What is income tax
This direct tax is levied on legal entities, and it is calculated from the amount of final profit generated at the end of the reporting period - from the profitability of the institution obtained after deducting the expenditure part. Collection operations are regulated by Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Legal entities are required to deduct a certain percentage of their income and send this amount to the budget system of the Russian Federation. Calculating income taxes in 2020 is an example of a critical operation that an accountant must perform correctly. If the fee is calculated with errors, the organization faces penalties from the Federal Tax Service. Our material provides up-to-date information: income tax - calculation, example for dummies, formula and calculation procedure.
So, the payers of the fee are legal entities that receive profit and are subject to the general taxation regime. Foreign enterprises (including those working through Russian representatives) conducting business on the territory of the Russian Federation and receiving income from financial and economic activities in the Russian Federation are required to pay tax. We will demonstrate with an example how to calculate the income tax of an organization that pays the fee.
By law, these categories of taxpayers are exempt from paying tax:
- institutions under special tax regimes (simplified, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax);
- individual entrepreneurs;
- gambling companies;
- organizations taking part in preparations for large-scale events of national importance (for example, enterprises involved in preparations for the World Cup in Russia).
Real ways to optimize income tax
1. Formation of reserves that will cover possible expenses in the future.
In other words, it is a write-off of current expenses that the company plans to incur in the future. Current legislation allows organizations to create reserves to cover overdue accounts receivable, to issue vacation pay to employees, etc. It should be noted that the formation of the reserve is aimed at approaching the moment of recognition of expenses, and not at increasing expenses in general. In cases where the planned expenditure does not occur, the company must restore the reserve.
2. Moderate increase in associated costs as a way to optimize income tax.
This option is based on the possibility of overestimating the amount of company costs incurred as a result of its business activities. Such costs include payment for cleaning the rented premises, services to prevent the condition of working tools, etc.
3. Providing consulting services and activities aimed at employee education.
Costs aimed at implementing these activities are taken into account as part of other costs associated with the production of products. Thus, educational activities are very beneficial to the company, since it allows them to increase employee loyalty, use added value and optimize the tax base. In addition, an organization can reduce tax payments by providing various types of advisory services.
4. Depreciation of fixed assets as a way to optimize income tax.
An accountant of any organization takes into account the costs of depreciation of fixed assets when forming the tax base. But only a few know that they have the opportunity to include in expenses all non-accrued depreciation and costs of dismantling, recycling and removal of fixed assets.
5. Offset of overpaid amounts for income taxes for optimization purposes.
Often, when making payments, the taxpayer transfers a larger amount of tax than is necessary at the end of the year. Entrepreneurs should remember that they have the right to return the overpaid amount of income tax or offset it in a future period. However, you should not leave this issue for later, since the overpayment can only be offset within three years.
6. Creation of a group of companies in which some members use a simplified taxation system.
At the end of the reporting period, it is necessary to transfer the main amount of profit through companies using the simplified tax system. When using this optimization scheme, taxpayers should be very careful. If tax authorities come to the conclusion that there is a connection between the founders of the company, they will hold taxpayers accountable.
7. Use of the services of offshore companies in activities.
This method of optimizing income tax is absolutely legal. Nevertheless, if necessary, taxpayers will have to justify to the tax authorities the legality of creating a Civil Code.
Entrepreneurs, as a rule, use the services of organizations located in offshore zones to protect intangible assets. To do this, for example, copyrights are transferred to an offshore organization. Those companies located in Russia pay royalties for the use of this asset. Thus, organizations simply transfer finances to an offshore zone, thereby optimizing their tax burden.
Entrepreneurs applying this income tax optimization scheme must ensure that all payment-related documentation is accurate. This is necessary because the transfer of money abroad is subject to foreign exchange supervision.
8. Transfer of most of the assets to a company located on the simplified tax system.
This optimization scheme also requires the creation of a group of enterprises. At the same time, those organizations that use the main tax regime legally optimize their income tax expenses. The company using the simplified tax system is transferred to the company’s property - real estate, labor tools, transport, etc. Thus, the main company saves on property tax, and the “simplified” ones do not pay this tax.
9. Using leasing as a method of optimizing payment for profit.
The use of leasing involves the use of two methods of optimizing income tax. An entrepreneur can choose one of them or use both.
- Accrual of depreciation of the leased asset according to an accelerated scheme . When signing a leasing agreement, the taxpayer company and the lessor company indicate the need to establish a useful life (SPI) for the leased asset equal to the term of the agreement. Accordingly, SPI is reduced, depreciation charges increase, thereby optimizing income tax.
- Use of leaseback . An organization transfers its property to a leasing company and then leases it. In other words, the company is essentially taking out a loan against the equipment. In this case, income tax is reduced, as is property tax.
10. Formation of a reserve for doubtful debts.
Most firms cannot avoid the occurrence of accounts receivable in the course of their activities. They have the right to create a reserve for doubtful debts in order to protect the company from possible tax losses. Thus, the organization reduces its obligations to the budget to transfer amounts of income tax that should be received in the future.
Algorithm for legal creation of a reserve:
1. The founders have the right to include a clause providing for the possibility of creating a reserve in the constituent documents.
2. Conduct an inventory of accounts receivable as of the last day of the reporting or tax period.
3. Calculate the reserve amount:
- if the period for creating the debt exceeds ninety days, then the amount of the reserve includes the debt established during the inventory;
- if the period for creating the debt is from forty-five to ninety days, then the amount of the reserve includes fifty percent of the amount of debt established during the inventory;
- if the occurrence of the debt does not exceed forty-five days, then the amount of the debt does not change.
Those companies that meet a number of conditions have the right to use this optimization method:
- The calculation of income and expenses in an organization is carried out using the accrual method.
- The amount of the reserve should not exceed ten percent of the amount of revenue received in the reporting period.
- The creation of a reserve must be based on an accounting document (for example, a certificate) and must also be accompanied by an entry in the tax register.
This scheme is used in situations where it is necessary to cover losses on debts that are not possible to collect.
11. Formation of a repair fund and the use of various methods of calculating depreciation.
Formation of a reserve for repairs that the company plans to do. The use of this optimization method involves reducing the tax base for income tax by the amount of reserve contributions. At the same time, the amount of the reserve should not exceed the average amount of repair costs incurred by the company in the previous three years.
The taxpayer must write off reserve payments in equal amounts on the last day of the reporting period. In cases where the amount of the reserve exceeded the costs actually incurred by the company during repair work, the excess amount is taken into account in the company's income.
12. Calculation of depreciation using the non-linear method.
The organization has the right to decide for itself which method to use when calculating depreciation charges. The method of calculating depreciation must be reflected in the company's accounting documents.
When using the non-linear method, the depreciation rate is calculated as the quotient of the number 2 divided by the useful life of the object, multiplied by one hundred percent.
When the value of the object reaches a value equal to twenty percent of the initial amount, the depreciation rate is calculated differently. For the calculation, the residual value is used, which is divided by the total number of months remaining until the termination of the object’s joint venture.
13. Implementation of intangible assets as a method of optimizing income tax.
Algorithm for reducing the tax base:
- The head of the company signs an order to form a commission to conduct an inventory of the company’s intellectual property (IPR). Patent attorneys and (or) a patent specialist may be invited to participate in the inventory process.
- All intellectual property objects available in the company are checked and recorded.
- An act of inspection and assessment of the IP is drawn up. This document must contain a list of intellectual property, including the name of the objects, their useful life and cost.
- The period during which depreciation on assets will be charged is determined.
Members of the commission can discover the following OIP: useful developments, innovative ideas, scientific discoveries, works of art, databases and computer programs and much more.
- Intellectual property is registered. The type of intellectual property determines the need to obtain either a patent or a certificate.
- The OIS is registered.
- Intangible assets are revalued based on their market value.
- Depreciation is charged.
14. Optimization of the tax base by taking into account the costs of research and development.
The efficiency of this optimization method is much higher than the efficiency of previous methods. It involves reducing the tax base due to R&D expenses.
A specific list of R&D expenses is presented in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It should be noted that the recognition of expenses is not dependent on the results of research and development. Costs are recorded as other expenses in the reporting period in which the work was completed.
15. Merger of a company that incurs losses.
Another way to optimize income tax is to merge with an unprofitable organization. The use of this scheme has become possible since 2007, when legislative bodies lifted restrictions on the amount of losses that a company can carry forward to future periods.
There is one caveat. The reorganization carried out must be justified by the need to implement specific business objectives. This will avoid claims from tax authorities. For example, a company may justify its merger by the need to carry out industry consolidation, purchase assets, create a holding company, optimize its product line, etc.
In addition to optimizing income tax, this method provides for the possibility of deducting VAT that was paid by the affiliated company.
Representatives of the tax authorities are checking the reasons for the unprofitability of the merged company. The purpose of the audit is to identify facts of deliberate creation of losses.
Having decided to carry out a reorganization in the form of a merger, company representatives must notify FAS and Federal Tax Service employees about the changes being introduced.
Losses can be carried forward for ten years. The countdown of the period begins from the period following the tax period in which the unprofitable company was merged.
Thus, each company has several options for optimizing income tax. In order to maximize the effect of their use, the taxpayer should use the services of a tax consultant.
Basic rates
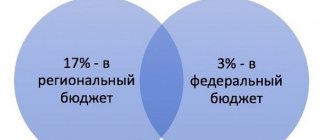
Calculate income tax at the rate for 2020 for taxpayers under the general tax regime - 20% of the obtained financial result of the activity. Until 2020, organizations contributed 18% to the regional budget and 2% to the federal budget. From the end of 2020, a different breakdown by budget level came into force (Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] dated 10/19/2016). Now taxpayers transfer 17% to the regional budget and 3% to the federal treasury. Local governments have the opportunity to reduce the tax rate transferred to the treasury of a particular region, but the regional rate should not be less than 13.5%, and the minimum overall rate should not be less than 16.5%.
Let's look at an example of how to calculate income tax for the general tax rate. Each region has established minimum values for certain types of taxpayers. For example, in Moscow, a reduction in the tax burden to 13.5% is confirmed by the Federal Tax Service for enterprises that employ people with disabilities, produce vehicles, or represent special economic zones, technopolises and industrial parks. In St. Petersburg, only those payers who work in the territory of the special economic zone pay a simplified regional contribution of 13.5%.
Some categories of taxpayers pay fees at special rates, the accrued amounts of which are sent exclusively to the federal budget. Special rates apply to the following categories of payers for certain types of income:
- foreign companies that do not have a Russian representative office, producing hydrocarbons and controlled foreign companies - 20%;
- foreign companies without a representative office in Russia pay a tax on income from the rental of vehicles and for international transport - 10%;
- Russian enterprises from dividends of foreign and Russian companies and from dividends from shares on depositary receipts - 13%;
- foreign companies receiving dividends from Russian enterprises and owners of yield on state and municipal securities - 15%;
- companies receiving income from interest on municipal securities and other income, according to paragraphs. 2 clause 4 art. 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - 9%.
Medical and educational institutions, residents of special economic zones and free economic zones in Crimea and the city of Sevastopol, organizations participating in regional investment projects and operating in the territory of rapid socio-economic development are exempt from paying the fee.
Object of taxation and tax rate
To find out how to calculate income tax, you must first determine the profit itself, which is the object of taxation. The concept of profit for tax purposes depends on the category of taxpayer:
- For Russian organizations and foreign companies operating through representative offices, this is income reduced by the amount of expenses.
- If an organization is part of a group of taxpayers, then the object of taxation for it is determined taking into account interaction with other companies of the group.
- For foreign companies that do not have representative offices, the income tax base is calculated as the amount of income received in the Russian Federation.
The second element necessary in order to determine how to calculate an organization's income tax is the tax rate. As of today, the base rate has been approved at 20% (Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This article also contains a large number of exceptions related to the type of activity, category of payer, type of income, etc.
Calculation formula
All step-by-step instructions on how to calculate income tax come down to using formulas. You will find the figures for them in the balance sheet and in the reporting. To calculate the amount of income, use the formulas:
TNP = D – PNO + SHE – IT;
TNU = R – PNO + SHE – IT,
Where:
- D - enterprise income;
- R - expenses of the enterprise;
- PNO - permanent tax obligations;
- ONA - deferred tax assets;
- ONO - deferred tax liabilities;
- TNP - current income tax;
- TNU - current tax loss.
Calculation examples
Let's look at an example of calculating income tax for a financial year. Let's say the company is on the general taxation system. Income for the reporting period amounted to 6,000,000 rubles. Costs for the same period are 2,000,000 rubles. Thus, net profit: 6,000,000.00 – 2,000,000.00 = 4,000,000.00. Here are instructions on how income tax is calculated in this case:
- Contributions to the regional budget will be: 4,000,000.00 × 17% = 680,000.00 rubles.
- Interest paid to the federal budget: 4,000,000.00 × 3% = 120,000 rubles.
Here are instructions on how income tax is calculated if an organization belongs to a separate category of taxpayers paying contributions to the regional treasury at a simplified tax rate of 13.5:
- Local budget: 4,000,000.00 × 13.5% = 540,000.00 rubles.
- The required 3% must be paid to the federal treasury: 4,000,000.00 × 3% = 120,000.00 rubles.
Let's look at another example of calculating corporate income tax using a formula with tables - for an LLC. According to the profit and loss statement in Form No. 2, LLC “Company” received income in the amount of 600,000.00 rubles. Cost structure according to the formula:
- 5000 rub. — permanent tax liability;
- 6500 rub. - Deferred tax assets;
- 35,000 rub. — accrued depreciation (linear method);
- RUB 50,000.00 - non-linear depreciation - for tax purposes.
The deferred tax liability is: 50,000 – 35,000 = 15,000 rubles.
Income tax for the reporting period: 600,000.00 × 20% (17% + 3%) = RUB 120,000.00.
Let's reflect the accounting records by indicators in the table:
| Wiring | Sum | Contents of operation |
| Dt 99 Kt 68 | 120 000,00 | Tax payment for the reporting year is taken into account |
| Dt 99 Kt 68 | 5000,00 | Permanent tax liability carried out |
| Dt 09 Kt 68 | 6500,00 | Deferred tax assets offset |
| Dt 68 Kt 77 | 15 000,00 | Deferred tax liability accepted |
Tax returns are submitted to the territorial Federal Tax Service before the end of the reporting period (year). The organization distributes payment amounts evenly and pays them in advance - monthly or quarterly throughout the reporting period. After the end of the year, the accountant transfers the remaining amount of income tax.
How to calculate income tax by year: example
We will show you how to calculate profit for the year using specific figures.
Signal LLC, operating in the production sector, summing up the results of work for 2020, received the following data in tax accounting for inclusion in the profit declaration:
- income from sales - 1,187,815,905 rubles;
- expenses associated with obtaining income from sales - 1,092,937,959 rubles;
- non-operating income - 25,325,673 rubles;
- non-operating expenses - RUB 18,820,380.
During 2020, the organization made a number of unprofitable sales of outdated process equipment. The total amount of such loss was RUB 2,539,141.
Signal LLC has a tax loss for 2020 in the amount of RUB 7,279,418.
For 2020, the organization accrued advances on profits in the total amount of 15,550,284 rubles, including to the all-Russian budget - 2,332,543 rubles, to the regional budget - 13,217,741 rubles.
By entering the figures from our example into the calculation of the profit tax for the year reflected in sheet 02 of the declaration for this tax, we get the following picture (in relation to the line numbers of sheet 02):
- Income from sales, line 010 - 1,187,815,905.
- Non-operating income, line 020 - 25,325,673.
- Expenses that reduce the amount of income from sales, line 030 - 1,092,937,959.
- Non-operating expenses, line 040 - 18,820,380.
- Losses, line 050 - 2,539,141.
- Total profit (loss), line 060 - 103,922,380.
- Tax base, line 100 - 103 922 380.
- The amount of loss or part of a loss that reduces the tax base, line 110 - 7,279,418.
- Tax base for calculating tax, line 120 - 96,642,962.
- Total tax rate, line 140 - 20, incl.:
- to the federal budget, line 150 - 3;
- subject's budget, line 160 - 17.
- Total amount of calculated tax, line 180 – 19,328,592, including:
- to the federal budget, line 190 - 2,899,289;
- subject budget, line 200 - 16,429,303.
- Total amount of accrued advance payments, line 210 - 15,550,284, including:
- to the federal budget, line 220 - 2,332,543;
- subject budget, line 230 - 13,217,741.
- Amount of tax to be paid:
- to the federal budget, line 270 - 566,746;
- subject budget, line 271 - 3,211,562.
Let us recall that all indicators involved in calculating the value of the tax base for calculating tax are detailed by composition in the appendices to sheet 02.
IMPORTANT! The declaration for 2020 must be submitted using a new form.
Advance payments
If the organization’s profitability amounted to no more than 15 million rubles (quarter) for the previous tax period, then it has the opportunity to pay an advance on income tax quarterly. The amount is calculated from the actual amount of income.
If the company has a profitability exceeding 15 million rubles, then it must make an advance payment monthly. An example of how to calculate an organization’s income tax: a specialist will calculate the fee based on the estimated level of income predicted based on the reporting data of the previous quarter.
Expenses and income of the organization
Income is the proceeds from the main types of financial and economic activities of the institution. Income is the enterprise's revenue from third-party resources. Such sources will be funds received from leased property, loans provided, etc.
Here is an example of how to calculate income tax in 2020. When calculating the payment, net income is accepted - without deductions for value added, excise taxes, etc. Accompanying documentation must be attached to the indicated income - payment orders, invoices, accounting data from the book of income and expenses.
Expenses are costs aimed at satisfying the production, general economic and basic needs of the organization (wages, materials, equipment, etc.). Expenses can also be indirect, for example, expenses aimed at paying off interest on loans. All costs must be reasonable and documented.
Taxpayers
Payers of income tax are:
- Russian organizations, in addition to those that have switched to special tax regimes - simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax, those involved in the gambling business and a number of others.
- Foreign organizations operating through permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation and (or) receiving income from sources in the Russian Federation.
Organizations that are responsible participants in a consolidated group of taxpayers are recognized as taxpayers with respect to corporate income tax for this consolidated group of taxpayers.
The following are exempt from income tax:
- Organizations on UTII or engaged in the gambling business (if their activities are broader, then they calculate and pay income tax on it in the general manner).
- Organizations on the simplified taxation system (simplified taxation system) and unified agricultural tax (agricultural producers) (but they are required to pay tax on income in the form of dividends and interest on state and municipal securities).
- Organizations associated with the preparation and holding of the 2020 FIFA World Cup and the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup in the Russian Federation: FIFA itself and its subsidiaries, as well as national football associations, confederations, suppliers of goods (works, services) to FIFA and media information providers.
What expenses are deducted from income?
To find out the amount of net profit, income is subtracted from expenses. All expenses must be confirmed and economically justified. To do this, the accountant must correctly prepare and maintain primary and tax documentation. When calculating profit, the following costs are taken into account:
- production;
- general economic;
- representative;
- transport;
- advertising, but not more than 1% of sales revenue;
- expenses for training and advanced training of personnel;
- interest on loans and credits.
What expenses are not taken into account when calculating?
When calculating income tax, the following costs are not taken into account:
- contributions to the authorized capital;
- penalties and fines;
- property and funds transferred to pay for loans and borrowings;
- advance payment for goods or services;
- the cost of property transferred free of charge and the costs of transfer;
- pension benefits;
- vouchers for treatment and rest of employees, etc.
A complete list of expenses that are not taken into account in the calculation is given in Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Labor costs
A separate item that always raises questions among accountants and managers is labor costs. What is important to know about their accounting?
Payments that can and should be taken into account are given in Article 255 of the Tax Code. Wages, vacation pay and compensation for unused vacation are the main items of labor costs. At the same time, subparagraph 25 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows you to take into account any expenses specified in the employment or collective agreement.
This includes costs for health insurance (provided that the insurance contract is concluded for at least a year), costs for the gym, free meals for employees and all other components of the social package. You can enter here everything that complies with labor protection legislation.
But the payments listed in Article 270 cannot be taken into account. These are bonuses issued from retained earnings, financial assistance, and vacation pay in excess of those provided for by law. The list of expenses that cannot be taken into account when calculating income tax is also open.
Recognition of income and expenses
The moment of recognition of income and expenses is the period in which the receipts or expenses taken into account when calculating fees are posted. This is important for calculating income tax for dummies. The moment of recognition directly depends on the method of recognition of income and expenses. There are cash method and accrual method.
If an organization has chosen the cash method, then it must record income when it is immediately received, and expenses when funds are written off. Under the cash method, tax payments are reflected on the days of receipt. write-offs. The cash method cannot be used by banking organizations. The organization has the right to recognize profitability (costs) upon receipt (write-off) in the case where revenue is recorded in the amount of no more than 1 million rubles for each quarter (the last 4 quarters are taken into account). If revenues exceed this threshold, then the company must switch to the accrual method.
Under the accrual method, all income and expenses are recorded in accounting when they arise, and tax payments are reflected on dates confirmed by primary documents. The actual date of payment does not matter.
An institution has the right to annually choose the method of recognizing income and expenses and notify the tax office about this by December 31 of the current year.