a separate list, which will become an integral part of the main document, drawn up in duplicate. The first of them must be handed over to the principal, and the second will remain with the commission agent.
Sales of vehicles
Commission trade in cars, motorcycles and other types of motor vehicles, which are subject to state registration in the manner prescribed by law, is carried out only if the principal confirms ownership of it. In addition, the vehicle must be deregistered in connection with its sale, and also have a temporary registration plate “transit”, which is issued by authorized state bodies.
The rules for commission trade of vehicles temporarily imported into Russia allow commission trade only if there are passports for this equipment, which are issued by the Russian customs authorities.
Commission trade in clothing
Trade in used clothing is in very high demand among the population. An item that is unnecessary for one person may be a necessary acquisition for another. Sometimes in such stores you can buy high-quality and rare (unique) things.
If you decide to open your own store for such trade, the following OKVED codes “Commission trade in clothing” will suit you:
- “47.79.3” – trade in other used goods;
- “47.71” – sale of clothing in specialized stores;
- "47.72" - sale of shoes.
Sales of certain types of items
Trade in consignment goods that are classified as antiques can only be carried out in accordance with the basic Rules. In this case, the requirements reflected in the legislation of the Russian Federation regulating the procedure for the sale of antiques must be met.
The rules for trading in consignment goods do not prohibit the acceptance for consignment of items made from precious stones and precious metals. However, in this case, the requirements reflected in the Rules for the sale of certain types of goods, which were approved by Resolution No. 55 of January 19, 1998, issued by the Government of the Russian Federation, must be complied with.
The rules for commission trade in non-food products do not prohibit the acceptance for commission and further sale of civilian weapons. Such relations are regulated by the Federal Law “On Weapons” and some other regulations, which reflect the rules for the circulation of ammunition and civilian weapons on the territory of Russia.
Gas stoves, as well as cylinders for them, can be accepted for commission. But at the same time, the committent must have the appropriate document. He will confirm their suitability for technical purposes. Such a document is issued by the gas service.
Features of the commission agreement by country
Russia
The commission agreement on the territory of Russia is governed by the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation[1]. In accordance with the terms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the features of certain types of commission agreements may be provided for by another law (except for the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)
and other legal acts (decree of the President of the Russian Federation, resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation, other legal acts)[2].
France
A commission agent in France is a legal or natural person who acts on his own behalf, or exclusively on behalf and in the interests of a legal entity. According to the French Commercial Code, the rights and obligations of the commission agent and the principal are similar to the rights and obligations of the parties to the agency agreement, and therefore the commission agreement is classified as one of the types of agency agreement in trade turnover[3].
Germany
Article 383 of the German Commercial Code defines a commission agent as a person who, on his own behalf, but at the expense of another person, as a business activity, undertakes the purchase and sale of goods and securities[3].
Items that are not accepted for sale
Commission trading rules introduce some restrictions on items that can be sold by a commission agent. Thus, he should not accept the following goods:
— withdrawn from circulation; — having restrictions or a ban on retail sales; — things and items that cannot be exchanged or returned for similar ones, but of different sizes and shapes, colors and dimensions, styles and configurations; — employees for the treatment of diseases and their prevention at home; - items of personal hygiene; - belonging to the categories “hosiery”, as well as “knitted and sewn underwear”; — materials made of polymers for storing food products, including those intended for one-time use; - are medicinal products; - related to household chemicals, as well as perfumes and cosmetics.
Registration of goods by commission agent
Once an item has been accepted for sale, a sales tag must be attached to it. If small items are to be sold, such as brooches, watches, beads, etc., the number of the document that was issued upon their acceptance is indicated directly on the price tag.
The product label, as well as the list of accepted goods, reflects information characterizing the condition of the product. This may be the following information:
- new or used item; — existing defects of the product; - degree of wear; - trademarks of the item of trade.
If vehicles were accepted for commission, then such information should include:
— name of the vehicle model and brand; - an identification number; — name of the vehicle; - year of issue; — engine, frame and chassis numbers.
If the vehicle was imported into the territory of the Russian Federation, then the label must contain information about its customs clearance. After completing the list of goods, it must be signed by both the principal and the commission agent. Two signatures are also provided on the label.
In the event that a product undergoes a commission that requires the provision of information regarding its compliance with necessary requirements, service life or suitability, but such information is not available, the commission agent will need to indicate this to the buyer when making a sale.
All goods for sale are accepted only upon presentation by the citizen of a passport or other document that serves as identification.
Rights and obligations of the parties to the transaction
The commission agent, with the consent of the principal, may provide him with additional services. They relate to the assessment and acceptance of goods at home, as well as the delivery of large items to the store, etc.
The principal has the right to refuse to execute the signed agreement at any time. In this case, this order is simply canceled. In this case, the commission agent has the right to demand compensation for losses caused by termination of the contract. The principal is obliged, within the time limits specified in the document signed when accepting the goods for commission, and if none are specified, then immediately, to dispose of the property held by the commission agent. If this does not happen, then objects and things can be deposited with third parties. Payment will have to be made to the committent. The commission agent also has the right to sell the remaining goods on terms that may be more favorable to partners.
Amount of remuneration and cost of goods
Determining the amount that will be indicated on the price tag is an important point in the relationship between the commission agent and the principal. In such cases, you need to adhere to the basic rule, which states that there should be no restrictions. Partners negotiate the sales price individually.
Regarding the commission agent's remuneration: he receives it in any case, whether the goods are sold or not. However, when drawing up a contract, it is also possible that the amount of monetary compensation is not clearly reflected. In such cases, it is determined based on generally accepted indicators existing in this area.
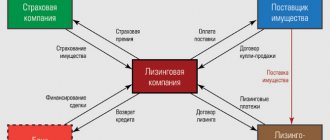
Commission services
Diagram of the relationships between different types of agency agreements
Under a transaction made by a commission agent with a third party, the commission agent acquires rights and becomes obligated, even if the principal was named in the transaction or entered into direct relations with the third party for the execution of the transaction [4].
A commission agreement can be concluded for a certain period or without specifying the period of its validity, with or without indicating the territory of its execution, with or without the obligation of the principal not to grant third parties the right to carry out transactions in his interests and at his expense, the execution of which is entrusted to the commission agent. obligations, with or without conditions, regarding the range of goods that are the subject of the commission[5].
The commission agent has the right to reimburse all his expenses incurred in the performance of his duties as a commission agent, and also to receive a commission for the performance of his duties.
The commission agent is not liable to the principal for the fulfillment by a third party of the obligations of such a third party under transactions concluded by the commission agent in the interests of the principal. However, the commission agent and the principal may stipulate the existence of del credere in the commission agreement.
The services a commission agent provides to the principal in fulfilling his obligations are often called “commission services.”
The commission agent becomes obligated for transactions concluded with third parties, but he is not responsible for non-execution of transactions caused by the action or inaction of third parties, except in cases where the commission agent did not exercise the necessary care in choosing this person, or accepted guarantee for the execution of the transaction ( delcredere).
Differences from the contract of agency
The commission agreement has some differences with the agency agreement. Unlike a contract of agency, where an attorney acts on behalf of his principal, a commission agent in transactions with third parties acts on his own behalf, creating in these transactions obligatory rights and obligations directly for himself, and not for the principal.
However, everything that the commission agent received as a result of the fulfillment of obligations under such transactions concluded by him as a commission agent with a third party (persons) becomes the property not of the commission agent, but directly of the principal, regardless of what is indicated in the transactions concluded commission agent with a third party(ies).
As already noted, under an agency agreement the attorney acts on behalf of the principal, and under a commission agreement the commission agent acts on his own behalf. Another difference between a commission agreement and an agency agreement is that under an agency agreement the attorney undertakes to perform any legal actions, and not just transactions, while under a commission agreement the commission agent performs only transactions, that is, actions aimed at creating, changing or terminating rights and responsibilities.
Differences from an agency agreement
An agency agreement differs from a commission agreement in that the agent undertakes to perform both legal actions, including transactions, and actual ones. Moreover, depending on the terms of the agreement, the agent can act both on behalf of the principal (mandate agreement model) and on his own behalf (commission agreement model). Thus, an agency agreement is a concept that includes, among other things, two named types of agreement: an agency agreement or a commission agreement (legal actions), on the one hand, and an agreement for the provision of paid services (actual actions), on the other hand, in addition, As can be seen from the description of the agency agreement, the latter also includes a trust management agreement.
Conducting sales
Trade in consignment goods is not carried out without price tags and other elements that contribute to the formation of a general idea of the characteristics of the products offered. This is the main selling requirement. What should you pay attention to when trading on commission? It is worth keeping in mind that the sale should be organized the very next day after the goods were accepted for consignment. Otherwise, the principal will have to receive a penalty from the partner. As a rule, its size is 3% of the remuneration amount. However, a more serious value may be established in the concluded agreement.
There are other rules:
— goods can be sold only on terms that partners consider most profitable for themselves; — the criteria for the most favorable conditions for sale are determined by the principal taking into account standard rules that are generally accepted for a certain segment; - standard rules may not be used at all if this is beneficial for the partner and he cannot coordinate his actions for objective reasons, informing the principal later when he is in touch.
Commission trading also provides for the return of the product to the consignor if, after acceptance, certain defects were discovered in it. It is worth keeping in mind that the interaction between the parties to the contract will depend on the agreement they have adopted, which must necessarily be based on the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Only in this case can both the commission agent and the principal be confident in the protection of their rights.
What about the money?
According to the rules of commission trading, already at the stage of concluding an agreement between the supplier and the commission agent, it is necessary to decide how the remuneration will be calculated, how it should be transferred, and in what form the financial amounts should be transferred. A whole range of important factors play a role, the most significant of which is the variety of products intended for sale.
As can be seen from world practice, trading on commission goods with the lowest percentage of profit for the commission agent is the sale of a simple, homogeneous product that does not have technically complex elements or structures. This includes raw materials. If the product is in the complex category, you can expect to earn decent commissions, but the transaction costs will be higher. In any of the options, there is a chance that the commission agreement will not be fulfilled for reasons that the principal cannot influence. In such a situation, the commission agent retains the right to receive remuneration and compensation for expenses associated with the agreement.
Control and compensation
So, the final stage of the concluded deal begins. After selling the goods, the commission agent must make a payment. But at this stage, problems often arise, especially if the contract does not contain a specific amount of remuneration or there is no description of the method of transferring the amount due to the commission agent.
Errors often appear when a commission agent keeps records of commission trade manually. This also causes criticism from the partner. What to do to prevent such situations? It is advisable that the partner accepting the goods for sale use the 1C program for commission trading.
Upon completion of the transaction, the principal must pay the commission agent the remuneration itself, as well as the amount of additional costs that arose during the execution of his instructions.
However, there are other cases. For example, when a transaction ends in failure to fulfill the contract due to the fault of the principal. In this case, in addition to the remuneration due, the commission agent has the right to receive compensation.
If for one reason or another the party accepting the goods for sale refuses to fulfill the contract, then it shall reimburse the expenses that occurred before the moment of refusal.
Calculations of the amounts required for payment are made in the reports of commission agents. They are provided to the other party immediately after the fulfillment of obligations. The certificate of services rendered may also contain relevant information. Such a report must be accompanied by documents that prove the accuracy of the contractor’s calculations.
You don’t have to pay taxes on commissions from retail trade
Does an organization have the right to pay UTII in relation to retail trade in goods received under a commission agreement? Is it legal not to take into account income in the form of commissions from the retail sale of goods when calculating the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system?
Question: An organization using the simplified tax system carries out retail trade of its own goods in a rented store with an area of less than 150 square meters. m. Also, the organization, on its own behalf, sells goods received under a commission agreement.
Under the terms of the commission agreement, the organization receives a commission, which is the difference between the price of the goods at which it was received from the principal and the price of its sale to the buyer.
Does an organization have the right to pay UTII in relation to retail trade in goods received under a commission agreement?
Is it legal not to take into account income in the form of commissions from the retail sale of goods when calculating the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system?
Answer:
In accordance with paragraphs. 6 paragraph 2 art. 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Code), taxpayers carrying out entrepreneurial activities in the field of retail trade through shops and pavilions with a sales floor area of no more than 150 square meters for each trade organization may be transferred in accordance with the regulatory legal acts of the representative bodies of municipal districts, city districts, laws of federal cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg on the application of the taxation system in the form of a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities.
Based on Art. 346.27 of the Code, retail trade is recognized as business activity related to the trade of goods (including in cash, as well as using payment cards) on the basis of retail purchase and sale contracts. This type of business activity does not include the sale of excisable goods specified in paragraphs. 6 - 10 p. 1 tbsp. 181 of the Code, food and beverages, including alcohol, both in the manufacturer’s packaging and packaging, and without such packaging and packaging, in bars, restaurants, cafes and other public catering facilities, gas, trucks and special vehicles, trailers, semi-trailers, trailers, buses of any type, goods according to samples and catalogs outside the stationary distribution network (including in the form of mail (parcel trade), as well as through teleshopping, telephone communications and computer networks), transfer of medicines at preferential rates ( free) recipes, as well as products of our own production (manufacturing). For the purposes of Chapter 26.3 of the Retail Code.
At the same time, commission trade, according to the State Standard of the Russian Federation GOST R 51303-99 “Trade. Terms and definitions”, approved by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated August 11, 1999 N 242-st, is retail trade, which involves the sale by commission agents of goods transferred to them for sale by third parties - principals, under commission agreements.
Thus, for the purposes of Sec. 26.3 of the Code, commission trade, as one of the types of retail trade, is subject to taxation with a single tax on imputed income.
In case of sale of goods under commission agreements, it is necessary to be guided by the provisions of Art. 990 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes that under a commission agreement, one party (the commission agent) undertakes, on behalf of the other party (the principal), for a fee, to carry out one or more transactions on its own behalf, but at the expense of the principal. At the same time, under a transaction made by a commission agent with a third party, the commission agent acquires rights and becomes obligated, even if the principal was named in the transaction or entered into direct relations with the third party for the execution of the transaction.
The activities of a commission agent in retail trade are subject to a single tax on imputed income only if the commission agent sells goods on his own behalf through a trade organization that belongs to or is used by him in business activities on legal grounds (ownership, lease, etc. ).
Taking into account the above, if an organization carries out retail trade under commission agreements, then such an organization can be recognized as a taxpayer of the single tax on imputed income in relation to retail trade through stores, the area of each of which does not exceed 150 square meters. m, taking into account the provisions of clauses 2.1 and 2.2 of Art. 346.26 of the Code. If the taxpayer combines the use of a simplified taxation system and a taxation system in the form of a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities and in relation to business activities in the form of retail trade under commission agreements pays a single tax on imputed income, then income in the form of commission fees , received within the framework of these agreements when calculating the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified taxation system, should not be taken into account by it.
Reason: Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 2, 2012 N 03-11-06/3/74
A selection based on materials from the Financier information bank of the ConsultantPlus system. Compiled by Kashirskaya E.V.
Accounting
The final buyer, purchasing the goods he needs, enters into a transaction with the commission agent. It doesn’t matter to him whether this thing is ordinary or handed over by the principal for sale. But accounting for commission trade has some differences from standard sales of goods. What is reflected in the balance sheet?
Commission trading transactions have the following:
— upon receipt of goods, its amount is reflected in the debit of account 004; - after the sale (shipment) of the goods, the accountant performs an operation on the credit of account 004 and debit 62.1 in combination with the credit of account. 76 or 60 (using the 1C program for commission trading, TN or TTN must be printed at this stage); — the preparation of the report by the commission agent is formalized by posting debit to the account. 90 – credit account. 76 (60), as well as debit account. 90 – credit account. 68 for the amount of VAT due for payment to the budget (at this stage, accounting for commission trade is formalized by stamping the product report, as well as the act); — statements recording the receipt of amounts of money are drawn up by postings dt account. 51 – ct. 62, as well as dt sch. 76 (60) – ct. 51.
Receipt of goods on commission
In 1C 8.3 we create “Receipts: goods, services, commission” from the main menu in “Purchases-Receipts (acts, invoices)”.
Fig. 1 Receipt: goods, services, commission
Using the “+ Receipt” button, we create a new document “Goods, services, commission”.
Fig.2 Goods, services, commission
We go into it and fill in the following fields:
- Invoice No. – number and date of the invoice from the supplier;
- Number – the number and date of the invoice in our program, the number is entered automatically, the date is indicated independently;
- Counterparty – Supplier or Principal;
- Agreement is an agreement with the Principal, when creating which we must indicate its type: With the principal (principal) for sale.
Fig. 3 Agreement – agreement with the Principal
- Organization – our organization (Commissioner);
- Warehouse – a warehouse to which goods are received;
- Calculations - pay attention to the calculation account 76.09 (example calculations).
Fig. 4 Calculations - pay attention to the accounting account 76.09 (example calculations)
Next, in the tabular part of the document, use the “Selection” button to select an item, fill in the quantity, amount and VAT rate. Please pay attention to the accounting account – 004.01 Goods in warehouse. This is an off-balance sheet account, the 1C 8.3 program set it up automatically, based on the type of agreement we specified. Please note that an invoice is not required here.
Next, we carry out the document and check the wiring using the DtKt button. The goods went to the off-balance sheet account 004.01 Goods in warehouse.
Fig.5 The goods went to the off-balance sheet account 004.01 Goods in warehouse
Implementing organizations
Thrift stores are open throughout Russia. The goods they sell arouse the interest of buyers. For example, Kuzbass Commission Trade LLC offers its customers household and audio equipment, mobile phones and computers, as well as components for modern gadgets. This organization operates in the city of Kemerovo and has its own official website, where you can familiarize yourself with its details, opening hours and the products offered.
There is also a whole chain of stores called the “Commission Trade Center”. At the retail outlets of this organization, it is offered to purchase both new and used goods at the most affordable prices for the mass buyer.
Where does this chain of stores carry out commission trading? Novokuznetsk and Osinniki, Kaltan and Mezhdurechensk, Kemerovo and Myski, Kiselevsk and Prokopyevsk, Leninsk and Belovo, Guryevsk and Kuznetsky are the cities in which this organization operates.
Commission trade in cars
Many citizens of the Russian Federation refuse to buy used cars from private individuals in favor of proven and reliable organizations. The demand in this area is quite high, so the business of selling used cars can be very profitable. Before accepting a car for consignment trade, you should have it diagnosed at a service center.
The OKVED code “Commission trade in cars” is not included in the group “47.79”; it refers to a different type of activity. The code is selected as follows:
- In section “G” of the classifier we move to class “45”, then to subclass “45.1” “Trade in motor vehicles”.
- We are looking for the grouping “45.11”, this will be the required code for commission trade in motor vehicles.
The coding “45.11” is suitable for trading in both new and used cars and light-duty trucks. The sale of SUVs weighing no more than 3.5 tons also applies here.
As an additional code to OKVED “Commission trade in motor vehicles”, you can specify the code “47.99”.
Possible codes for commission trading are presented in our table.
Read also: Changing OKVED codes: step-by-step instructions